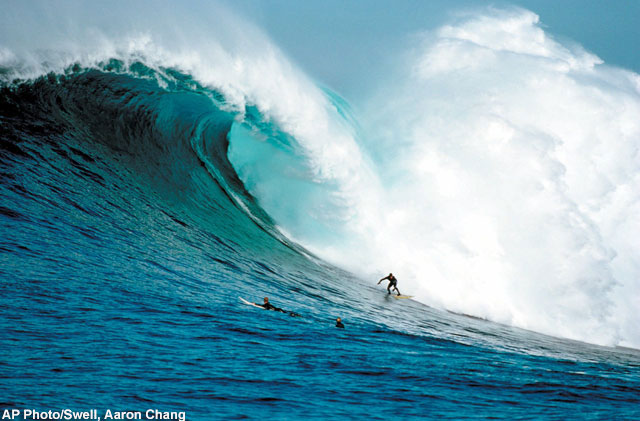
Hurricane's Waves Soared to Nearly 100 Feet
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Waves nearly 100 feet tall were recorded last year in the Gulf of Mexico when Hurricane Ivan headed toward shore, forcing scientists to rethink what is normal.
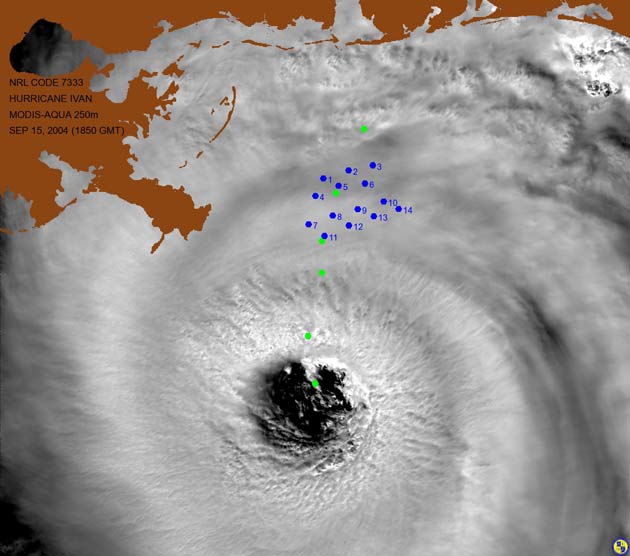
The center of the category 4 hurricane, with winds raging up to 150 miles per hour, passed right over six of the Naval Research Laboratory's wave-tide gauges, churning up waves more than 90 feet high.
"We were a little surprised that the waves were so large," Bill Teague of the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) at Stennis Space Center told LiveScience. "But the reason we were surprised is because this was the first time measurements had been taken of large waves."
Teague and his colleagues at the NRL had placed several wave-tide gauges in the Gulf of Mexico to study water currents and wave heights. The gauges measured the pressure of the water above them which translates to wave height.
The findings are detailed in the Aug. 5 issue of the journal Science.
'Fairly common'
The average of the largest 1/3 of the waves that passed the devices was about 58 feet.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"It was very fortuitous for our moorings to be installed right in the path of Ivan," Teague said. "From theses measurements we have learned that waves over 90 feet are not rogue waves, but are actually fairly common in hurricanes."
Wave measuring devices are commonly destroyed or swept away by turbulent waters like these, but Teague's instruments, which sit on the sea floor rather than bob on the water''s surface, made it through the storm.
According to Teague, the size of extreme waves caused by hurricanes has long been underestimated.
"The measurements that we made will be very useful in wave prediction models," he said.
How waves grow
While tsunamis are generally created by catastrophic disturbances on the sea floor, regular waves are generated by wind. The area of water affected by wind is called a ?fetch.'
As wind blows across the fetch, tiny "capillary" waves form. They're about the thickness of a hair. These tiny waves eventually create little ripples, which cause more friction with the wind, and more energy is transferred from the wind to the water.
"The rougher the water becomes, the easier it is for the wind to transfer its energy," said David Wang, also of the NRL.
When wind blows harder of over a longer time period, more energy is transferred to the water. The biggest waves don't come from the fastest winds, which can blow erratically over a small area, but rather from winds that blow more constantly across large stretches of water, creating a longer fetch.
Hurricanes create large, local waves over small areas, but the waves don't always make it all the way to the shore. The big waves that crash on our shores are from large storms that move steadily over across thousands of miles of ocean.
Long trek
For instance, the sets of waves that surfers drool over at Huntington Beach in Southern California originate from storms in the North Pacific Ocean. The waves travel over 3,000 miles over the course of four days. Antarctic storms produce waves that travel even further.
Although they can besuper tall, these extreme waves only have a period – the time between the crest of one wave and the next – of about 10 seconds and a wavelength of a few hundred feet.
Tsunamis, on the other hand, can have a period more than an hour long and a wavelength more than a hundred miles.
"Tsunamis are only a foot or two in height because they are so long," Teague said. "They only get huge when they hit shallow water and begin to back-up on themselves."
There isn't much need to worry about these extreme hurricane waves reaching the shore, though.
"They break up and dissipate when they start feeling the bottom. They don't last that long," Teague said. "They don't travel that far, but they can bust up everything [in their path]."
- 2005 Hurricane Guide
- Forecast Boosted: Expect 7-9 More Hurricanes
- New Method Predicts Monster Waves
Deadliest, costliest, busiest months, worst states, plus this year's storm names
Hurricane Gallery
Monster Waves
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus