Nicoletta Lanese
Nicoletta Lanese is the health channel editor at Live Science and was previously a news editor and staff writer at the site. She holds a graduate certificate in science communication from UC Santa Cruz and degrees in neuroscience and dance from the University of Florida. Her work has appeared in The Scientist, Science News, the Mercury News, Mongabay and Stanford Medicine Magazine, among other outlets. Based in NYC, she also remains heavily involved in dance and performs in local choreographers' work.
Latest articles by Nicoletta Lanese

New Jersey man dies from meat allergy triggered by tick bite
By Nicoletta Lanese published
A man in New Jersey has died from a meat allergy that people can develop after being bitten by certain tick species.

A woman's homemade juice led to life-threatening 'toxic squash syndrome'
By Nicoletta Lanese published
In the first reported case of its kind in Canada, a woman fell violently ill after consuming the juice of a bitter gourd.
Canada has lost its 'measles elimination status' — here's what that means
By Nicoletta Lanese published
A large, ongoing outbreak that began in Canada in 2024 has cost the country its measles elimination status.

One molecule could usher revolutionary medicines for cancer, diabetes and genetic disease — but the US is turning its back on it
By Nicoletta Lanese published
The U.S. government is divesting from mRNA vaccines, but will other uses of the technology be spared? In a time of uncertainty, scientists worry that revolutionary treatments for cancer, immune dysfunction and genetic disease may be left on the lab bench.
'This is a completely different level of anti-vaccine engagement than we've ever seen before,' says epidemiologist Dr. Seth Berkley
By Nicoletta Lanese published
Interview Epidemiologist Dr. Seth Berkley spoke to Live Science about the importance of vaccine equity and the obstacles undermining it, as well as the political challenges to vaccines being raised in the U.S.

Future pandemics are a 'certainty' — and we must be better prepared to distribute vaccines equitably
By Dr. Seth Berkley published
Book Months before COVID-19 was declared a pandemic, efforts were already underway to ensure low-income countries would get access to future vaccines against the infection. The book "Fair Doses" tells that story and discusses the ongoing fight for vaccine equity around the world.
A toddler accidently ate gonorrhea bacteria from a lab dish
By Nicoletta Lanese published
In a bizarre medical case published in 1984, a young boy was inadvertently exposed to an STI-causing bacteria in a lab dish.

Black eyes, orbital fractures and retinal detachment: Pickleball-related eye injuries are on the rise in the US
By Nicoletta Lanese published
A new analysis suggests the rate of pickleball-related eye injuries has increased dramatically in the U.S. as the sport gains popularity.

A woman's nausea was triggered by a huge mass in her stomach — which doctors dissolved with diet soda
By Nicoletta Lanese published
A woman's abdominal discomfort turned out to be caused by a build up of food in her stomach. And the treatment involved diet soda.
'The Big One' could be even worse than COVID-19. Here's what epidemiologist Michael Osterholm says we can learn from past pandemics.
By Dr. Michael Osterholm, Mark Olshaker published
The new book "The Big One" describes lessons learned from past pandemics and how they might be applied to mitigate the dangers of future outbreaks.

Scientists created human egg cells from skin cells — then used them to make embryos
By Nicoletta Lanese published
In a proof-of-concept experiment, scientists demonstrated that you can create and fertilize human eggs in the lab using sperm, genes from skin cells, and the "shells" of existing egg cells.
'Groundbreaking' gene therapy is first treatment for Huntington's disease to slow the condition
By Nicoletta Lanese published
Results from a three-year trial suggest an experimental gene therapy for Huntington's disease can slow the progression of the deadly condition by 75%.

If tiny lab-grown 'brains' became conscious, would it still be OK to experiment on them?
By Nicoletta Lanese published
A perspective paper published this week argued that brain organoids could soon gain consciousness, and we should consider stricter regulations around them.
CDC committee votes to change measles vaccine guidance for young children
By Nicoletta Lanese published
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has recommended against using the MMRV vaccine in children under 4. This could eliminate a choice for kids' first dose of measles, mumps, rubella and chickenpox prevention.

Even brief exposure to air pollution can push the placenta into an inflammatory state, lab study suggests
By Nicoletta Lanese published
A study of human placentas suggests that urban air pollution may push the organ's resident immune cells into an inflammatory state.

Have you gotten this year's COVID vaccine?
By Nicoletta Lanese published
Federal guidance about the 2025-2026 COVID-19 vaccine has raised questions and confusion around the shots. Have you tried to get one this year?

Breakthrough cystic fibrosis drug that extends life by decades earns its developers a $250,000 'American Nobel'
By Nicoletta Lanese published
One of this year's coveted Lasker Awards went to three scientists who helped invent a life-saving treatment for cystic fibrosis, a genetic disease.
'We have basically destroyed what capacity we had to respond to a pandemic,' says leading epidemiologist Michael Osterholm
By Nicoletta Lanese published
Live Science spoke with leading epidemiologist Michael Osterholm about his new book, "The Big One," which discusses the next pandemic and how to mitigate its harm.

Just 1 dose of LSD could relieve anxiety for months, trial finds
By Nicoletta Lanese published
An early trial with about 200 people tested the effects of LSD on generalized anxiety disorder and found promising results.

Formaldehyde-free hair-straightening products may still threaten health, concerning study finds
By Nicoletta Lanese published
Formaldehyde-free hair-straightening products have been marketed as a safer option, but they may pose a risk to kidney health, a case series suggests.
First-ever pig-to-human lung transplant attempted in brain-dead person in China
By Nicoletta Lanese published
In a first, scientists in China transplanted a lung from a pig into a human so they could see how the host immune system handled the procedure.
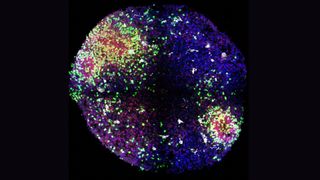
'Minibrains' reveal secrets of how key brain cells form in the womb
By Nicoletta Lanese published
Miniature models of the brain have revealed a "previously unappreciated" role of microglia, a type of cell found within the organ. The finding could help unpack how disorders such as autism arise.

If 'pregnancy robots' were real, would you use one?
By Nicoletta Lanese published
A viral story raised the idea of using robots outfitted with artificial wombs to incubate human babies from conception to birth. If such technology existed, would you consider using it?

$14,000 pregnancy robot from China isn't real. But is a similar technology possible?
By Nicoletta Lanese published
A story circulating on social media this week featured a seemingly made-up scientist who is developing an equally imaginary "pregnancy robot." Virality ensued.

FDA recalls more bagged, frozen shrimp over possible radioactive cesium contamination
By Nicoletta Lanese last updated
The FDA is warning consumers not to eat certain frozen shrimp products sold at Walmart after other products from the same company tested positive for a radioactive substance.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
