Earth as Art: A Rocky Desert
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
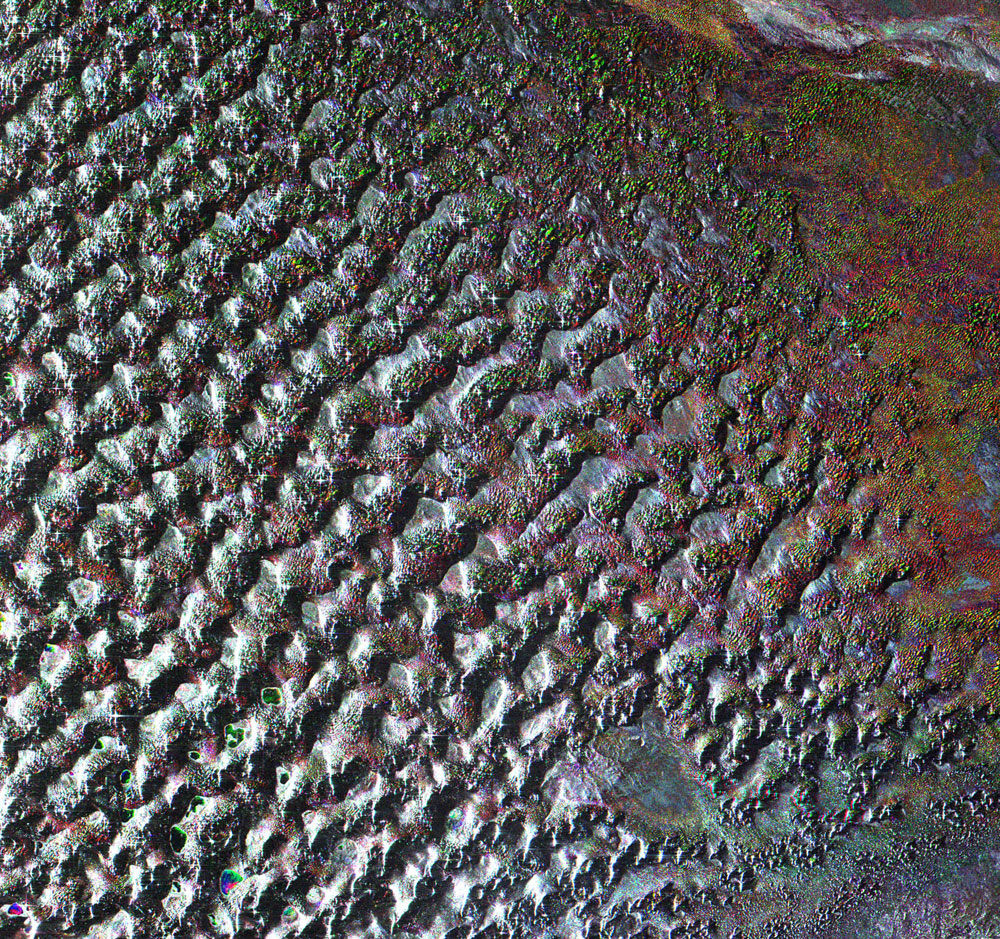
Deserts typically conjure images of barren stretches of shifting sand dunes, but Asia's Gobi Desert is covered with bare rock.
The Gobi, which is about 1,600 kilometers (990 miles) in extent from east to west and about 1,000 km (620 miles) from north to south, has a total area of 1,300,000 square km (800,000 square miles), making it the largest desert in Asia and the fourth largest in the world. The desert stretches across vast areas of the Mongolian People's Republic and the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region of China.
This image of the Gobi, made by the Envisat satellite's Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar in August 2009, shows the terrain of the desert. The Gobi is formed by a series of small basins within a larger basin rimmed by upland. The basin floors are unusually flat and level, and are formed of a desert pavement of small gravel atop granite or metamorphic rock, according to a European Space Agency statement.
The name "Gobi" means "waterless place" in Mongolian. The desert receives 200 to 250 millimeters (8 to 10 inches) of rain along the northern and eastern edges, while its southeastern portion is completely waterless.
Small lakes that are kept filled by groundwater are visible in the image dotting the landscape. Archaeological evidence shows the lakes have existed for a very long time, with Stone Age dwellers living along their borders, the ESA statement said.
Numerous important fossils have been found in the Gobi Desert , including the first dinosaur eggs.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus











