Giant rotating string of galaxies is 'probably the largest spinning object' in the known universe
A giant rotating filament of the cosmic web may be the largest spinning structure ever seen, and could help reveal how galaxies form.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Astronomers have spotted what is likely the "largest spinning object" ever discovered, and its rotation could hold important clues about how galaxies develop.
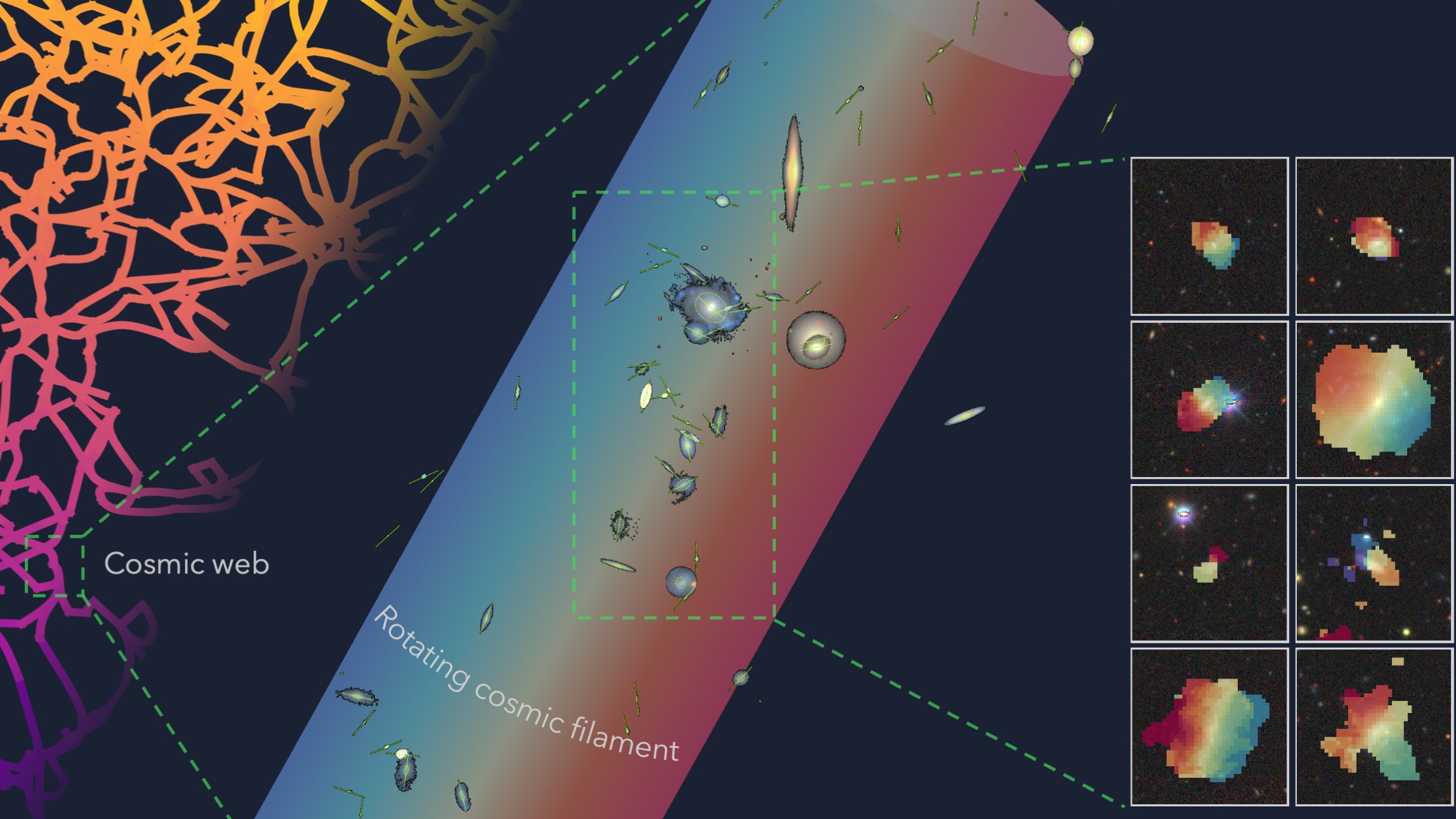
The whirling structure, located 140 million light-years from Earth, is a long, threadlike string of gas that's about 5.5 million light-years long and 117,000 light-years wide — wider than our Milky Way galaxy. The cosmic filament has 14 hydrogen-rich galaxies linked to it in a chain, like charms on a bracelet. These galaxies were what gave away the filament's existence, the researchers explained in a paper published today (Dec. 3) in the journal the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
"The initial discovery itself was a surprise," study co-lead author Lyla Jung, an astronomer at the University of Oxford, told Live Science in an email. "We noticed a striking alignment of galaxies glowing at the same distance." Jung and her colleagues were using MeerKAT, an array of 64 connected radio telescopes in South Africa, when they made the unusual find.
After taking measurements, the researchers found that the filament itself appears to be rotating at around 68 miles per second (110 kilometers per second). What's more, the galaxies around it are rotating as well — most in the same direction as the gaseous thread. This suggests that structures like this one may play a key role in galaxy formation by influencing the speed and direction of a star cluster's spin.
The filament represents "probably the largest spinning object" astronomers have discovered to date, Madalina Tudorache, an astronomer at the University of Oxford who is also part of the research team, told Live Science. Such structures have long been predicted in simulations, but until recently, we lacked telescopes sensitive enough to directly detect them, she added.

The team suspects that similar rotating filaments will be discovered in the near future as researchers continue to ever-deeper reaches of the cosmos with next generation telescopes. Many such filaments link to each other in a vast cosmic web that funnels matter throughout the universe, forming large, interlinked clusters of galaxies.
This observation was collected as part of the MIGHTEE (MeerKAT International GHz Tiered Extragalactic Exploration) survey, which is spearheaded by Oxford physicist Matt Jarvis and is currently ongoing. Future MIGHTEE data may shed further light on the filament's behavior or facilitate the discovery of other rotating cosmic threads. The find may also help to inform forthcoming surveys from new instruments, like the Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"I think it's really helping us understand the universe," Tudorache said.

Joanna Thompson is a science journalist and runner based in New York. She holds a B.S. in Zoology and a B.A. in Creative Writing from North Carolina State University, as well as a Master's in Science Journalism from NYU's Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program. Find more of her work in Scientific American, The Daily Beast, Atlas Obscura or Audubon Magazine.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










