
First video of an earthquake fault cracking has revealed another surprise
A stunning video of the ground cracking during a magnitude 7.7 earthquake in Myanmar is revealing new surprises.

By Harry Baker published
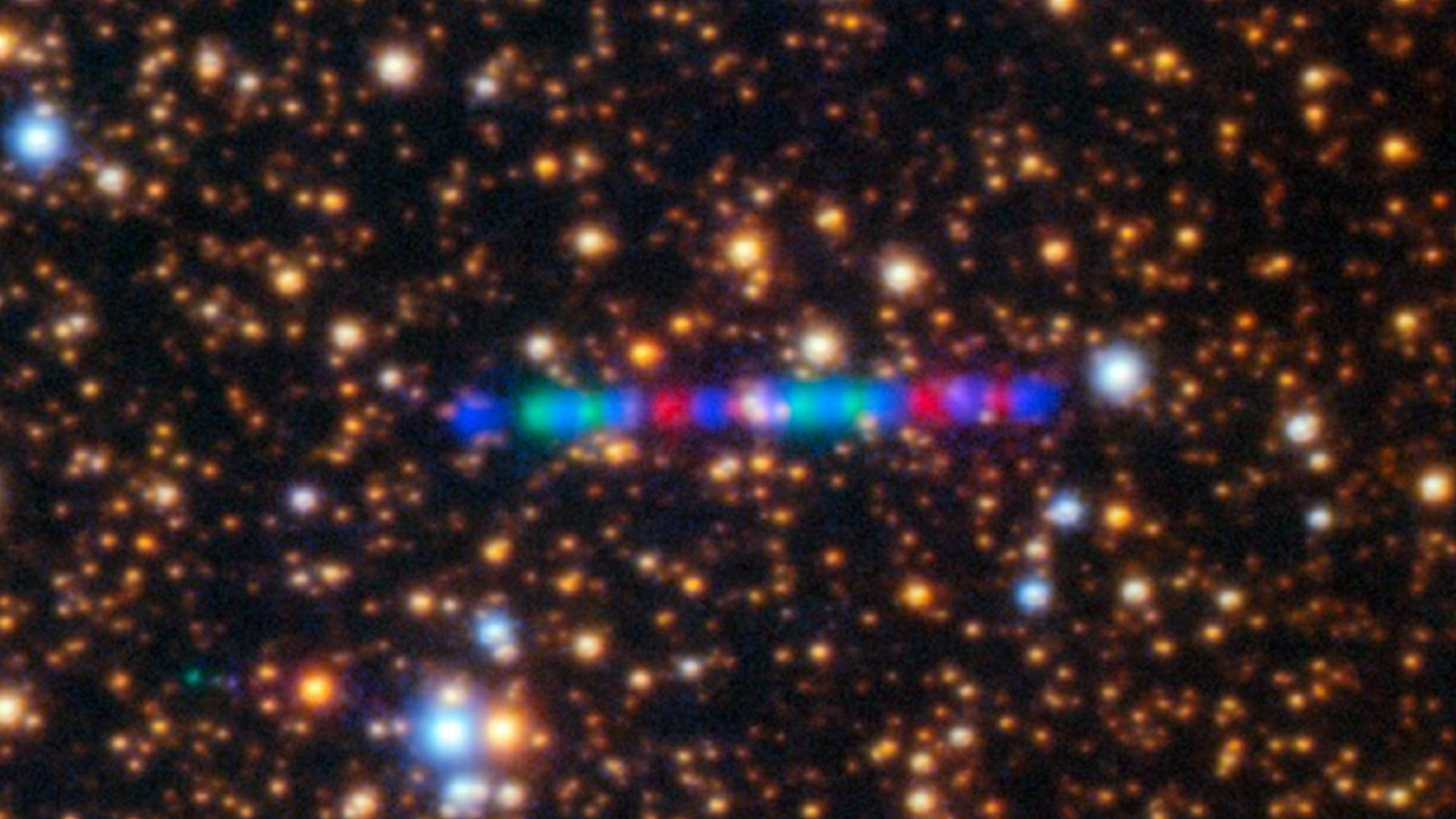
New photos, including a striking technicolor timelapse, show off the newly discovered interstellar object 3I/ATLAS as it shoots toward us through the solar system.

By Brandon Specktor published
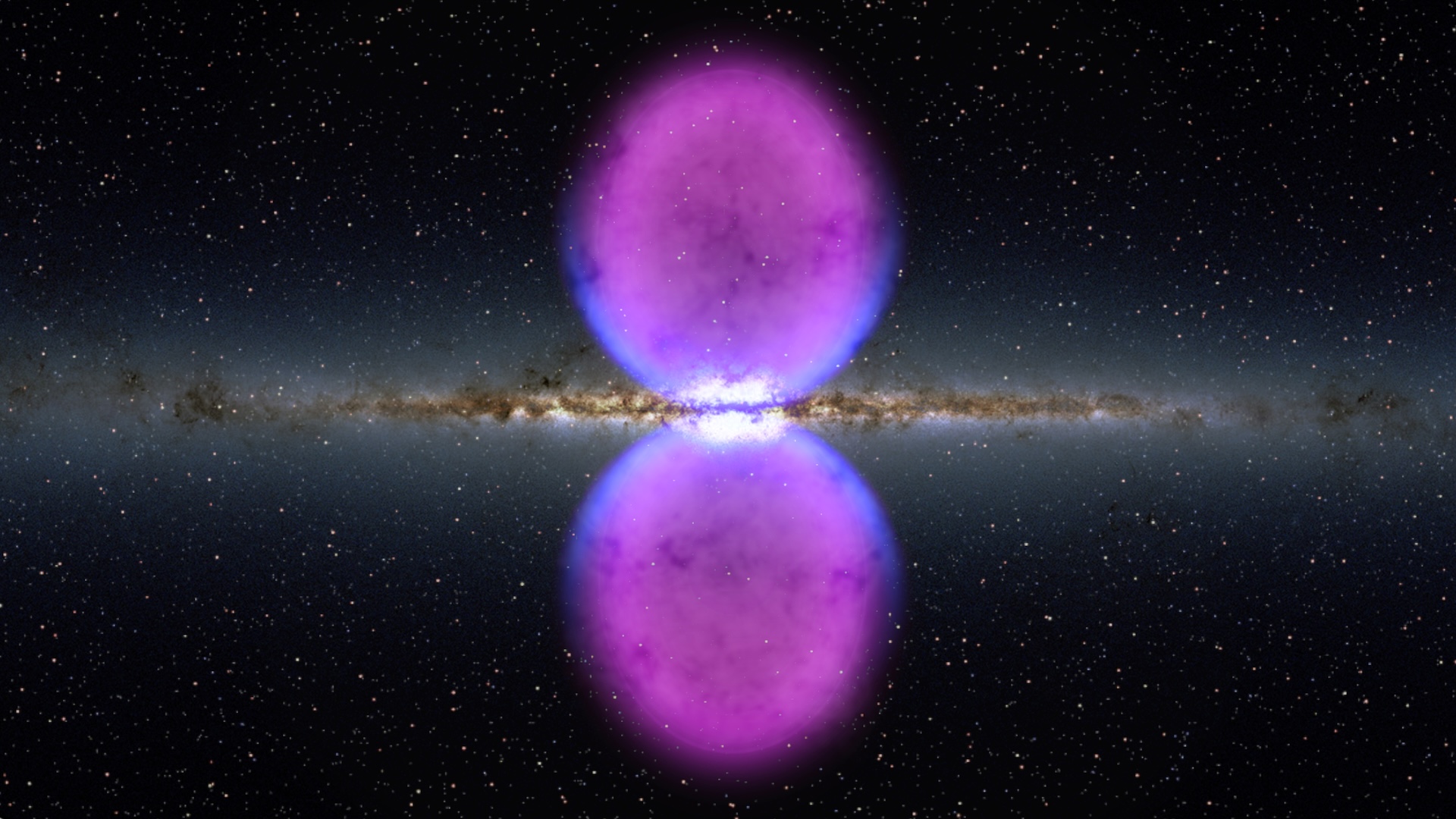
Twin orbs of superhot plasma at the Milky Way's center known as the "Fermi bubbles" contain inexplicable clouds of cold hydrogen, new research reveals. They could help scientists figure out when our galaxy's black hole last erupted.

By Tim Penn published
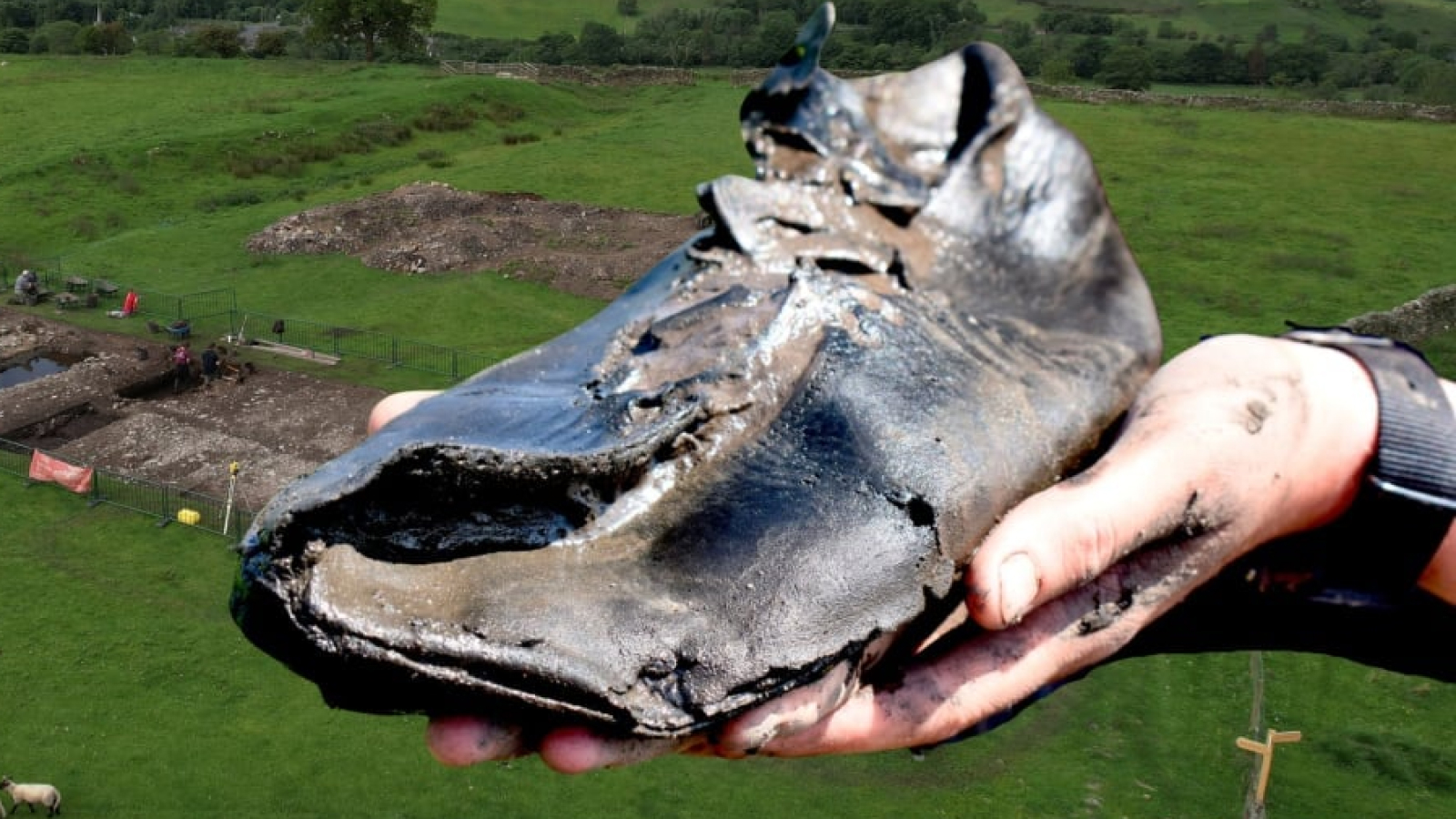
Archaeologists aren't "baffled" by giant shoes but see them as a way to test different theories about how Roman soldiers coped with new environments along Hadrian's Wall.

Discover the research changing our understanding of the world

Extraordinary images of our sublime universe

Science questions, answered

Test your knowledge on all things science with our weekly, free crossword puzzle!
Test your knowledge of everything from space to nature

A look at the weird and wonderful species that live on our planet
Unusual case reports from the medical literature

A window onto extraordinary landscapes on Earth
Medical conditions you may never have heard of before
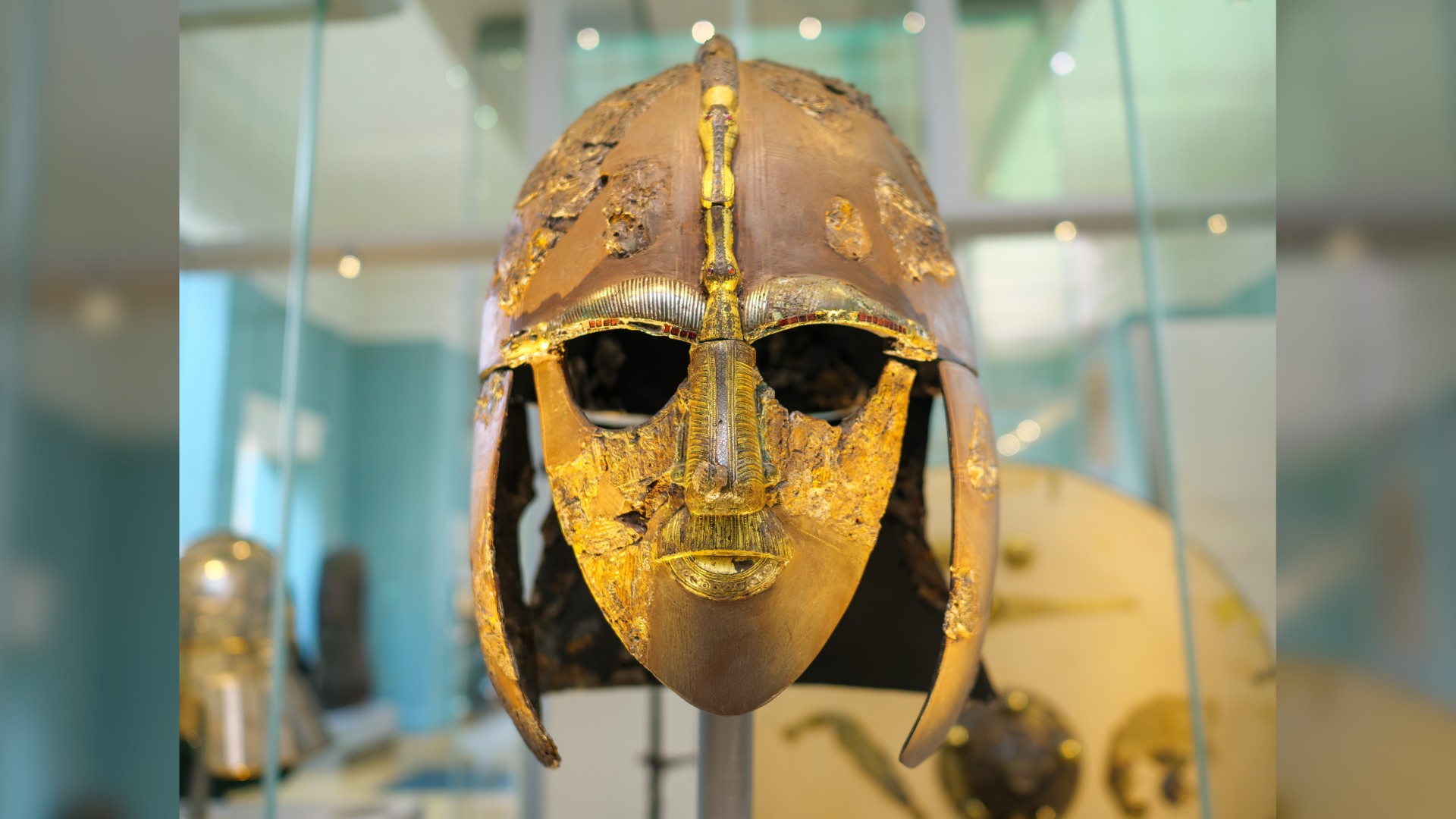

A glimpse into how people lived in the past
Incredible images of our planet from above

