WhaleWatch: New Program Could Help Protect Whales

Throughout the year, the waters off the U.S. West Coast host a diverse group of whales. But the area is also home to busy shipping lanes and fishing activity, putting whales at risk for ship strikes and entanglement in fishing nets.
A new program is being developed by the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Oregon State University and the University of Maryland to help prevent these accidents. Called WhaleWatch, it's being designed to give ship captains a better idea of where whales are most likely to congregate. It could also help NOAA adjust shipping lanes if necessary, and take other measures needed to prevent unnecessary whale deaths, said Daniel Palacios, a researcher with NOAA's Southwest Fisheries Science Center.
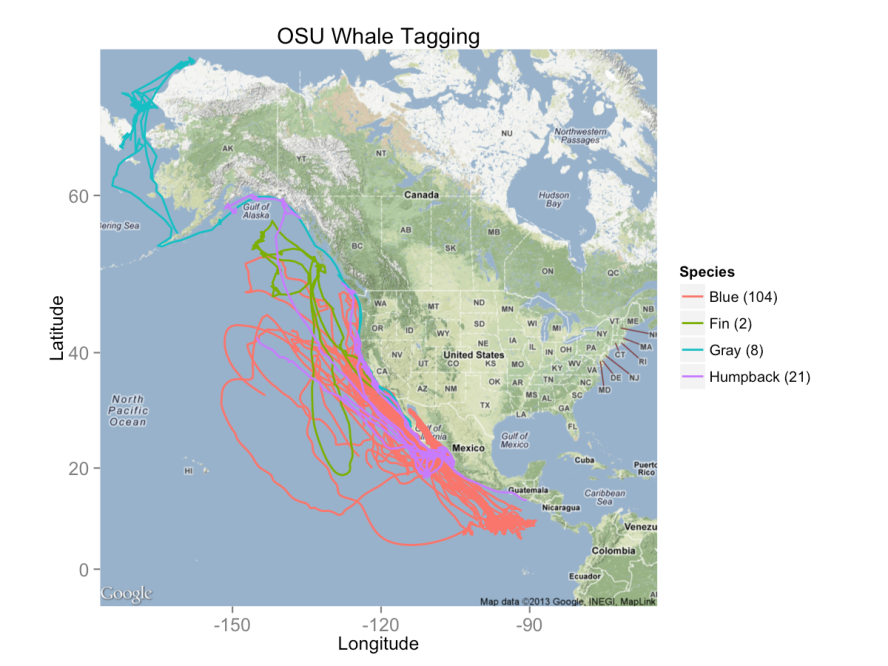
WhaleWatch, which is due to be finished in about 1.5 years, is being developed using data from tags placed on as many as 150 whales over the last 20 years, Palacios told OurAmazingPlanet. This information has allowed researchers to determine a set of physical measurements — such as water depth, temperature and plankton productivity — where whales are usually found. Much of it depends on how these conditions affect the location and abundance of krill, a small shrimp-like animal that is a favorite food of these great whales, he said.
The program will take these variables, which can be measured by satellites, and issue a periodic online map showing where certain whales are most likely to be found, Palacios said.
The program is based upon TurtleWatch, a product developed by NOAA researchers that's used by longline fishermen in Hawaii, and which has helped reduce the number of entanglements of loggerhead sea turtles there, Palacios said. TurtleWatch similarly produces maps of where the endangered turtles are most likely to be found, namely in warm waters where wind currents converge, said Evan Howell, TurtleWatch developer and a researcher at NOAA's Pacific Islands Fisheries Science Center in Honolulu.
The data for WhaleWatch comes from tags placed on blue, fin, gray and humpback whales from off the U.S. West Coast, Palacios said. This tagging work was led by Bruce Mate, a researcher at Oregon State University and Palacios' collaborator, Palacios said.
Reach Douglas Main at dmain@techmedianetwork.com. Follow him on Twitter @Douglas_Main. Follow OurAmazingPlanet on Twitter @OAPlanet. We're also on Facebook and Google+.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

