Charles Choi
Charles Q. Choi is a contributing writer for Live Science and Space.com. He covers all things human origins and astronomy as well as physics, animals and general science topics. Charles has a master of arts degree from the University of Missouri-Columbia, School of Journalism and a bachelor of arts degree from the University of South Florida. Charles has visited every continent on Earth, drinking rancid yak butter tea in Lhasa, snorkeling with sea lions in the Galapagos and even climbing an iceberg in Antarctica.
Latest articles by Charles Choi

Neanderthals, modern humans and a mysterious human lineage mingled in caves in ancient Israel, study finds
By Charles Choi published
A newly excavated cave in Israel holds burials and artifacts suggesting that multiple human species commingled and shared ideas there during the Paleolithic.

1.4 million-year-old jaw that was 'a bit weird for Homo' turns out to be from never-before-seen human relative
By Charles Choi published
The newfound species belongs to the genus Paranthropus, whose nickname is "nutcracker man."

How do Hula-Hoops work?
By Charles Choi published
How do Hula-Hoops keep from falling down as we twirl them around?

Why do bats hang upside down to sleep?
By Charles Choi published
Bats often hang upside down when they sleep instead of sitting right side up or lying down — why?

Why are my feet two different sizes?
By Charles Choi published
Why is one foot sometimes larger than the other?

How does arsenic kill?
By Charles Choi last updated
Arsenic is a naturally occurring element with properties similar to those found in phosphorus. It is also a deadly toxin that is difficult to detect.

No Descendants Are Left from the First Eskimos
By Charles Choi published
A new study of human DNA -- and the largest genetics study yet of ancient peoples -- reveals that the Paleo-Eskimos are genetically distinct from both the Neo-Eskimos and modern Native Americans.

Probiotics May Help Prevent Peanut Allergies, Animal Study Shows
By Charles Choi published
Certain types of gut bacteria could ward off food allergies, according to a new study in mice.

Computer Games Better Than Medication in Treating Elderly Depression
By Charles Choi published
Older people with depression may benefit more from playing computer games aimed at improving their thinking skills than from taking an antidepressant drug, a new study suggests.

How Mysterious Natural Arches Form
By Charles Choi published
Rock formations such as arches, pillars, and pedestal can look as though they defy gravity. But new research how such amazing rock formations take shape.

Natural Arm Swing Saves Runners' Energy
By Charles Choi published
Runners actually save energy by swinging their arms when they run, a new study finds. Runners burn more calories when the arms are held still.

World's Biggest Fish Seek New Home
By Charles Choi published
Whale sharks -- the world's largest fish -- are appearing more frequently near the Azores islands, due to climate change, a new study finds.

Bizarre Dinosaur Had 4 'Wings,' Long Tail Feathers
By Charles Choi published
Changyuraptor had long feathers on both its forelimbs and its hind limbs, giving it the appearance of having four wings, researchers say.
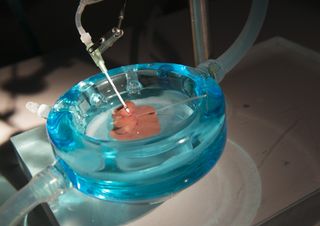
New 'Supercooling' Technique Helps Preserve Organs
By Charles Choi published
Liver transplants could get a boost from a new technique that could allow the organs to be stored for longer before they are transplanted into patients.

Bacteria in Arteries May Be 'Ticking Time Bombs,' Researchers Say
By Charles Choi published

New Test Spots Malformed Proteins Linked to Mad Cow Disease
By Charles Choi published
The human form of mad cow disease could be detected early on with an experimental blood test that looks for the misfolded proteins linked with it, researchers say.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.