Our roundup the biggest discoveries and top science in the news each week
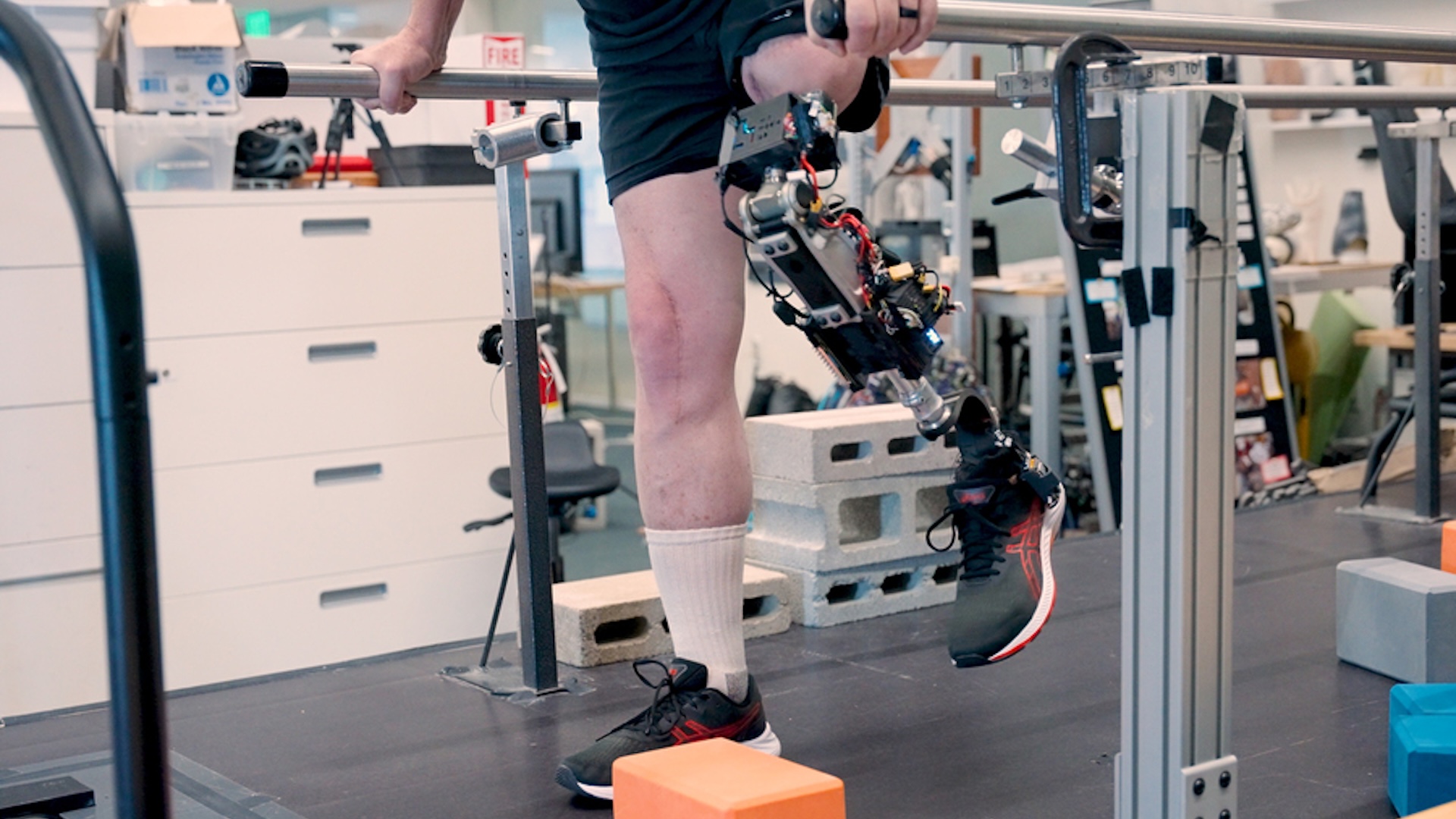

By Skyler Ware published
A bionic knee that directly attaches to the thigh bone and uses implanted electrodes can make a prosthetic leg feel more like a part of the body, a new study finds.
By Nicoletta Lanese published
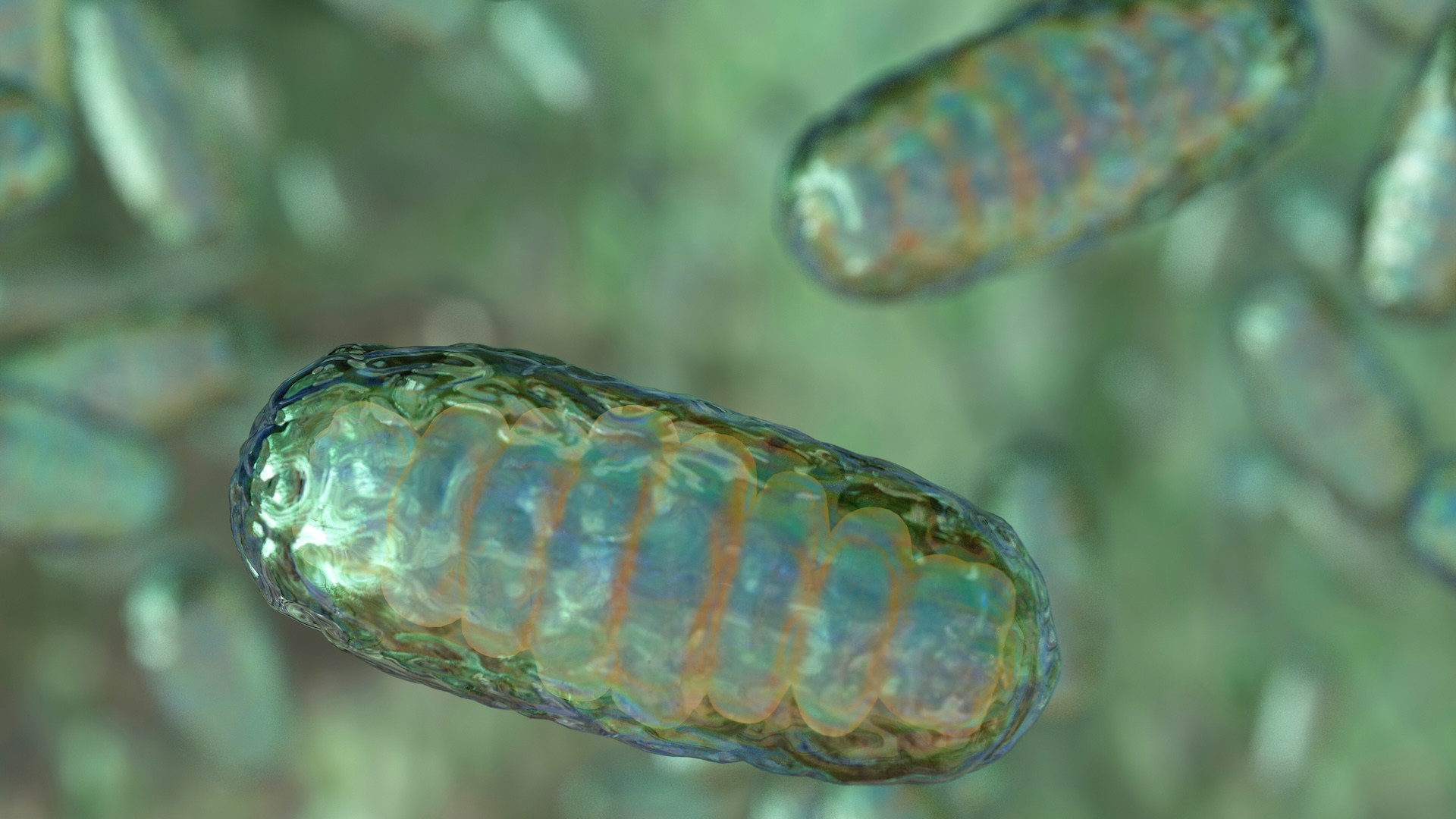
A groundbreaking trial in the U.K. has released data on eight babies born through a special IVF procedure to lower their risk of mitochondrial DNA disease.
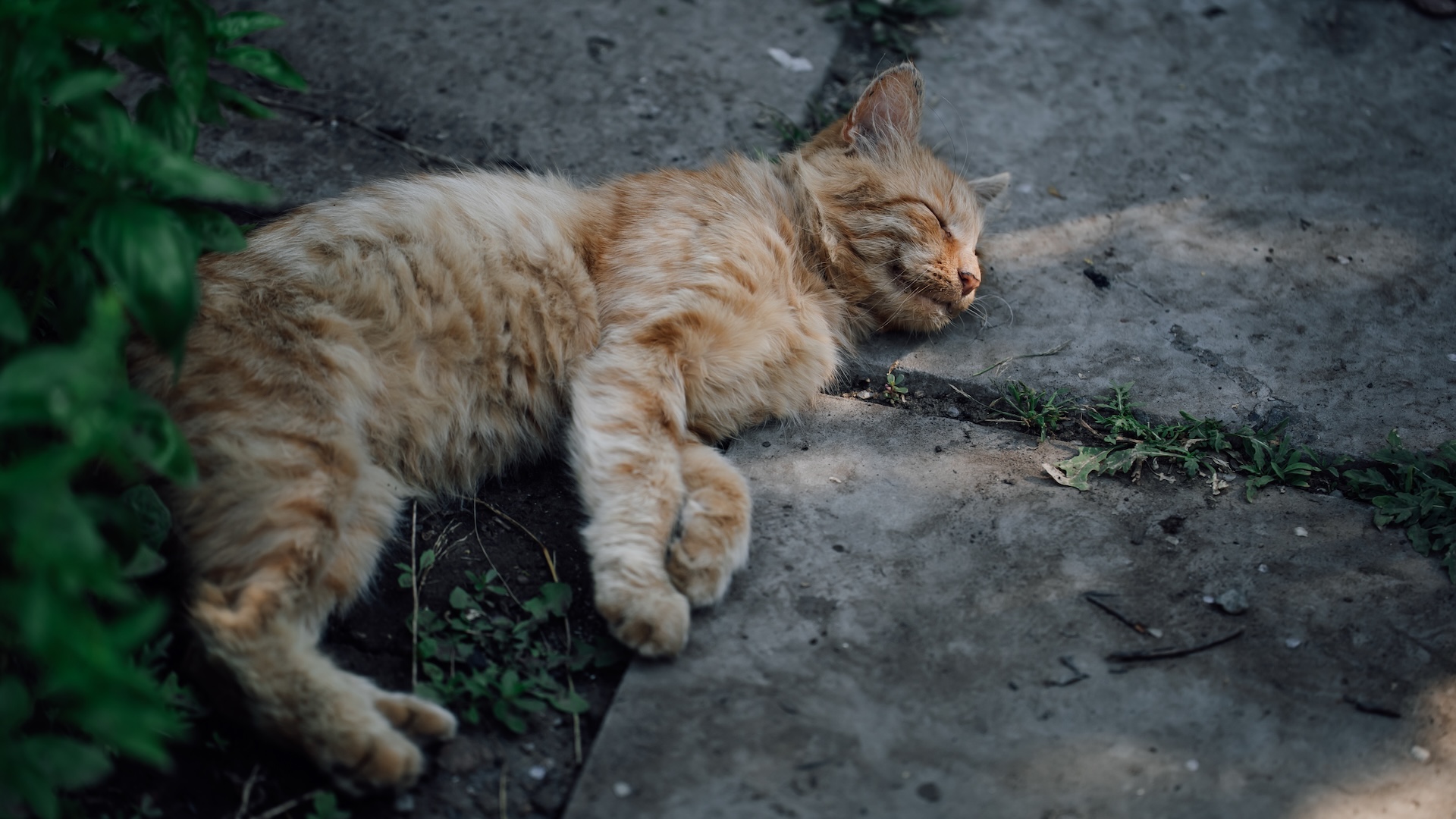

By Marilyn Perkins published
Cat owners have noticed their pets seem to go crazy for concrete blocks. Why?

By Victoria Atkinson published
A new study of schoolchildren in France suggests that boys are not innately better at math. Some aspect of schooling appears to drive the "gender gap."

By Edward White published
Fundamentalists don't necessarily examine evolution and then reject it; they tend to start with the conclusion that it must be false and work backwards.

By Alexander McNamara last updated
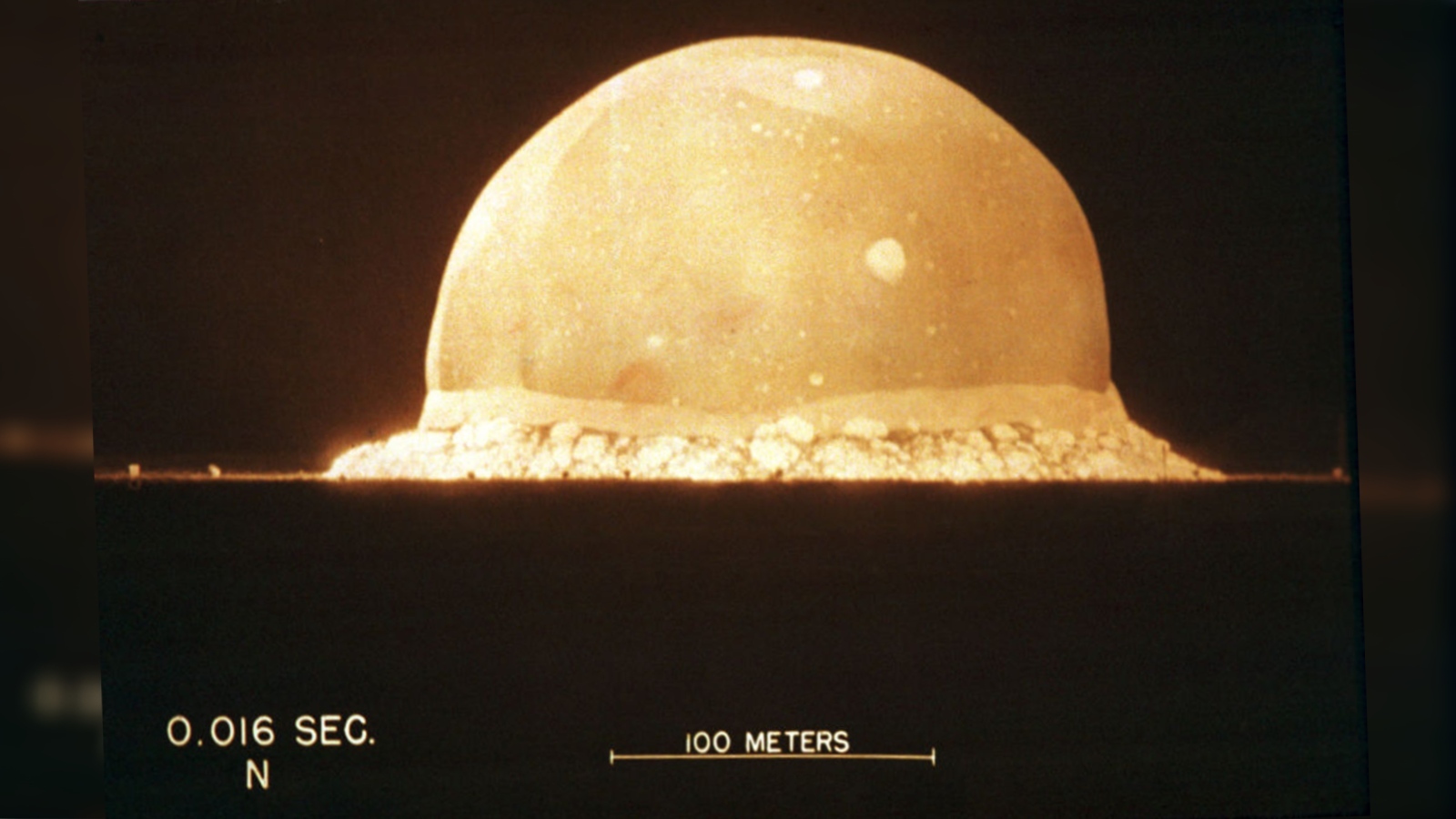
In this except from the biography of J. Robert Oppenheimer, we hear from the people at the historic first test of the atomic bomb in New Mexico.

By Shalma Wegsman published
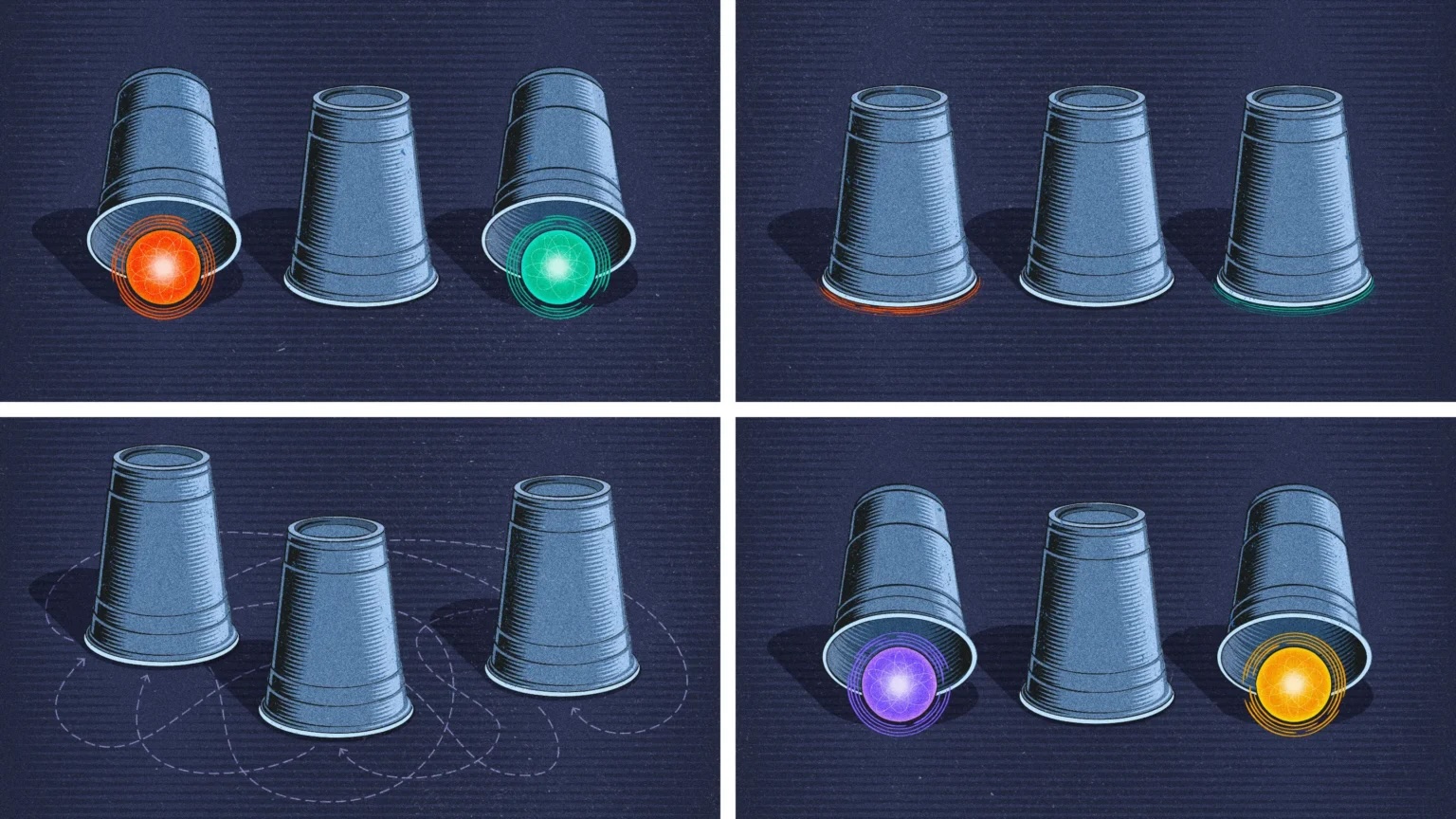
A new proposal makes the case that paraparticles — a new category of quantum particle — could be created in exotic materials.

By Stephen L. Levy published
Almost everything on Earth is made up of atoms, but where do these fundamental building blocks come from?

By Joanna Thompson published
A fiery letter written by Albert Einstein in 1954 is going to auction. The letter details Einstein's thoughts on his part in developing atomic weapons, and hails Mahatma Gandhi as a political genius.

By Ben Turner published
The new super-strong copper alloy can be used to build better airplanes and spacecraft.
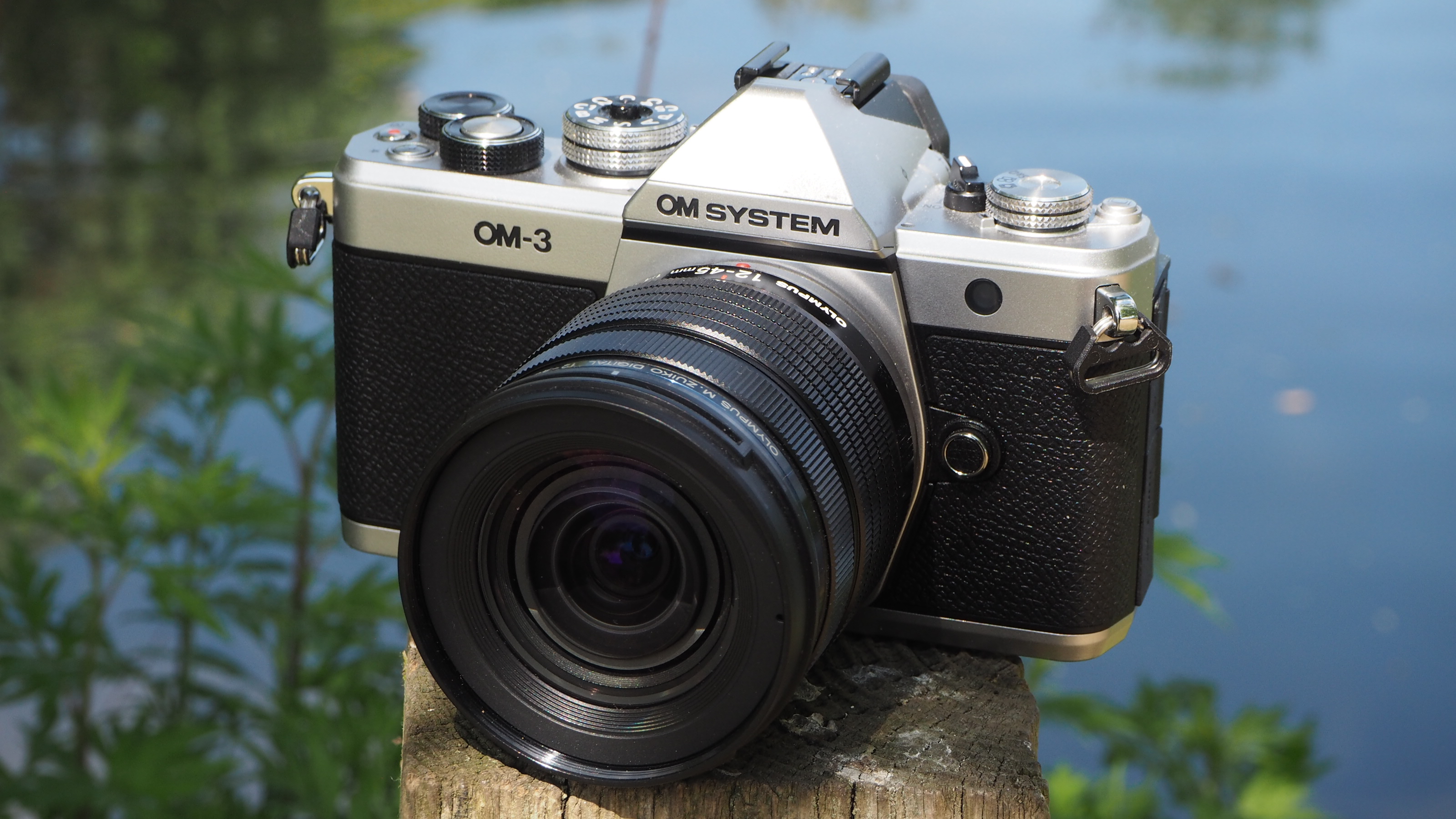

By Gavin Stoker published
Review Shorter version of strapline (75 characters max)
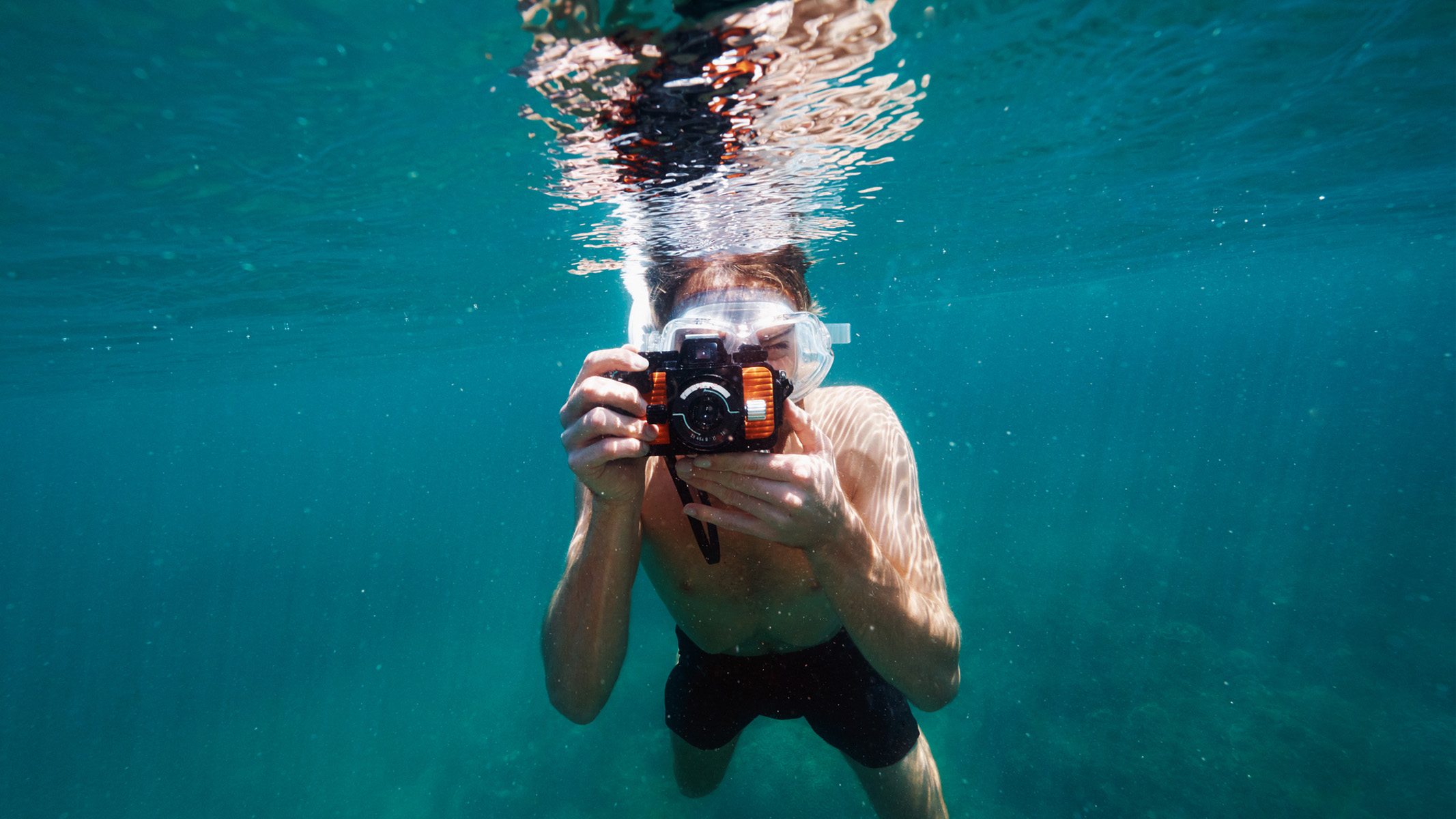

By Jacob Little published
The best cameras for marine observation, surveying and recording your underwater adventures — just in time for Prime Day.
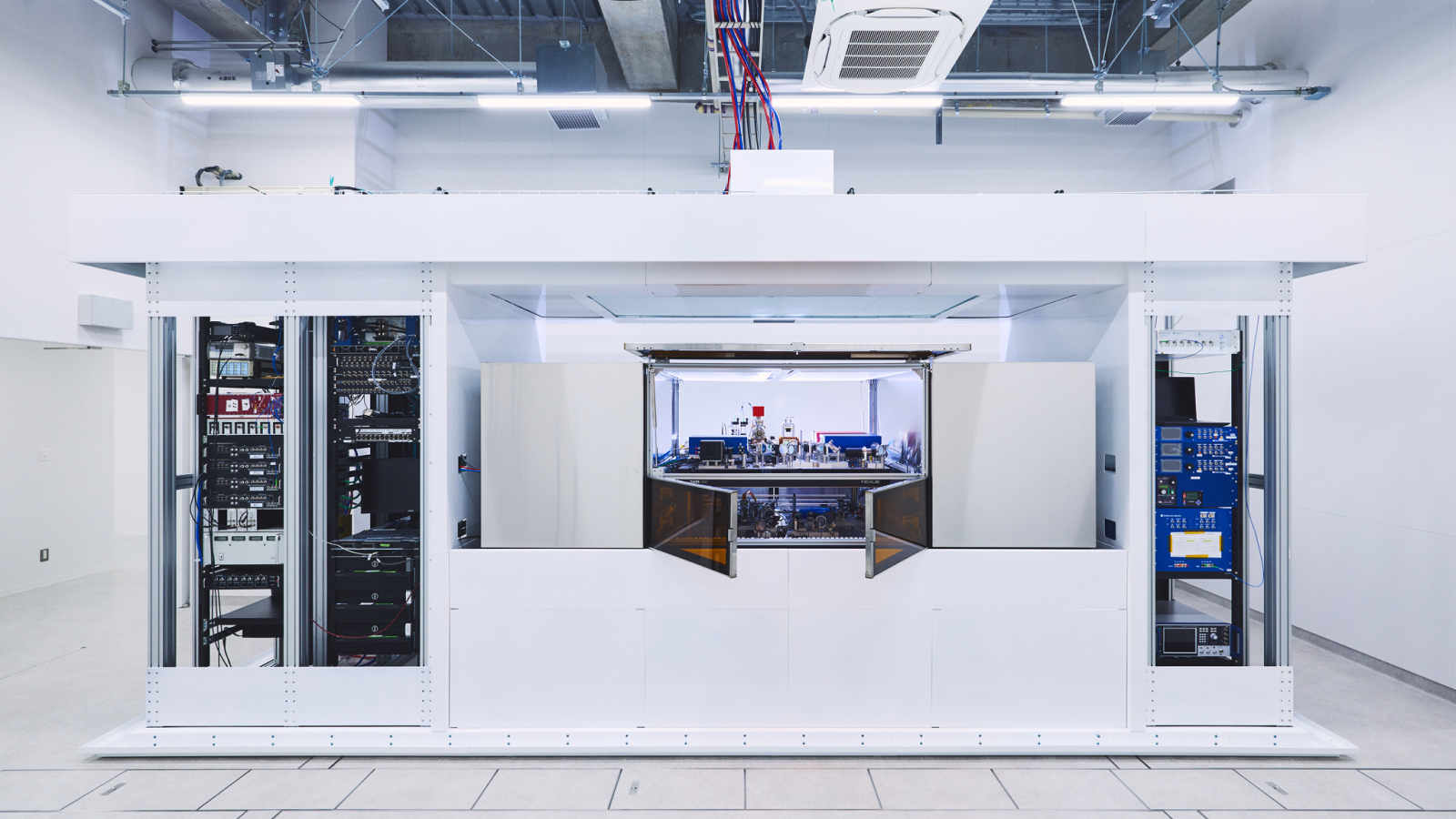

By Keumars Afifi-Sabet published
Scientists demonstrate a process called "magic state distillation" in logical qubits for the first time, meaning we can now build quantum computers that are both error-free and more powerful than supercomputers.
Please login or signup to comment
Please wait...