Health news, features and articles
Understanding how the body works — and what happens when things change — is paramount to improving the health and wellbeing of every person on the planet. Our team of expert health writers and editors are here to demystify the latest medical advances, explain how the latest health news affects you, and help you understand which exercise equipment can really help improve your fitness. Whether you're after facts about the human body or the secrets to extreme longevity, our health articles and features aim to leave you better informed, up to date with the latest discoveries, and even more curious about human health.
Editor's Picks
-

Psychedelics may rewire the brain to treat PTSD. Scientists are finally beginning to understand how.
-
-

'Night owls' may have worse heart health — but why?
-

'There's no reason to ban us from playing': Analysis debunks notion that transgender women have inherent physical advantages in sports
-
Latest about Health
-
-

'The limits of human longevity have still not been reached,' study suggests
By Florian Bonnet Published -
 Book
BookEmerging embryo-selection technologies are currently 'little more than snake oil.' But someday, they could widen social inequities.
By Daphne O. Martschenko Published -

What is rigor mortis, and why does it happen?
By Isabel Gil Published -
'Universal' nasal-spray vaccine protects against viruses, bacteria and allergens in mice
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -
 Opinion
OpinionNew tech allows parents to 'score' IVF embryos for desirable traits — and it's in desperate need of regulation
By Sam Trejo Published -
 Buying guides
Buying guidesBest air purifiers for pet owners 2026: Remove pet dander, hair and odors
By Tantse Walter Last updated -
 Buying guides
Buying guidesBest fitness trackers for beginners 2025: From Apple Watch to Garmin Forerunner 165
By Lloyd Coombes Last updated
-
Explore Health
Aging
-
-

'The limits of human longevity have still not been reached,' study suggests
By Florian Bonnet Published -

Lifespan may be 50% heritable, study suggests
By Victoria Atkinson Published -

Can AI detect cognitive decline better than a doctor? New study reveals surprising accuracy
By Anirban Mukhopadhyay Published -
Gray hair may have evolved as a protection against cancer, study hints
By Victoria Atkinson Published -

Aging and inflammation may not go hand in hand, study suggests
By Clarissa Brincat Published -

'Aging clocks' can predict your risk of disease and early death. Here's what to know.
By Patrick Sullivan Published -
Special protection may help human eggs stay fresh as the body ages
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

Aging: What happens to the body as it gets older?
By Mindy Weisberger Published -
Brain scans could reveal your true biological age
By Patrick Sullivan Published
-
Allergies
-
-
 BUYING GUIDE
BUYING GUIDEBest air purifiers for allergies 2026: Breathe easy this winter
By Molly Cleary Last updated -

New Jersey man dies from meat allergy triggered by tick bite
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -
 REFERENCE
REFERENCEDo air purifiers help with allergies?
By Kerry Taylor-Smith Last updated -

Is playing in the dirt good for kids' immune systems?
By Emily Cooke Last updated -
 REFERENCE
REFERENCEDo air purifiers help with dust?
By Katie Treharne Last updated -

Could allergies be 'deleted' someday?
By Rebecca Sohn Last updated -

Can you really be allergic to the sun?
By Anna Gora Published -

What causes metal allergies?
By Anna Gora Published -

The 5 most common seasonal allergies
By Anna Gora Published
-
Anatomy
-
-
Why don't teeth count as bones?
By Marilyn Perkins Published -
Human skeleton quiz: What do you know about the bones in your body?
By Kristina Killgrove Published -

What's the strongest muscle in the human body?
By Clarissa Brincat Last updated -

Staring at the March 29 solar eclipse can cause eye damage in seconds — and you won’t even feel it happening
By Emily Cooke Published -

New cells discovered in eye could help restore vision, scientists say
By Emily Cooke Published -
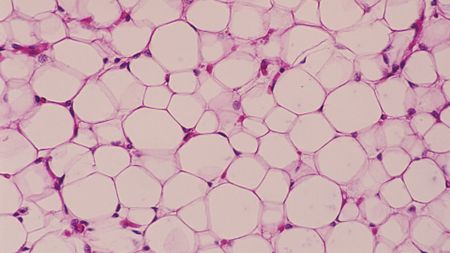
Scientists describe new type of fat in human bellies
By Marianne Guenot Published -

'Vestigial' human ear-wiggling muscle actually flexes when we're straining to hear
By Clarissa Brincat Published -
How many more calories does muscle burn than fat?
By Kamal Nahas Published -
Scientists discover new kind of cartilage that looks like fat-filled 'Bubble Wrap'
By Nicoletta Lanese Published
-
Exercise
-
-
 Buying guides
Buying guidesBest fitness trackers for beginners 2025: From Apple Watch to Garmin Forerunner 165
By Lloyd Coombes Last updated -
 Buying Guide
Buying GuideBest fitness trackers 2026: From smart rings to multisport GPS watches
By Andrew Williams Last updated -
 Buying Guide
Buying GuideBest budget fitness trackers 2026: Cheap but mighty
By Maddy Biddulph Last updated -
 Buyers guide
Buyers guideBest running shoes for supination 2026: Find the perfect fit for your feet
By Harry Bullmore Last updated -
 Reviews
ReviewsAmazfit Active Max review: The best budget smartwatch of 2026?
By Anna Gora Published -
 Buying guides
Buying guidesWhat to buy as a beginner runner: Must-haves vs non-essentials
By Kate Carter Published -
 Buying guides
Buying guidesBest Garmin smartwatches for runners 2026, tried and tested
By Andrew Williams Published -
 Reviews
ReviewsGarmin Enduro 3 review: The longest-lasting sports watch series gets a price cut
By Andrew Williams Published -
 Reviews
ReviewsRenpho Lynx smart ring review: Somewhat disappointing
By Anna Gora Published
-
Food & Drink
-
-

Liquid-nitrogen-infused cocktail popped a man's stomach like a balloon
By Kamal Nahas Published -

Is there such a thing as 'too much' protein?
By Christoph Schwaiger Published -

New US food pyramid recommends very high protein diet, beef tallow as healthy fat option, and full-fat dairy
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

An otherwise 'fit' man had a stroke after drinking 8 'high-potency' energy drinks a day
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

A woman's homemade juice led to life-threatening 'toxic squash syndrome'
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

A toxicologist explains when you can safely cut the moldy part off food, and when it's best to toss it
By Brad Reisfeld Published -

FDA recalls more bagged, frozen shrimp over possible radioactive cesium contamination
By Nicoletta Lanese Last updated -

Man sought diet advice from ChatGPT and ended up with dangerous 'bromism' syndrome
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -
Can weight loss drugs help you drink less alcohol?
By Marianne Guenot Published
-
Genetics
-
-
 Book
BookEmerging embryo-selection technologies are currently 'little more than snake oil.' But someday, they could widen social inequities.
By Daphne O. Martschenko Published -
 Opinion
OpinionNew tech allows parents to 'score' IVF embryos for desirable traits — and it's in desperate need of regulation
By Sam Trejo Published -
Many men lose their Y chromosomes as they age. It may shorten their lives.
By Jenny Graves Published -

Science history: 'Father of modern genetics' describes his experiments with pea plants — and proves that heredity is transmitted in discrete units — Feb. 8, 1865
By Tia Ghose Published -

These genes were thought to lead to blindness 100% of the time. They don't.
By Stephanie Pappas Published -

DNA from ancient viral infections helps embryos develop, mouse study reveals
By Clarissa Brincat Published -

Leonardo da Vinci's DNA may be embedded in his art — and scientists think they've managed to extract some
By Sascha Pare Published -
5 genetic 'signatures' underpin a range of psychiatric conditions
By Clarissa Brincat Published -
Woman had her twin brother's XY chromosomes — but only in her blood
By Mindy Weisberger Published
-
Heart & Circulation
-
-

'Night owls' may have worse heart health — but why?
By Isha Ishtiaq Published -
Man's autopsy reveals unexpected 'boomerang-shaped' structure in his heart
By Lauren Schneider Published -

Men develop cardiovascular disease 7 years before women
By Clarissa Brincat Published -
People with more 'brown fat' have healthier cardiovascular systems. A new study in mice may explain why.
By Zunnash Khan Published -

This 'marker' may be more predictive than cholesterol for heart disease
By Mary J. Scourboutakos Published -

Scientists are developing a 'self-driving' device that helps patients recover from heart attacks
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -
Heart attacks are less harmful at night. And that might be key to treating them.
By Zunnash Khan Published -
Heart quiz: What do you know about the body's hardest-working muscle?
By Marilyn Perkins Published -
Gum disease treatment slows the thickening of arteries, clinical trial shows
By Sophie Berdugo Published
-
Immune System
-
-
An experimental mRNA treatment counters immune cell aging in mice
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

Insomnia and anxiety come with a weaker immune system — a new study starts to unravel why
By Kamal Nahas Published -
Mitochondria aren't only the 'powerhouses of cells' — they also battle germs
By Andrew Monteith Published -
Twin study reveals signs of MS that might be detectable before symptoms
By Michael Schubert Published -

Scientist who discovered body's 'fire alarm' against invading bacteria wins $250,000 Lasker prize
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

Why are some people's mosquito bites itchier than others'? New study hints at answer
By Michael Schubert Published -
Scientists breed most human-like mice yet
By Emily Cooke Published -
Master regulator of inflammation found — and it's in the brain stem
By Emily Cooke Published -
Women have 4 times men's rate of autoimmune disease. The X chromosome may be to blame.
By Emily Cooke Published
-
Medicine & Drugs
-
-

'Universal' nasal-spray vaccine protects against viruses, bacteria and allergens in mice
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -
Needle-free insulin? Scientists invent gel that delivers insulin through the skin in animal studies
By Sayan Tribedi Published -

IVF hormones could be delivered with painless 'microneedle' patch someday, early study hints
By Theresa Sullivan Barger Published -

Antibiotic resistance is the 'silent pandemic' — here are four steps to stop it
By André O. Hudson Published -

Wegovy now comes in pill form — here's how it works
By Clarissa Brincat Published -

Metal compounds identified as potential new antibiotics, thanks to robots doing 'click chemistry'
By Victoria Atkinson Published -
US government overhauls the childhood vaccine schedule in unprecedented move
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

New drug could prevent diabetes complications not fixed with blood sugar control, study hints
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

New antivenom works against 17 dangerous African snake species, study suggests
By Sayan Tribedi Published
-
Neuroscience
-
-

Psychedelics may rewire the brain to treat PTSD. Scientists are finally beginning to understand how.
By Jane Palmer Published -
'Pain sponge' derived from stem cells could soak up pain signals before they reach the brain
By Payal Dhar Published -

'Zombie' cells may drive common form of epilepsy
By RJ Mackenzie Published -

A man's sudden seizures were set off by sudoku
By Sophie Berdugo Published -
'Mitochondrial transfer' into nerves could relieve chronic pain, early study hints
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

Neuroscience word search — Find all the parts of the brain
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -
Tiny implant 'speaks' to the brain with LED light
By Payal Dhar Published -

Brain scans reveal 'dial' that helps keep us from getting lost
By RJ Mackenzie Published -

Injecting anesthetic into a 'lazy eye' may correct it, early study suggests
By Clarissa Brincat Published
-
Reproductive Health
-
-

In a first, study links maternal genes to risk of pregnancy loss
By Zoe Cunniffe Published -

Risk of death from pregnancy in the US is 44 times higher than that from abortion, new analysis reveals
By Marianne Guenot Published -
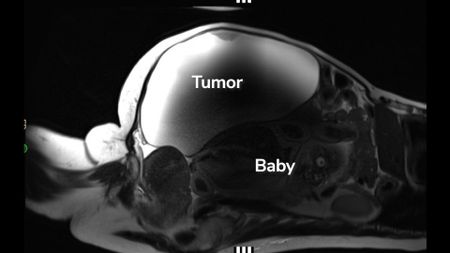
'Unprecedented': Woman delivers full-term abdominal pregnancy while also having 22-pound cyst removed
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -
Could aging eggs be 'rejuvenated'? New tool may help pave the way to fertility-extending treatments
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -
Study links GLP-1 use to some pregnancy risks — but the research has key caveats
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

New blood test can predict risk of postpartum depression with more than 80% accuracy
By Michele Cohen Marill Published -

Don't use cannabis during pregnancy or breastfeeding, leading OBGYN group says
By Elise Ceyral Published -

Scientists created human egg cells from skin cells — then used them to make embryos
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -
 Opinion
OpinionDangers of falling birth rates in the US have been 'dramatically overstated,' experts say
By Leslie Root Published
-
Sex
-
-

How long can human sperm survive?
By Emma Bryce Published -

Do animals have orgasms?
By Elana Spivack Published -
Do sperm really race to the egg?
By Ashley Hamer Published -

Sex leaves 'microbial traces' on genitalia, even when a condom is used — scientists call it the 'sexome'
By Emily Cooke Published -
Scientists made mice with Y chromosomes female by deleting just 6 tiny molecules
By Sahana Sitaraman Published -

Man's years of premature ejaculation had a rare cause
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

Viagra alternatives? Study of mouse erections hints at new ways to treat erectile dysfunction
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

Erectile dysfunction risk may rise on lengthy space missions, rat study reveals
By Emily Cooke Published -
'Sex drive switch' discovered in male mouse brain that kicks their libido into overdrive
By Emily Cooke Published
-
Sleep
-
-
Sleep deprivation harms the gut via the vagus nerve, early study reveals
By Sahana Sitaraman Published -

Are you a night owl or an early bird?
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

Scientists infiltrated volunteers' dreams to boost their creative thinking
By RJ Mackenzie Published -

Do your dreams change as you age?
By Abby Wilson Published -
Study reveals why the brain 'zones out' when you're exhausted
By Sophie Berdugo Published -

'DST just seems so pointless': Poll reveals most Live Science readers want to eliminate daylight saving time
By Sophie Berdugo Published -

Do people dream in color or black and white?
By Abby Wilson Published -

Would you get rid of daylight saving time?
By Sophie Berdugo Published -

Scientists have just defined five sleep profiles — and some could help spot mental illness
By Theresa Sullivan Barger Published
-
Surgery
-
-
'The ban assumed the danger was making pigs too human': Why human organs aren't grown in pigs in the US
By Monika Piotrowska Published -
 Science news this week
Science news this weekScience news this week: NASA finds best evidence of life on Mars and scientists invent visible time crystals
By Ben Turner Published -
 Science news this week
Science news this weekScience news this week: A key Atlantic current nears collapse, the world's biggest iceberg shatters, and mouse brains rewrite neuroscience
By Ben Turner Published -
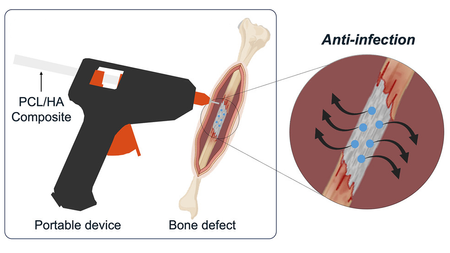
Scientists develop 'glue gun' that 3D prints bone grafts directly onto fractures
By Kristina Killgrove Published -
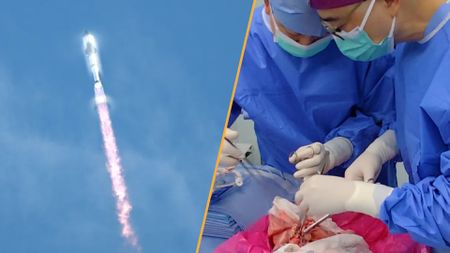 Science news this week
Science news this weekScience news this week: A world first pig-to-human lung transplant, and SpaceX’s Starship nails a test flight
By Ben Turner Published -

Early test of new laser-free eye treatment shows promise
By Olivia Ferrari Published -
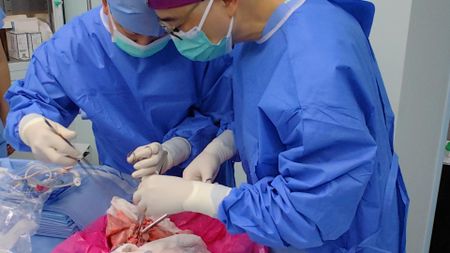
First-ever pig-to-human lung transplant attempted in brain-dead person in China
By Nicoletta Lanese Published -

Are women less sensitive to anesthesia than men?
By Sahas Mehra Published -
In 'extremely rare' case, Michigan resident dies from rabies after receiving transplanted kidney carrying the virus
By Jess Thomson Published
-
Viruses, Infections & Disease
-
-
Diagnostic dilemma: 83-year-old man's unusual form of syphilis had an 'uncertain' source
By Sophie Berdugo Published -
 Opinion
OpinionVaccine denial sets Americans up for more chronic illness
By Janna K. Moen Published -
'DNA origami' could be key for making an effective HIV vaccine, early study hints
By Zunnash Khan Published -
Cancer vaccine shows promise against HPV-related throat tumors in early study
By Clarissa Brincat Published -

Teenager contracts rare 'welder's anthrax,' marking the ninth known case ever reported
By Sophie Berdugo Published -

Only certain types of brain-training exercises reduce dementia risk, large trial reveals
By Kamal Nahas Published -
AI-supported breast cancer screening spots more cancers earlier, landmark trial finds
By Jennifer Zieba Published -
The 'mono' virus raises the risk of MS and cancer in some. 22 genes hint at why.
By Stephanie Pappas Published -

'Nose-in-a-dish' reveals why the common cold hits some people hard, while others recover easily
By RJ Mackenzie Published
-
More about Health
-
-
 Buying guides
Buying guidesBest fitness trackers for beginners 2025: From Apple Watch to Garmin Forerunner 165
By Lloyd Coombes Last updated -
 Buying Guide
Buying GuideBest fitness trackers 2026: From smart rings to multisport GPS watches
By Andrew Williams Last updated -
 Buying Guide
Buying GuideBest budget fitness trackers 2026: Cheap but mighty
By Maddy Biddulph Last updated
-
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus









