Amerigo Vespucci: Italian explorer who named America
Amerigo Vespucci was a 16th century navigator, after whom the American continents are named.

Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci is best known for his namesake: the continents of North and South America. But why were these continents named after him, especially since his voyages happened after Christopher Columbus arrived on the continent, in 1492?
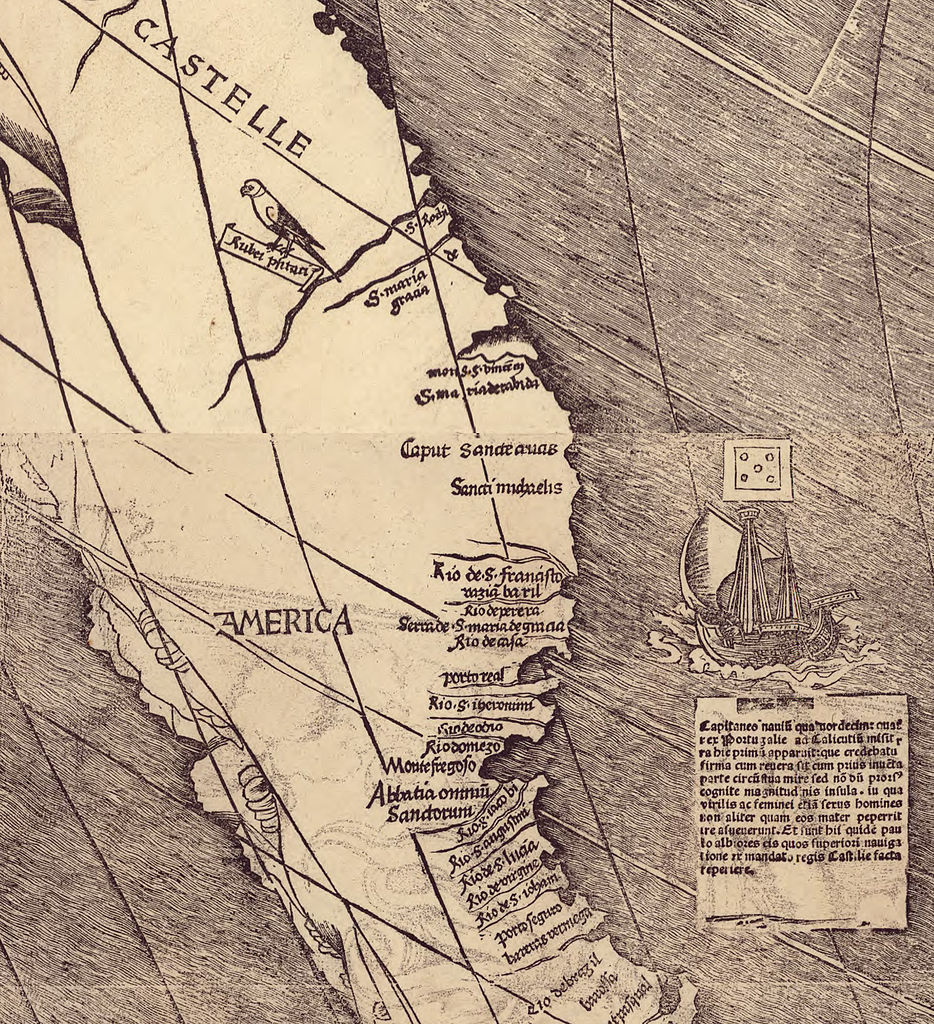
Vespucci was the first person to recognize North and South America as distinct continents that were previously unknown to Europeans, Asians and Africans, according to Avihu Zakai ("Exile and Kingdom: History and Apocalypse in the Puritan Migration to America", Cambridge University Press, 2002). Prior to Vespucci's discovery, explorers, including Columbus, had assumed that the New World was part of Asia. Vespucci made his discovery while sailing near the tip of South America in 1501, according to The New World Encyclopaedia.
Amerigo Vespucci was one of many European explorers during the Age of Exploration, or Age of Discovery, which took place from the mid-1400s to mid-1500s. "The Age of Exploration was prompted by different motivations," said Erika Cosme, administrative coordinator of education and digital services at The Mariner’s Museum and Park in Virginia. "In the 15th century, Europe, Asia, and Africa were at the epicenter of a global exchange of goods; also, for Europeans, curiosities of different cultures continued to emerge. This Afro-Eurasian economy created an interwoven connection between India, China, the Middle East, Africa and Europe."
Spurred by curiosity and economic incentive, explorers traveled distances that were great feats for their day. But what makes the time period so important, said Cosme, was the role it played in "shaping the world that we know today." Recognizing the Americas was a major part of that understanding.
Early life
Amerigo Vespucci was born on March 9, 1454, in Florence. As a young man, he was fascinated with books and maps, according to the Mariners Museum. The Vespuccis were a prominent family and friends with the powerful Medicis, a family who ruled Italy for more than 300 years and were prominent during the Renaissance. After being educated by his uncle, Vespucci himself worked for the Medicis as a banker and later supervisor of their ship-outfitting business, which operated in Seville, Spain. He moved to Spain in 1492, according to Biography.com
This business allowed Vespucci to see the great explorers' ships being prepared and to learn about the business of exploration. Goods like salt from Mali, coffee beans from Ethiopia, spices from India and the Molucca Islands and ginger, silk and tea from China were in high demand, said Cosme, who works in developing The Mariners' Museum's extensive Age of Exploration area.
Countries profited off trade and hoped to find riches like gold, silver and gems, Cosme explained . "European leaders saw exploration as a way to expand their empires and increase national glory."
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
At the time, explorers were searching for a northwest route to the Indies — the lands and islands of Southeast Asia — which would make trade easier and bring their country wealth, according to Britannica. "It would often take years to complete a trip," said Cosme. "By the mid-15th century, Muslims controlled the majority of the trade routes to Asia. This meant they could charge high prices for incoming and outgoing goods and vessels traveling to and from Europe and Asia. The desire to find ocean routes that were faster, safer, and cheaper stimulated a search to find a better way of getting to these places."
Vespucci's business helped outfit one of Columbus's voyages, and in 1496 Vespucci had the opportunity to talk with the explorer. Both men were fascinated by the works of Marco Polo, who influenced many explorers' love of seafaring and exploration, said Cosme.
This meeting further encouraged Vespucci's interest in travel and discovery. Like many explorers of the age, he wanted to gain new knowledge and see the world with his own eyes. "The Age of Exploration coincided with the Renaissance, which lasted from about 1300 to 1600," said Cosme. "Many people were gaining genuine curiosity about the world. Sciences like astronomy and cartography were surging. People wanted to know more about the geography, people, and cultures outside their own."
Vespucci's business was struggling, which made his decision to voyage even simpler. Furthermore, he possessed critical knowledge for seafaring, like cartography and astronomy, which were essential tools for early navigation, said Cosme. Now in his 40s, Vespucci decided to leave business behind and embark on a journey while he still could.
First voyage and letter controversy
"Amerigo Vespucci took at least three voyages westward," said Cosme. There is some controversy among historians about when Vespucci set sail on his first voyage. Many accounts place the sail date in 1499, seven years after Columbus landed in the Bahamas. On the 1499 voyage, Vespucci sailed to the northern part of South America and into the Amazon River. He gave places he saw names like the "Gulf of Ganges," thinking, as his explorer contemporaries did, that he was in Asia. He also made improvements to celestial navigation techniques. Vespucci predicted Earth’s circumference accurately within 50 miles, according to Springer.
But a letter dated in 1497 suggests that the 1499 voyage may have in fact been Vespucci's second trip, according to Fordham University. The letter is written in Vespucci's voice, though some historians dispute his authorship and the facts of the document, claiming it a forgery. The letter, written to the Gonfalonier of Florence (a high official on the city-state's supreme executive council), accounts a 1497 expedition to the Bahamas and Central America. If the accounts of this letter are true, then Vespucci reached the mainland of the Americas a few months before John Cabot and more than a year before Columbus.
1501 voyage and recognition of South America
On May 14, 1501, Vespucci set sail to the New World under the Portuguese flag on what would be his most successful voyage, according to Edward Shaw ("Discoverers and Explorers," Weitsuechtig, 1900.)
Vespucci's ships traveled along the South American coast down to Patagonia, according to The New World Encyclopaedia. Along the way, he encountered the rivers Rio de Janeiro and Rio de la Plata. During this voyage, Vespucci came to suspect that he was looking at a continent entirely different from Asia.
"Vespucci was both familiar with and fascinated by the accounts of Marco Polo and his time in Asia. The book by Polo gave great detail on the geography, people, and rich opportunities of the continent. Based on this information, Vespucci could make assumptions about the land they were exploring," Cosme said.
"For starters, Vespucci noticed that the sky which they sailed under had different constellations that were not visible in Europe," Cosme said. "He also took note of the coastlines they traveled, recording their distance and length of time traveled. Vespucci, again a very skilled cartographer and astronomer, carefully studied and pondered over all of his information.
"He found that the areas and land masses they had explored were actually larger and different than previous accounts of Asia's descriptions. This led him to the conclusion that what they had explored was indeed an entirely new continent."
He verified his suspicion when sailing south to within 400 miles of Tierra del Fuego, the southernmost tip of South America, according to an article by Wired. This confirmed that he was encountering a new continent that extended far further south than anyone had guessed.
While on this voyage, Vespucci wrote letters to a friend in Europe describing his travels and identifying the New World as a separate continent from Asia. These letters also chronicle his encounters with the indigenous people and describe their culture. Vespucci described the natives' religious practices and beliefs, their diet, marriage habits, and, most appealingly to readers, their sexual and childbirth practices. These letters were published in several languages and sold well (better than Columbus' letters, according to Stanford University) across Europe. This pleased Vespucci who, who recorded his adventures to better leave "some fame behind me after I die."
Later voyages and other accomplishments
Vespucci's later voyages were not as successful as the 1501 expedition, and , according to Britannica, scholars are unsure of exactly how many later voyages he embarked upon. In 1503, he sailed to Brazil, but when his fleet failed to make any new discoveries, the ships disbanded. Vespucci pressed on, however, and discovered the island of Bahia and South Georgia before returning to Lisbon ahead of schedule ("The First Four Voyages of Amerigo Vespucci," Forgotten Books, 2017) .
Vespucci may have gone on two more voyages, in 1505 and 1507, but accounts are unclear. In 1505, he became a naturalized citizen of Spain, and in 1508, he was named a Pilot Major of Spain, according to Frederick J Pohl ("Amerigo Vespucci", Columbia University Press, 1944). This was a prestigious position that required him to use his considerable navigational skills. Vespucci helped develop and standardize navigational techniques and to select new pilots.
He worked at this post until his death on Feb. 22, 1512. He contracted malaria and died in Spain at nearly 58 years of age. Vespucci is buried in Florence.
The naming of America
Vespucci's reputation has gone through periods of ridicule, and at times he has been viewed as a schemer who attempted to steal glory from Columbus, according to History.Info. But in reality, it wasn't Vespucci's ambition that got two continents named after him: it was the work of a German clergyman and amateur cartographer called Martin Waldseemüller.
In 1507, Waldseemüller and some other scholars were working on an introduction to cosmology that would contain large maps, according to the U.S. Library of Congress. Waldseemüller proposed that a portion of Brazil that Vespucci had explored be named "America," a feminized version of Vespucci's first name. Waldseemüller wrote, "I see no reason why anyone should justly object to calling this part ... America, after Amerigo [Vespucci], its discoverer, a man of great ability."
The name stuck. Waldseemüller's maps sold thousands of copies across Europe. Some reports suggest, for example the Library of Congress, that Waldseemüller had second thoughts about the name America, but it was too late. In 1538, a mapmaker named Gerardus Mercator applied the name "America" to both the northern and southern landmasses of the New World, according to Yale University and the continents have been known as such ever since.
Regardless, there is no underestimating the value of Vespucci's contributions to Europeans. Cosme said, "Amerigo Vespucci used his own knowledge and skill, plus the written knowledge from scholars and explorers before him to uncover a Mundus Novus (Latin for "new world") to Europeans."
Additional resources
To learn more about the Waldseemüller map from which America would get its name, check out this article from the Library of Congress. To learn more about Vespucci himself, read this piece from The Mariners' Museum. Or try this article from PBS World Explorers.
Bibliography
- Avihu Zakai ("Exile and Kingdom: History and Apocalypse in the Puritan Migration to America", Cambridge University Press, 2002)
- Amerigo Vespucci, The New World Encyclopaedia
- Amerigo Vespucci, Ages of Exploration: Mariners Museum
- Amerigo Vespucci, Biography.com
- The Sea Route West to Cathay, Brittanica.com
- Edward Shaw ("Discoverers and Explorers", Weitsuechtig,1900.)
- Randy Alfred, "The Man is a Continent…Or Two" Wired, March 9th 2020
- Amerigo Vespucci, "The First Four Voyages of Amerigo Vespucci",Forgotten Books, 2017
- Frederick J Pohl ("Amerigo Vespucci", Columbia University Press, 1944)
- "1512: Amerigo Vespucci- The Man Who Stole The Glory From Christopher Columbus", History.Info
- John R Herbert, "The Map That Named America", Library of Congress
- "Mapamundi of 1538", Yale University
- Gyula Pápay, "Amerigo Vespucci's Contribution to the Modernization of Cartographic Representation" Springer (17th Century, 2020)
Jessie Szalay is a contributing writer to FSR Magazine. Prior to writing for Live Science, she was an editor at Living Social. She holds an MFA in nonfiction writing from George Mason University and a bachelor's degree in sociology from Kenyon College.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus