Facebook's Internet-Delivery Drone Completes First Test Flight

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
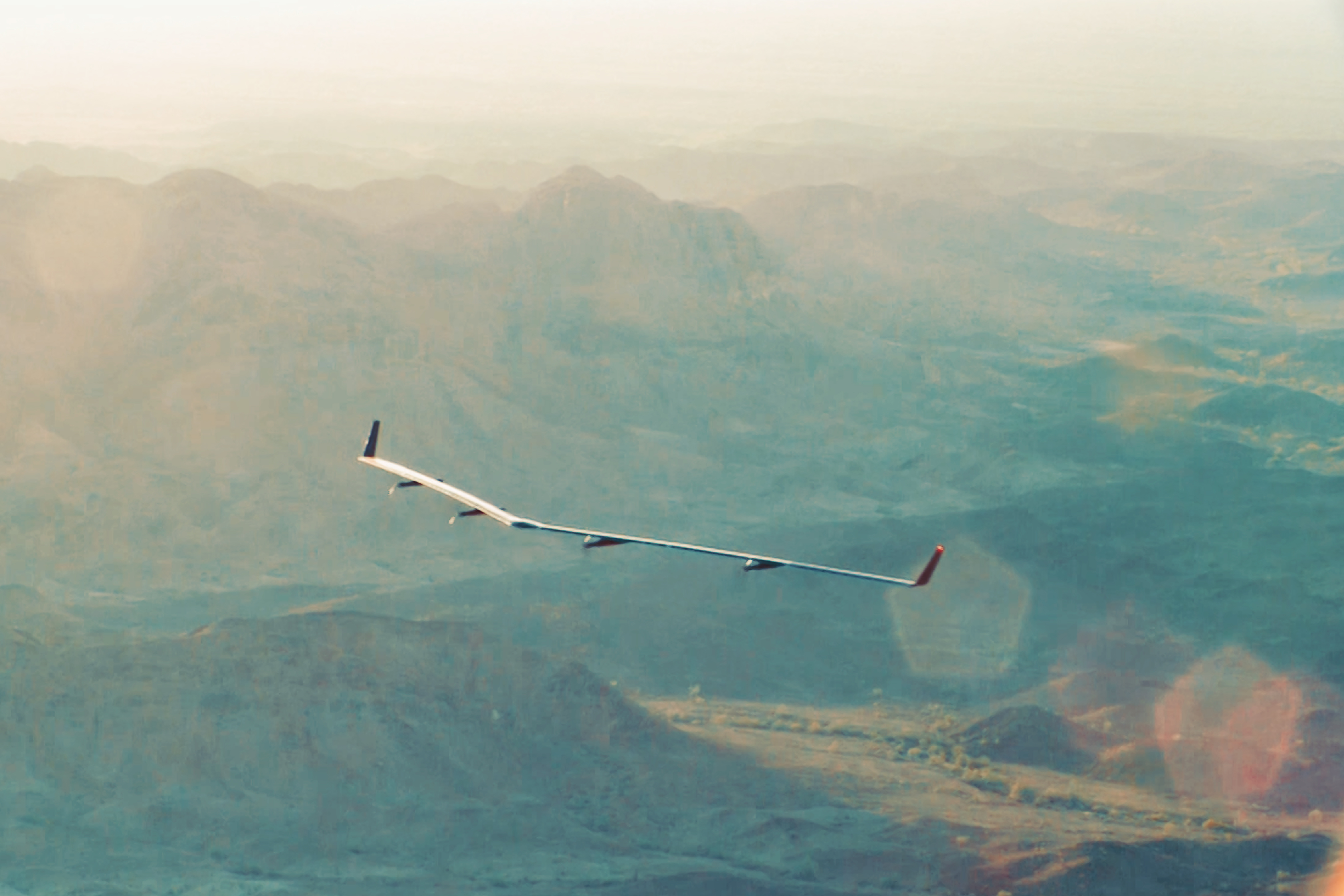
Facebook recently completed its first test flight of a solar-powered drone that is designed to beam down internet access to remote areas of the world.
The Aquila drone is being developed to broaden the scope of internet connectivity around the globe. "New technologies like Aquila have the potential to bring access, voice and opportunity to billions of people around the world, and do so faster and more cost-effectively than has ever been possible before," Jay Parikh, global head of engineering and infrastructure at Facebook, wrote in a blog post about the project.
When testing is finished, the autonomous aircraft will be able to circle a region measuring up to 60 miles (96.6 kilometers) in diameter, while using laser communications and millimeter wave systems (extremely high-frequency radio waves) to send connectivity down from an altitude of more than 60,000 feet (18,288 meters). [5 Surprising Ways Drones Could Be Used in the Future]
The huge unmanned airplane has a wingspan larger than a Boeing 737 airliner, but weighs hundreds of times less (about one-third of an electric car), according to Facebook, because of its carbon-fiber frame. In fact, half of Aquila's mass is made up of batteries, which enable the solar-powered plane to fly during the day and night.
"Aquila is designed to be hyper efficient, so it can fly for up to three months at a time," Parikh wrote. "The aircraft has the wingspan of an airliner, but at cruising speed it will consume only 5,000 watts — the same amount as three hair dryers, or a high-end microwave."
The recent test flight was the first for the full-scale drone, as previous tests used a one-fifth scale version of Aquila, according to the social media giant. Facebook said it plans to push Aquila to the limits in a lengthy series of tests over the coming months and years.
During the low-altitude test flight, Aquila flew for more than 90 minutes, which was three times longer than Facebook had planned. The flight's success included performance verifications of the drone's aerodynamics, batteries, control systems and crew training.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"In our next tests, we will fly Aquila faster, higher and longer, eventually taking it above 60,000 feet," Parikh wrote. "Each test will help us learn and move faster toward our goal."
There is still a long road ahead as the social media company continues to test its internet-delivery drone.
The current world record for solar-powered unmanned flight stands at two weeks, set by by defense technology company Qinetiq's Zephyr plane in 2010, according to the Federation Aeronautique Internationale (FAI). To reach Aquila's goal of delivering internet connectivity for up to three months at a time, Facebook said it will require significant advancements in science and engineering.
"It will also require us to work closely with operators, governments and other partners to deploy these aircraft in the regions where they'll be most effective," Parikh said.
Original article on Live Science.

 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus