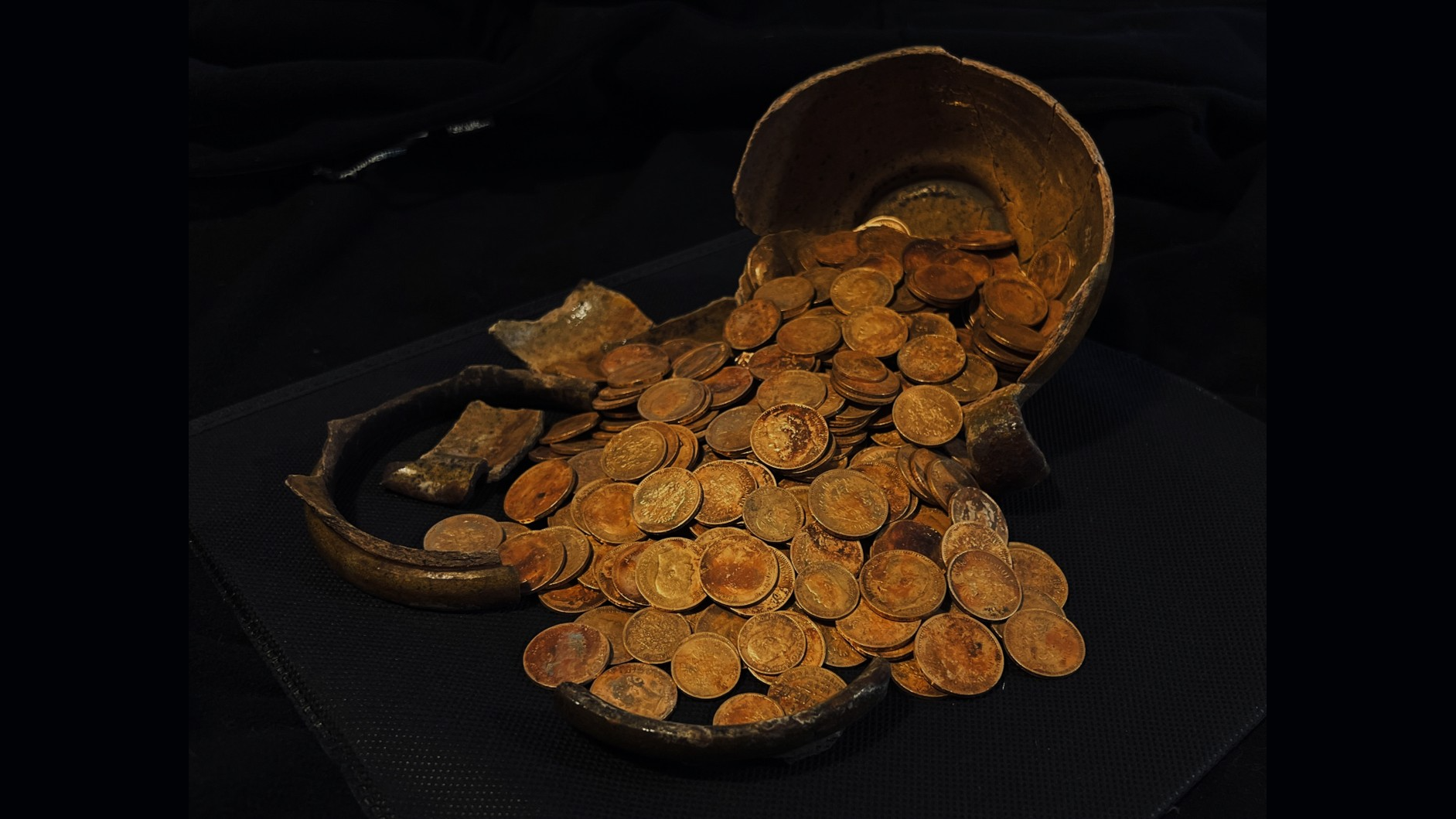
Rare 2,000-year-old war trumpet, possibly linked to Celtic queen Boudica, discovered in England
Archaeologists have announced their discovery of a metal hoard that contained an extremely rare example of a Celtic battle trumpet.

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Archaeologists have recovered a rare 2,000-year-old war trumpet in England that may have been used in Queen Boudica's wars against the Romans. The battle trumpet, also known as a carnyx, was part of a hoard of metal artifacts discovered ahead of residential construction in West Norfolk last year.
The hoard was announced Wednesday (Jan. 7) by Pre-Construct Archaeology, the company that led the original excavation, and Historic England, the organization that is coordinating the research and conservation efforts.
Artifacts in the hoard include the nearly complete animal-headed battle trumpet; a boar-headed military standard, or a decorated pole that identified a group of soldiers; five shield bosses, or ornaments that decorated the center of shields; and other metal items. According to Pre-Construct Archaeology, "finds of this kind are exceptionally rare in Britain and across Europe."
Article continues belowBattle trumpets were used primarily by Celtic tribes in Iron Age Europe and were often taken by Roman soldiers as war trophies, according to representatives for Historic England. "This newly excavated example is one of only three known from Britain and is one of the most complete found in Europe," they said in a statement.
The carnyx was a bronze wind instrument similar to a trumpet, but it had an elongated, vertical shape that ended in an open-mouthed animal, such as a boar. It was a common part of Celtic soldiers' military gear, along with chain mail, shields and spears.
Experts at the National Museum of Scotland have created a replica of a carnyx that, when played by musician John Kenny, gives an impression of what the battle trumpet sounded like.
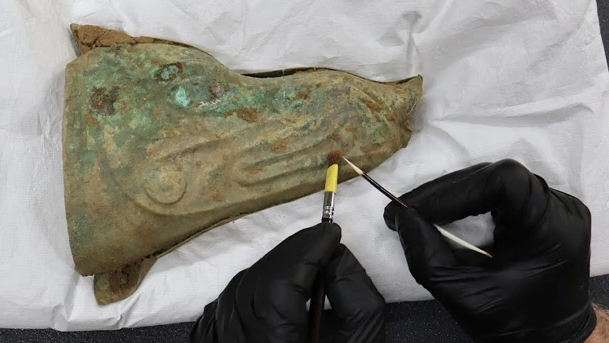
Given the estimated first-century-A.D. date of the metal hoard and its discovery in West Norfolk, the items may have been used by Celts who were attempting to resist the incursion of the Roman Empire.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
In A.D. 60, Boudica (also spelled Boudicca), queen of the powerful Iceni tribe that was based in what is now Norfolk, led a revolt against the Romans. But Boudica and the Iceni were defeated, paving the way for the Roman rule of Britain.
The hoard was removed from the ground in a single block so that its contents could be investigated with X-ray imaging and CT scans before being carefully excavated in the lab. Research and conservation work are ongoing, and the discovery of the hoard will be featured in an upcoming episode of BBC Two's "Digging for Britain."
Roman Britain quiz: What do you know about the Empire's conquest of the British Isles?

Kristina Killgrove is a staff writer at Live Science with a focus on archaeology and paleoanthropology news. Her articles have also appeared in venues such as Forbes, Smithsonian, and Mental Floss. Kristina holds a Ph.D. in biological anthropology and an M.A. in classical archaeology from the University of North Carolina, as well as a B.A. in Latin from the University of Virginia, and she was formerly a university professor and researcher. She has received awards from the Society for American Archaeology and the American Anthropological Association for her science writing.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus











