1969 Fireball Meteorite Reveals New Ancient Mineral
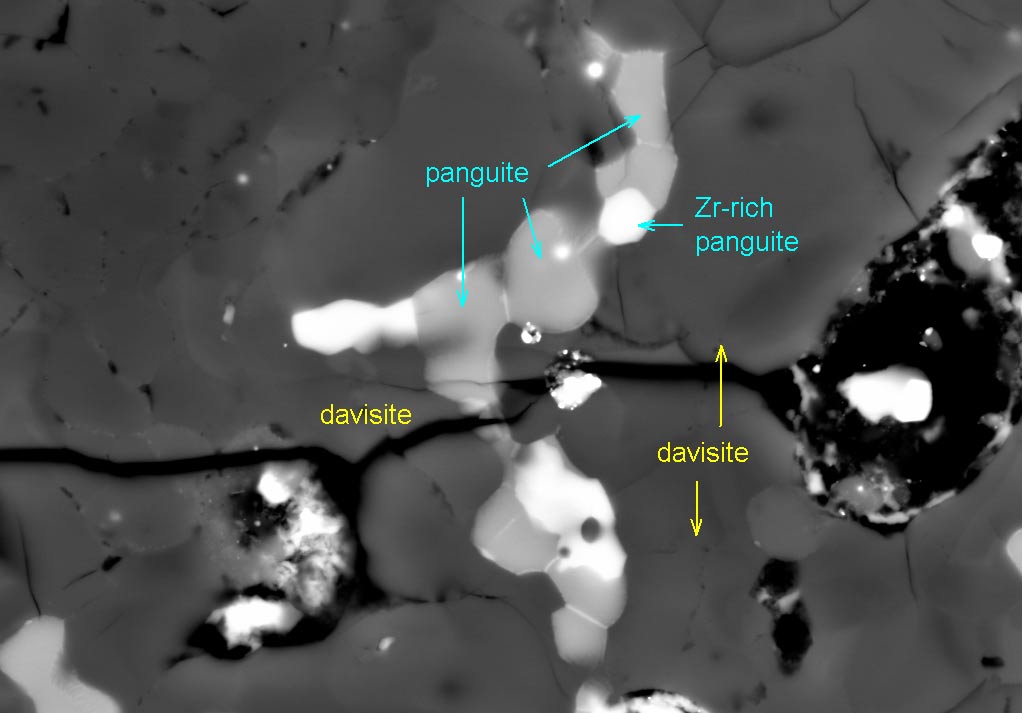

A fireball that tears across the sky is not just a one-time skywatching event — it can reap scientific dividends long afterward. In fact, one that lit up Mexico's skies in 1969 scattered thousands of meteorite bits across the northern Mexico state of Chihuahua. And now, decades later, that meteorite, named Allende, has divulged a new mineral called panguite.
Panguite is believed to be among the oldest minerals in the solar system, which is about 4.5 billion years old. Panguite belongs to a class of refractory minerals that could have formed only under the extreme temperatures and conditions present in the infant solar system.
The name of the titanium dioxide mineral, which has been approved by the International Mineralogical Association, honors Pan Gu, said in Chinese mythology to be the first living being who created the world by separating yin from yang (forming the earth and sky). [Infographic: The Science of Meteorites]
"Panguite is an especially exciting discovery since it is not only a new mineral, but also a material previously unknown to science," study researcher Chi Ma, a senior scientist at Caltech, said in a statement.
function reload_quiz_ads(){ reloadScripts(null, ['ad_imgBoard', 'ad_imgViewer']); }
Until now, panguite had neither been seen in nature nor created in a lab. "It's brand-new to science," Ma told LiveScience in an interview.
The scientists used a scanning-electron microscope to view the panguite within a so-called ultra-refractory inclusion embedded within the meteorite. Inclusions are the minerals that get trapped inside meteorites as they are forming. The ultra-refractory type includes minerals that can resist high temperatures and other conditions in extreme environments, such as those thought to exist as our solar system was forming.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
High-tech lab analyses revealed panguite's chemical composition and crystal structure, which Ma said is new, and as such, could be explored for novel engineering materials.
The Allende meteorite, where the mineral was hidden, is the largest of a class of carbonaceous chondrites found on Earth. Chondrites are primitive meteorites that scientists think were remnants shed from the original building blocks of planets. Most meteorites found on Earth fit into this group. (When meteors hit the ground they are called meteorites.)
Before they reach terra firma, most meteorites are fragments of asteroids (space rocks that travel through the solar system), while others are mere cosmic dust shed by comets. Rare meteorites are impact debris from the surfaces of the moon and Mars. The Allende meteorite likely came from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, scientists say.
Studying panguite and other components of the Allende meteorite are essential for understanding the origins of the solar system, Ma said. In fact, Ma's team has discovered nine new minerals, including panguite, in the Allende space rock.
The new mineral is detailed in the July issue of the journal American Mineralogist.
Follow LiveScience on Twitter @livescience. We're also on Facebook & Google+.
Jeanna Bryner is managing editor of Scientific American. Previously she was editor in chief of Live Science and, prior to that, an editor at Scholastic's Science World magazine. Bryner has an English degree from Salisbury University, a master's degree in biogeochemistry and environmental sciences from the University of Maryland and a graduate science journalism degree from New York University. She has worked as a biologist in Florida, where she monitored wetlands and did field surveys for endangered species, including the gorgeous Florida Scrub Jay. She also received an ocean sciences journalism fellowship from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. She is a firm believer that science is for everyone and that just about everything can be viewed through the lens of science.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus