Vera C. Rubin Observatory discovers enormous, record-breaking asteroid in first 7 nights of observations
In its preliminary data release, taken from just seven nights of observations, the powerful Vera C. Rubin Observatory has discovered an enormous, fast-spinning asteroid that sets a new record.

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Scientists analyzing the first images from the Vera C. Rubin Observatory have discovered the fastest-spinning asteroid in its size class yet.
The record-breaking space rock, called 2025 MN45, is larger than most skyscrapers on Earth at about 2,300 feet (710 meters) wide. The massive rock completes a rotation in about 113 seconds — making it the fastest-spinning known asteroid over 1,640 feet (500 meters) in diameter.
The research, published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters Wednesday (Jan. 7), is part of an asteroid survey aimed at improving our understanding of how these small bodies formed and evolved.
The study is the first peer-reviewed paper from the Rubin Observatory's LSST Camera — the largest digital camera in the world — which will repeatedly scan the Southern Hemisphere's night sky over 10 years to create an unprecedented time-lapse movie of the universe.
Rocks that roll
Asteroids are essentially large space rocks, and many are remnants of how our solar system appeared early in its 4.5 billion-year-old history, before the evolution of planets and moons. Therefore, by studying asteroids, scientists can figure out how our solar system changed over the eons.
Scientists found 2025 MN45 using the preliminary data release from the Rubin Observatory, which has already revealed thousands of previously unknown asteroids around the solar system after just seven nights of observations. (The 10-year LSST survey has yet to formally begin, but is expected to start in the next few months.)
The asteroid's remarkably fast spin excited the team, as it provides clues about the ancient rock’s composition.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"Clearly, this asteroid must be made of material that has very high strength in order to keep it in one piece," Sarah Greenstreet, an assistant astronomer at the National Science Foundation's National Optical-Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory, said in a statement. "It would need a cohesive strength similar to that of solid rock."
"This is somewhat surprising," added Greenstreet, who also leads a Rubin working group about near-Earth objects and interstellar objects, "since most asteroids are believed to be what we call 'rubble pile' asteroids, which means they are made of many, many small pieces of rock and debris that coalesced under gravity during solar system formation or subsequent collisions."
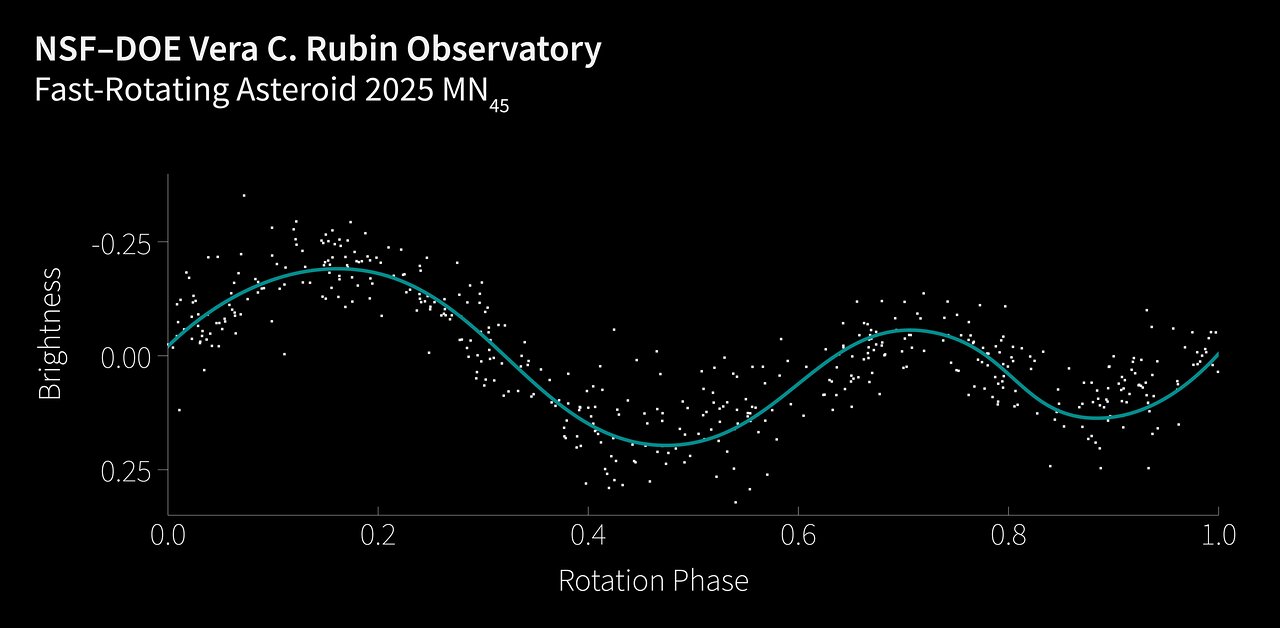
Thousands more to come
In general, fast-spinning asteroids could have reached that state after a collision with another space rock, the study team said. It is also possible that 2025 MN45 is a remnant of a much larger asteroid that was shattered by a cosmic crash.
Most asteroids in the solar system are in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. But most fast-spinning asteroids that astronomers have observed are much closer to Earth, simply because they are easier to see, the study authors noted. 2025 MN45 is a main-belt object, where most asteroids (as they are loose piles of rubble) must take at least 2.2 hours to rotate in order to avoid fragmentation. Anything that rotates faster than that "must be structurally strong," they wrote.
That said, 2025 MN45 is not the only fast spinner in the main asteroid belt. In addition to 2025 MN45, Rubin's first dataset includes 16 "super-fast" rotators, each of which has a rotational period of between 13 minutes and 2.2 hours, as well as two "ultra-fast" rotators with spins of less than two minutes each. All of these asteroids are also longer than 100 yards (90 m), and all but one of the newfound asteroids lives in the main belt.
The commissioning data from Rubin, which was released last June, underwent a deeper look in the new paper, which was also discussed Wednesday at a news conference at the 247th meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Phoenix.
The huge set of observations has about 1,900 never-before-seen asteroids, according to the statement. There will be many more to come when Rubin formally begins its 10-year survey of the sky in the coming months.

Elizabeth Howell was staff reporter at Space.com between 2022 and 2024 and a regular contributor to Live Science and Space.com between 2012 and 2022. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House, speaking several times with the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, "Why Am I Taller?" (ECW Press, 2022) is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










