Human evolution: Facts, news, features and articles about the past 300,000 years of Homo sapiens
Oldest discovered Homo sapiens skeletons: 315,000 years old
Where these early fossils were found: Jebel Irhoud, Morocco
What experts found: The fossil skeletons of 22 humans
In 1758, Swedish biologist Carl Linnaeus gave humans a scientific name: Homo sapiens, which means "wise human" in Latin. Although Linnaeus grouped humans with other apes, it was English biologist Charles Darwin who laid out an explanation for how humans came to be. His theory of evolution, first described in 1859, explained how humans slowly changed over time to be better suited to the environments where they lived. Many of our traits, from our ability to walk on two legs to our big brains, are a result of this evolution.
For the past 150 years, scientists have been working to understand where humans came from and how we got here. This research is based on skeletons from all over the world and even modern DNA. Scientists now know that our species goes back at least 300,000 years — and that we're still evolving.
5 fast facts about human evolution
- Humans and chimpanzees shared an ancestor 7 million years ago.
- All humans today are descended from people who evolved in Africa.
- Evolving to walk on two feet has led to problems like back and knee pain.
- Babies are born with more than 300 bones in their skeleton, but by adulthood, they have only 206.
- Wisdom teeth are an evolutionary "leftover" — and some people don't ever grow them.
Everything you need to know about human evolution
How are humans related to apes?
Humans' closest relatives are other apes, such as chimpanzees and bonobos. In fact, we share nearly 99% of the same genes, or letters in our DNA, with chimpanzees. Even though we have a lot of similarities, our "last common ancestor" was an ape-like species that lived more than 7 million years ago. That means thousands and thousands of generations ago, the same group of primates gave rise to the distant ancestors of us, chimpanzees, bonobos and gorillas.
You may wonder why, if humans evolved from ape-like species, there are still gorillas and chimpanzees around today. It's because humans and living apes took two different directions after they split from each other. Apes were busy scampering around on four legs, swinging from trees and living in forests. Their four-legged bodies worked well in these environments.
Meanwhile, for some mysterious reason, human ancestors began to walk upright on two feet, and this new habit, called bipedalism, set the evolution of human skeletons on a distinct path from our ape cousins. Walking on two feet helped our long-ago ancestors move around the African grasslands. Walking upright also freed up their hands to make and use tools. Walking on two legs allowed human ancestors to move into new parts of Africa and then all across the world over millions of years, making us the most adaptable species on Earth.

Where did humans first evolve?
Our species, known in biology as Homo sapiens, first evolved in Africa over 300,000 years ago. The earliest human fossils come from a place called Jebel Irhoud in Morocco, on the northern coast of Africa. Paleoanthropologists — experts in human fossils — point out that, while these early humans' skulls may look different than ours, they were using tools and creating art.
But some scientists think our species is even older than this. Using information from modern humans' DNA, genetics experts have created a model showing that humans may have evolved 1 million years ago and then split into groups that lived in South, West and East Africa. These groups would have mostly lived apart but met up every now and then to socialize, share information and have babies together.

When did humans spread around the world?
Almost 2 million years ago, long before humans evolved, our ancient ancestor Homo erectus decided to leave Africa and wander north. Some groups spread into Eastern Europe, China and Southeast Asia, probably hunting for food and shelter. After Homo sapiens evolved from the African descendants of H. erectus, humans began exploring the rest of the world, starting this new journey at least 200,000 years ago.
This trek took groups of humans through the Mediterranean by 195,000 years ago. They reached Northern Europe around 48,000 years ago, occupied Papua New Guinea and Australia by 50,000 years ago, and arrived at some of the far-flung islands of the Pacific 30,000 years ago. The last places to be reached by humans were North and South America; our ancestors were in a spot in what is now New Mexico by 21,000 years ago and arrived at the tip of southern Chile by 14,000 years ago.

Why do humans have different skin colors?
Until about 14,000 years ago, most humans had dark skin, brown hair and brown eyes, experts who study ancient genetics have discovered. But somewhere between 14,000 and 3,000 years ago, mutations — changes in the letters in our DNA — started to crop up. These mutations — which caused light-colored skin, hair and eyes — became much more common than before, particularly in people living in less sunny environments like Northern Europe.
One explanation for why people in more northern areas tend to have lighter skin is that the sun's rays are less powerful when they strike farther north. At these locations, people have a harder time getting enough vitamin D, a nutrient that helps boost our immune system and build strong bones. Lighter skin makes it easier for a person in less-sunny climates to get enough vitamin D, so in those places, lighter skin gave people an advantage.
But in sunny regions, darker skin was more useful. That's because dark skin has more of a special chemical, called melanin, that protects humans from the sun's powerful rays. A certain kind of sunlight, called UV radiation, can pass through the skin and damage our DNA, which can then lead to cancer. But melanin blocks those rays.
Today, people with any skin color can survive anywhere in the world. That's because humans have learned how to get vitamin D from foods like milk and fish and to stay in the shade, slather on sunblock, or wear clothes and hats to protect us from UV rays.

Are humans still evolving?
By the basic definition of evolution — a change in characteristics that are inherited, or passed on through genes from parents to children — yes, humans are still evolving! But you may have to look really close to see it.
One obvious example is wisdom teeth, those molars that finally show up in your late teens or early 20s. We used to have bigger, stronger jaws because we needed to chew tough foods. Today, some people have a mutation that causes them to not have wisdom teeth. This mutation is becoming more common because we eat soft, cooked foods now and don't need to do all the chewing our ancestors did.
But scientists can also see that individual genes are changing in humans over time. One example is a gene called EPAS1, which helps a person function better when the air doesn't have much oxygen, such as in high mountains. Scientists found that 87% of Tibetans have one form of this gene, while only 9% of Chinese have the same form. Tibetan ancestors split off from Han Chinese people only around 2,700 years ago, which means that this gene quickly took over in ancient Tibetans because it was so helpful in their high mountain environments. That's some of the fastest evolution ever seen in humans.
Human evolution pictures
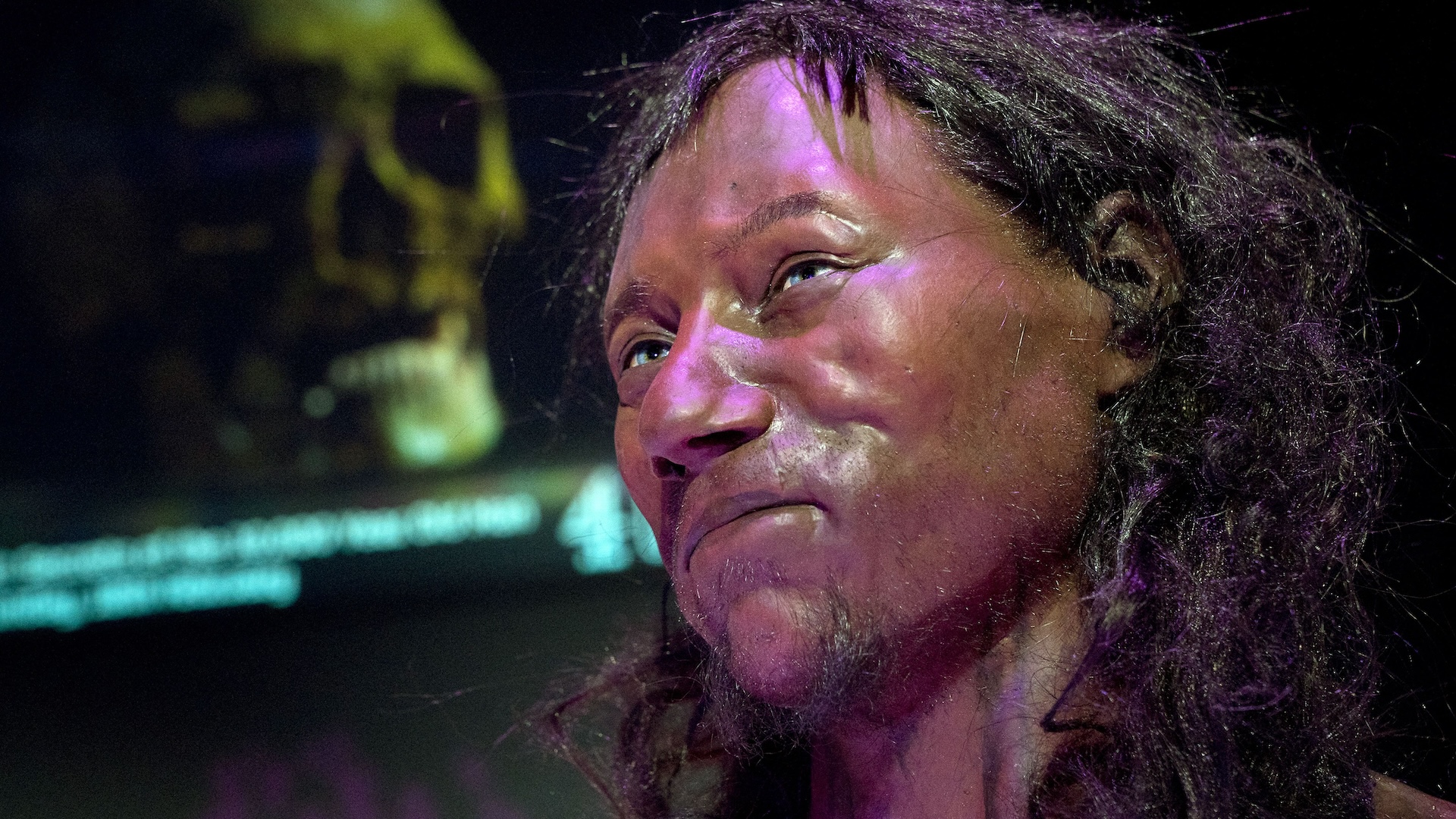

Most human ancestors were dark-skinned
A 10,000-year-old skull found in Britain and known as "Cheddar Man" was reconstructed with dark hair and dark skin, which most humans had before around 3,000 years ago.
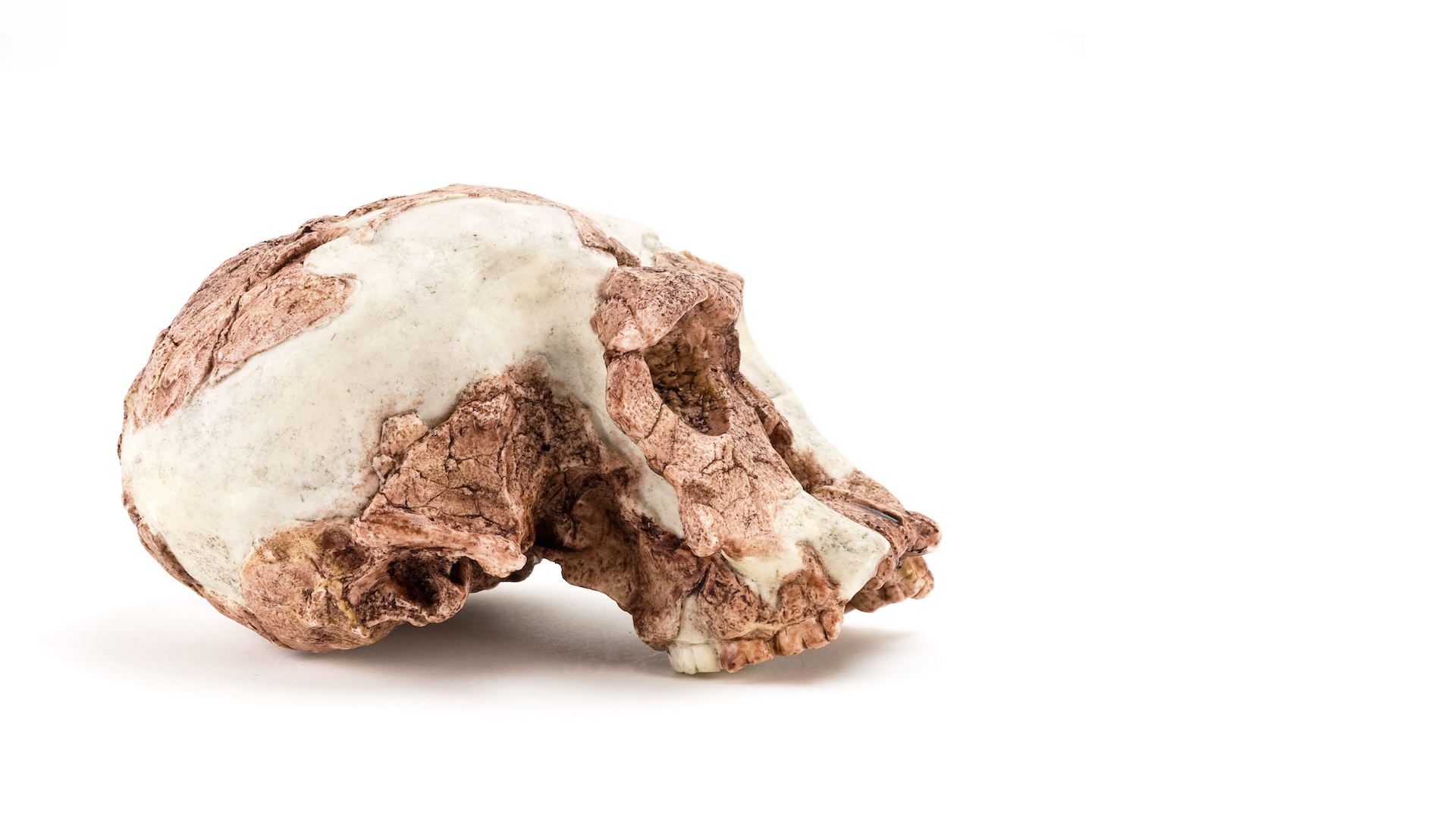

Earliest biped
We don't know what the first creature to walk on two feet was, but one possibility is something named Sahelanthropus tchadensis, which lived around 7 million years ago.
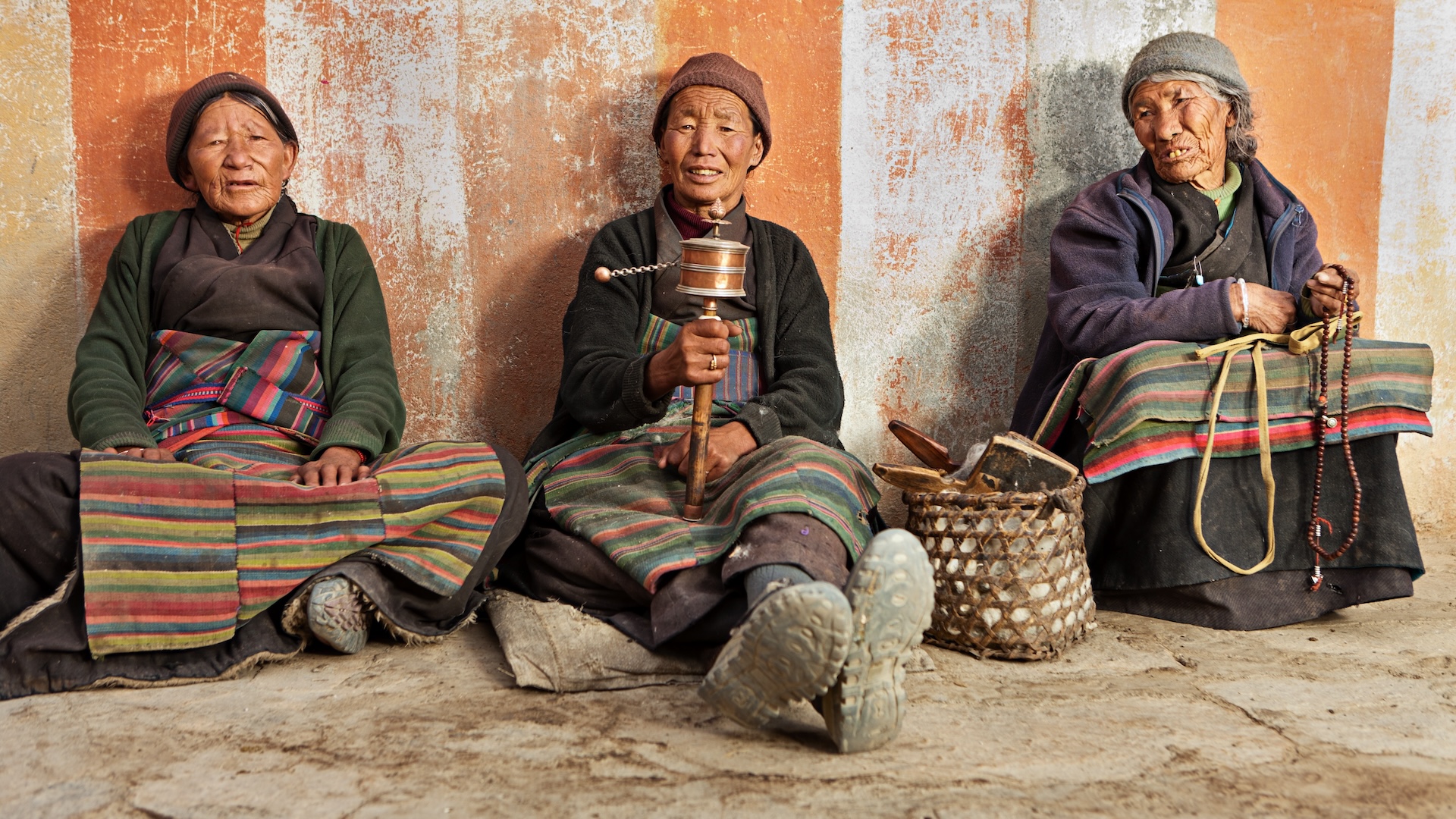

Tibetans evolved quickly
Most Tibetan people have a gene that helps them survive at high altitudes with low levels of oxygen — an example of recent human evolution.
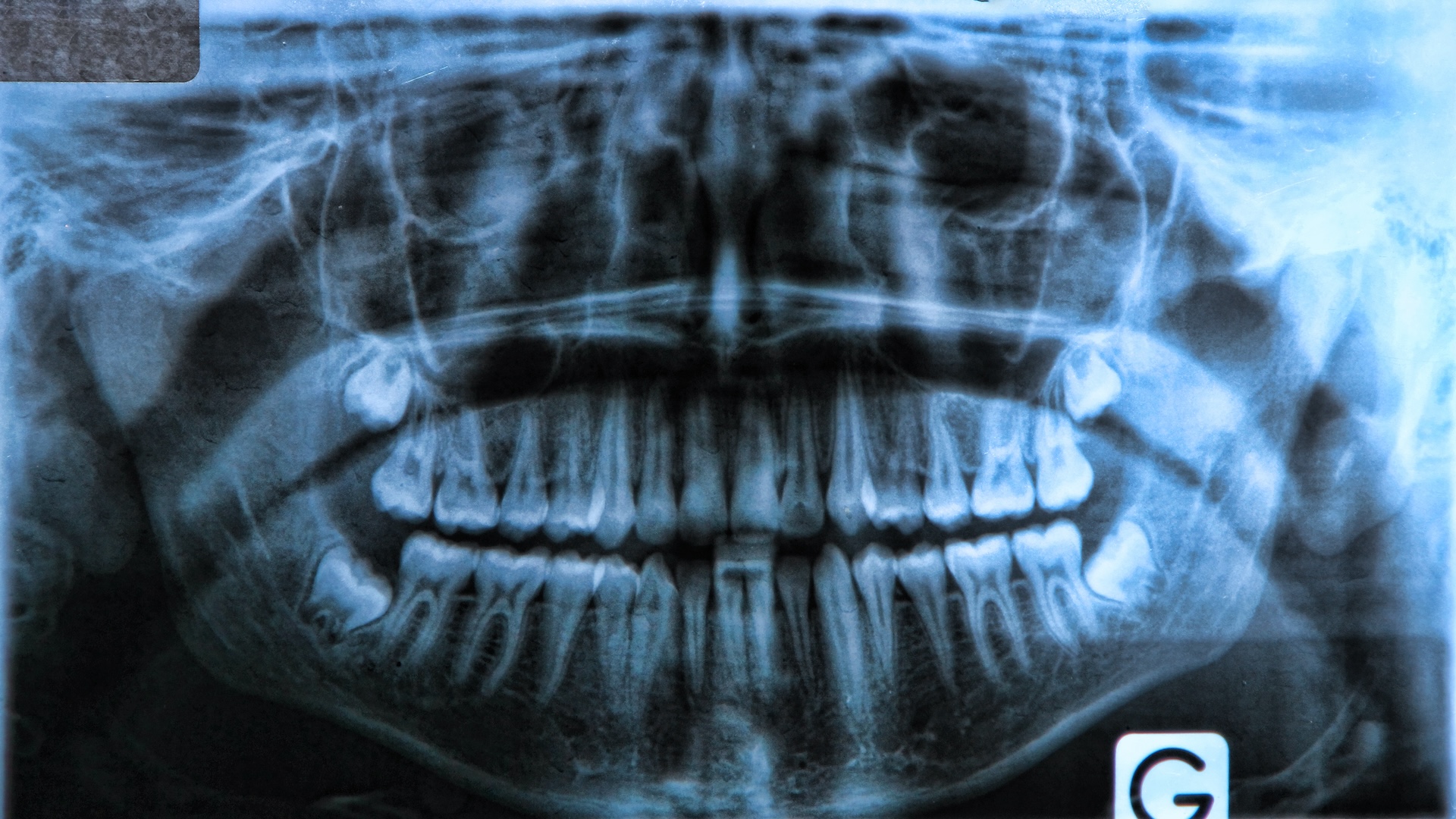
Wisdom teeth are disappearing
More and more people are missing wisdom teeth thanks to a change in our DNA. Many people have to get their wisdom teeth removed because they cause pain or don't fit in their mouth. This is because human jaws have shrunk through evolution.
Discover more about human evolution
- Humans might be making genetic evolution obsolete
- Why did Homo sapiens outlast all other human species?
- What's the difference between Neanderthals and Homo sapiens?

Kristina Killgrove is a staff writer at Live Science with a focus on archaeology and paleoanthropology news. Her articles have also appeared in venues such as Forbes, Smithsonian, and Mental Floss. Kristina holds a Ph.D. in biological anthropology and an M.A. in classical archaeology from the University of North Carolina, as well as a B.A. in Latin from the University of Virginia, and she was formerly a university professor and researcher. She has received awards from the Society for American Archaeology and the American Anthropological Association for her science writing.
Explore Human Evolution
Latest about Human Evolution

Humans and Neanderthals interbred — but it was mostly male Neanderthals and female humans who coupled up, study finds
By Kristina Killgrove published
A preference for pairings between male Neanderthals and female Homo sapiens may answer the question of why there are "Neanderthal deserts" in human chromosomes.

'Absolute surprise': Homo erectus skulls found in China are almost 1.8 million years old — the oldest evidence of the ancient human relatives in East Asia
By Sophie Berdugo published
A new date for Homo erectus skulls found in central China provides new insight into how and when ancient human relatives reached eastern Asia.

Research group claims preeclampsia doomed the Neanderthals, but experts say it's just a 'thought experiment'
By Kristina Killgrove published
Preeclampsia, a complication of pregnancy that involves high blood pressure, could have led to a decline in Neanderthals' fertility, a new study suggests.

What are ghost lineages, remnants of the past that still exist in our DNA today?
By Tom Metcalfe published
Ghost lineages reveal themselves through ancient genes that still exist in living beings today.

Remote region in Greece has one of the most genetically distinct populations in Europe
By Kristina Killgrove published
A genetic analysis of the Deep Maniots living in Greece's southern Peloponnese region has revealed a close-knit, patriarchal community with roots in the Bronze Age.

More than 43,000 years ago, Neanderthals spent centuries collecting animal skulls in a cave; but archaeologists aren't sure why
By Sophie Berdugo published
Neanderthals repeatedly returned to the cave to store horned animal skulls, revealing this cultural tradition was transmitted over time.

430,000-year-old wooden handheld tools from Greece are the oldest on record — and they predate modern humans
By Owen Jarus published
Archaeologists have found the oldest-known surviving examples of handheld wooden tools.

160,000-year-old sophisticated stone tools discovered in China may not have been made by Homo sapiens
By Owen Jarus published
Archaeologists have found the oldest known evidence of hafted tools in East Asia, and they challenge a previously held assumption about stone tool use.

480,000-year-old ax sharpener is the oldest known elephant bone tool ever discovered in Europe
By Aristos Georgiou published
The "very rare" find provides an extraordinary glimpse into the ingenuity of early human relatives who lived around half a million years ago.
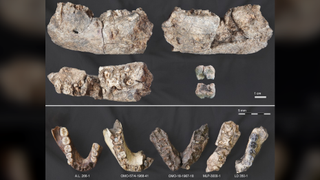
2.6 million-year-old jaw from extinct 'Nutcracker Man' is found where we didn't expect it
By Kristina Killgrove published
A fossil jaw of a distant human relative was discovered much farther north than previously thought possible, revealing new information about diversity in human evolution.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










