First Vera Rubin Observatory image reveals hidden structure as long as the Milky Way trailing behind a nearby galaxy — Space photo of the week
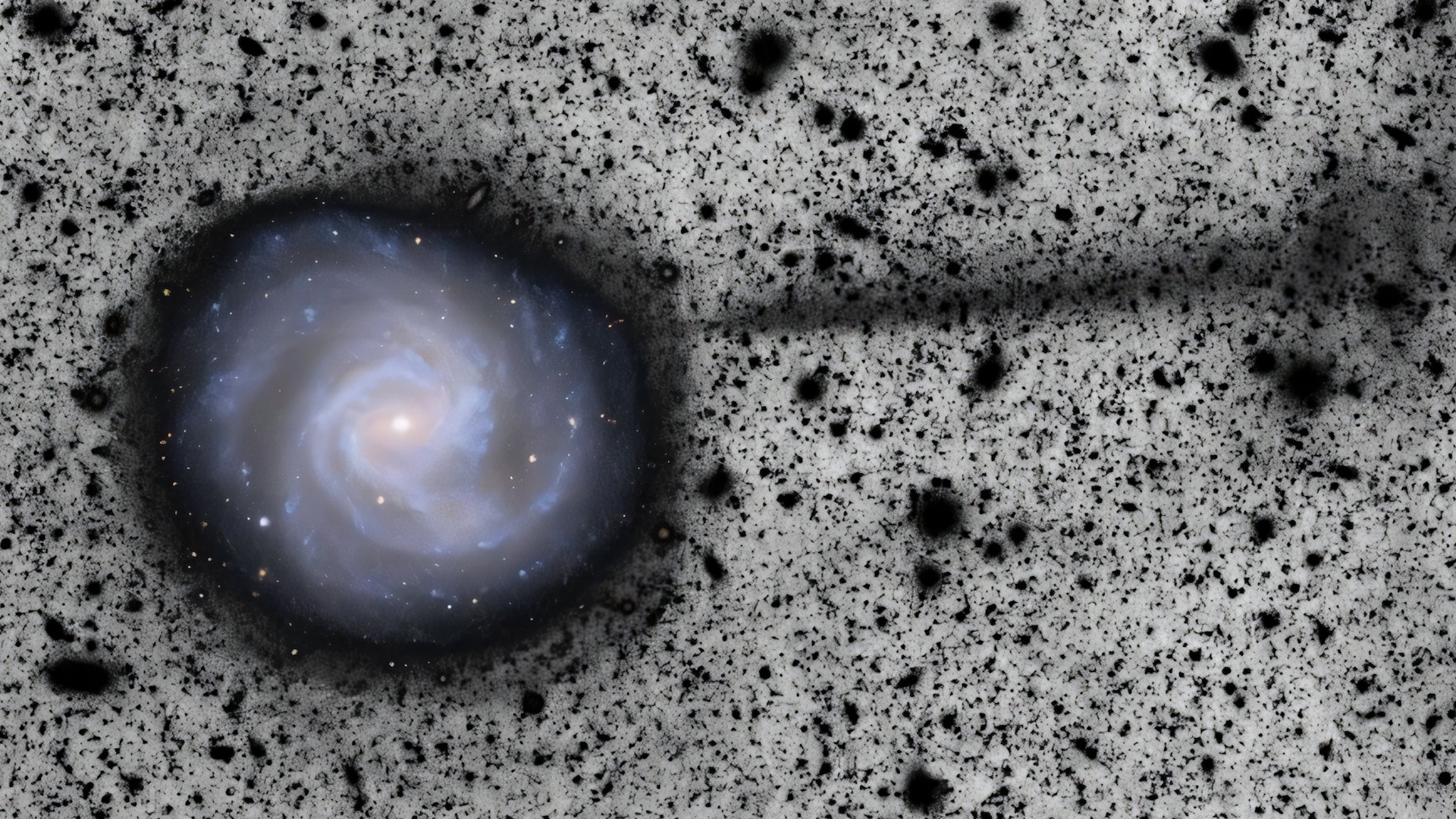
First-light images from the Vera C. Rubin Observatory have revealed a 163,000-light-year stream of stars emanating from the M61 galaxy, suggesting a violent past.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
What it is: Barred spiral galaxy Messier 61, AKA NGC 4303
Where it is: 55 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo
When it was shared: Oct. 28, 2025
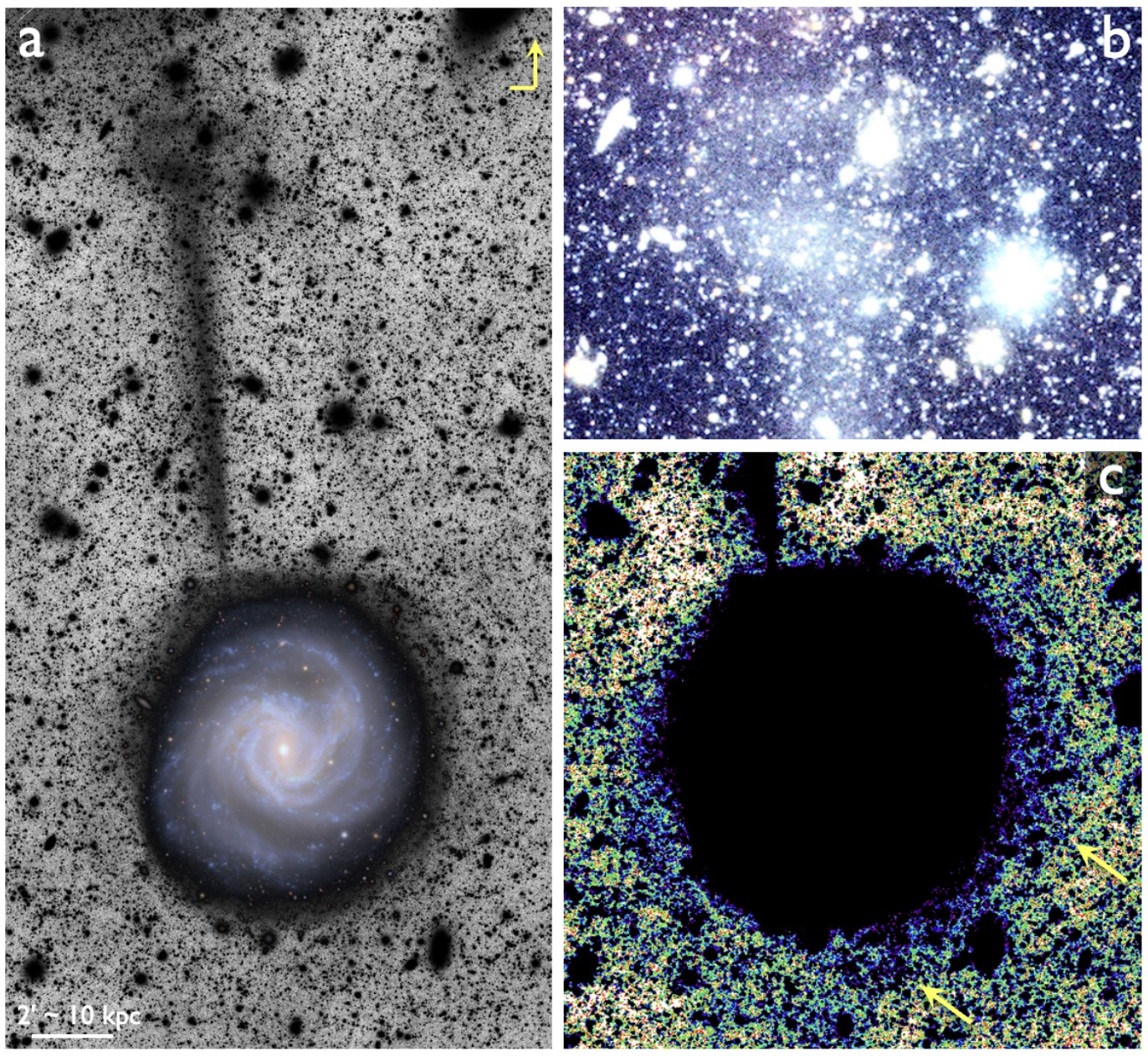
Even before its full science operations have begun, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile has already helped astronomers find something remarkable. The observatory's first images, revealed in June, contained a deep view of the Virgo cluster, the closest and best-studied cluster of galaxies. And in the bottom-right of the image, eagle-eyed astronomers saw something unexpected — a razor-thin stream of stars arcing away from one of the cluster's galaxies.
The barred spiral galaxy Messier 61 (M61, otherwise known as NGC 4303) is well known and has been studied for decades. However, only Rubin's unique sensitivity to objects with low surface brightness has been able to reveal this newfound star stream.
The stream stretches roughly 50 kiloparsecs (about 163,000 light-years), which is comparable to the diameter of our Milky Way galaxy. That makes it longer than most known stellar streams in our galaxy, which are mostly only a few tens of thousands of light-years in length.
The faint, galaxy-length breadcrumb trail is thought to consist of the leftovers of a dwarf galaxy that was torn apart by M61's gravity. This breakup may also have been the catalyst for a starburst — a massive increase in new star formation — that began in M61 about 10 million years ago.
The feature is reminiscent of the Sagittarius Stream — a long, looping structure that encircles the Milky Way and whose stars originated in the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy, scientists wrote in a study uploaded Oct. 28 to the pre-print server arXiv, which is due to be published in the journal Notes of the American Astronomical Society.

A satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy is thought to have caused new spiral arms of stars to form within the Milky Way. All of this suggests that most large galaxies may form by consuming other, smaller galaxies around them.
"It is remarkable that the stream went long unnoticed around a Messier galaxy," the authors wrote in the study. "We expect a treasure trove of substructures to be unveiled around other galaxies with future Rubin data."
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Rubin is about to embark on its 10-year Legacy Survey of Space and Time mission, during which it will create a high-definition time-lapse record of the universe.
For more sublime space images, check out our Space Photo of the Week archives.

Jamie Carter is a Cardiff, U.K.-based freelance science journalist and a regular contributor to Live Science. He is the author of A Stargazing Program For Beginners and co-author of The Eclipse Effect, and leads international stargazing and eclipse-chasing tours. His work appears regularly in Space.com, Forbes, New Scientist, BBC Sky at Night, Sky & Telescope, and other major science and astronomy publications. He is also the editor of WhenIsTheNextEclipse.com.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










