Science News: Recent scientific discoveries and expert analysis
Read the latest science news and recent scientific discoveries on Live Science, where we've been reporting on groundbreaking advances for over 20 years. Our expert editors, writers and contributors are ready to guide you through today's most important breakthroughs in science with expert analysis, in-depth explainers and interesting articles, covering everything from space, technology, health, animals, planet Earth, and much more.

Explainers | Everything you need to know about the science news that matters.

Science Spotlight | Shining a light on new science transforming our world.
Latest news

'Cikai Korran came here and saw': Visitors from India graffitied dozens of Egyptian tombs 2,000 years ago
By Owen Jarus published
Ancient inscriptions written in Indian languages have been discovered on Egyptian tombs in the Valley of the Kings.

Planting trees in the sea could act as a huge carbon sink and save millions of dollars in storm damage every year. What is stopping us from doing it?
By Sarah Wild published
A new study reveals restoring mangroves could save $800 million in storm damage, protect 140,000 people from flooding, and remove almost triple the amount of CO2 produced by cars in the U.S. every year.

'City killer' asteroid will narrowly miss the moon, James Webb Telescope reveals
By Brandon Specktor last updated
The "city killer" asteroid 2024 YR4 won't hit Earth or the moon when it whizzes by in 2032, the latest James Webb Space Telescope observations confirm.

Scientists find 2 marsupial species, thought to have gone extinct 6,000 years ago, living in the forests of New Guinea
By Sascha Pare published
The pygmy long-fingered possum and the ring-tailed glider, two marsupials believed to have died out thousands of years ago, are still alive in Papuan Indonesia.

'Striking' footage captures the moment a red fox preys on a wolf pup — a behavior never seen on film before
By Bryony Ravate published
Scientists in Italy captured a red fox entering a den as part of a project to understand wolf population dynamics in the country.

China puts a sodium-ion battery into an EV for the first time — it can drive 248 miles on a single charge
By Rory Bathgate published
A new vehicle is the first mass-produced passenger EV with a viable sodium-based alternative to conventional lithium-ion batteries.

Groundbreaking new drug shows promise for treating children with a devastating form of epilepsy
By Eva Amsen published
An experimental treatment reduces seizures and other symptoms in children with a type of epilepsy called Dravet syndrome.

Daylight Saving Time 2026 is coming
By Jeanna Bryner last updated
When does daylight saving time begin in 2026? Here's a look at when the time changes this year, and why we change our clocks in the first place.

Scientists taught robots to swim through mazes using Einstein's relativity
By Alan Bradley published
The tiny bots follow patterns of light and "artificial space-time," navigating like craft following the curved space around a black hole.

The sword in the sea: How one lucky graduate student found his second Crusader sword while taking a swim off Israel's coast
By Kenna Hughes-Castleberry published
A 12th-century sword spotted jutting out of the seabed in Israel was designed for one-handed combat during the Crusades.

Sodium-ion batteries are getting ready for prime time. How can they improve EVs?
By Rory Bathgate published
With potential safety improvements and lower manufacturing costs, Na-ion batteries are coming of age at precisely the right time.

Chinese EV maker claims it's engineered the world’s first semi-solid-state EV battery with huge 620-mile range
By Alan Bradley published
The experimental manufacturing process could one day deliver a vehicle with a 1,000-plus mile range, researchers say.

Climate disasters caused societal upheaval 3,000 years ago in China, study of 'oracle bones' hints
By Kristina Killgrove published
Some civilizations in inland China underwent dramatic changes and population drops 3,000 years ago. Now, researchers are using oracle bones, archaeological evidence and climate modeling to find out why.
Can you tie a knot in four dimensions? A mathematician explains
By Zsuzsanna Dancso published
An academic dives into the physics of multiple dimensions and whether it's possible to tie a knot in 4D.
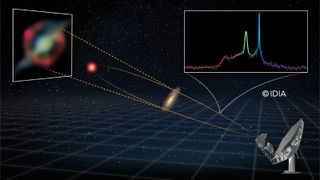
'Truly extraordinary': Mega-laser shooting at us from halfway across the universe is the brightest 'cosmic beacon' we've ever seen
By Harry Baker published
Astronomers have discovered the brightest and most distant "megamaser" to date. The cosmic energy beam is shooting toward Earth from 8 billion light-years away and was spotted thanks to a weird space-time trick first predicted by Einstein.

Chewed-up orca fins on Russian beach point to cannibalism, and scientists say it may explain why some pods are so tight-knit
By Chris Simms published
Detached orca fins scored with distinctive tooth marks suggest that killer whale cannibalism is happening — and it might explain some complex orca societies.

NASA fixes Artemis II rocket for April launch to take astronauts around moon
By Patrick Pester published
NASA's Artemis II is on track to shoot for the moon in April after engineers fixed the helium issue that grounded the mission's rocket last month.

Birds are declining faster and faster in 3 US hotspots, new study finds
By Patrick Pester published
Researchers have revealed that North American birds are declining at an accelerating rate in three regional hotspots associated with intense agriculture.

Meet the world's smallest AI supercomputer — it packs 'doctorate-level intelligence', its makers say, and can fit into your pocket
By Alan Bradley published
The portable computing powerhouse is capable of running 120-billion-parameter LLMs, roughly three times larger than GPT-3, without needing to access the internet or the cloud.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus












