New eye implants combined with augmented-reality glasses help blind people read again in small trial
Of the 38 patients with age-related macular degeneration, 80% were able to read again after having the eye implant and using the glasses.

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
A surgically implanted chip and augmented-reality glasses are helping some people who have lost sight to read again.
In a small trial, about 80% of people who had lost vision due to age-related macular degeneration (AMD) were able to read letters and words a year after receiving the treatment, according to a study published Monday (Oct. 20) in The New England Journal of Medicine.
"In the history of artificial vision, this represents a new era," study co-author Mahi Muqit, an ophthalmologist at University College London and the Moorfields Eye Hospital in the U.K., said in a statement. "Blind patients are actually able to have meaningful central vision restoration, which has never been done before."
AMD is the most common cause of blindness in adults over 65. The disease affects the macula, or the central part of the retina, and leads to vision loss in the center of the eye. In advanced AMD, a process known as geographic atrophy causes significant damage to retinal cells, which can cause full blindness in that eye. Geographic atrophy affects about 5 million people worldwide.
"Before receiving the implant, it was like having two black discs in my eyes, with the outside distorted," Sheila Irvine, a participant in the study who was diagnosed with AMD, said in the statement.
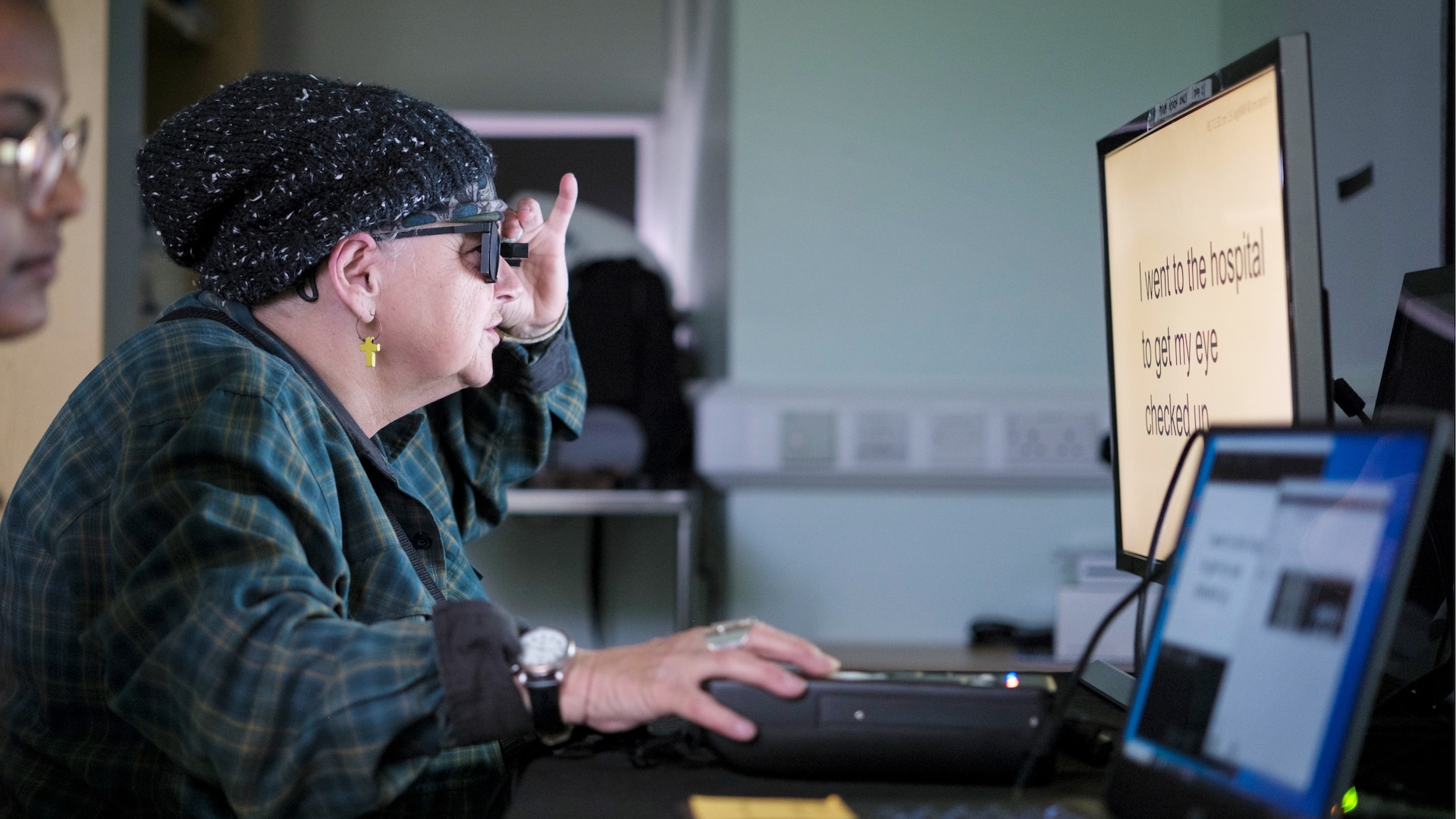
In a small clinical trial, 38 European patients with AMD had a small electronic chip implanted under the center of their retina below cells that had died. The chip wirelessly connects to a pair of augmented-reality glasses attached to a small computer that they each wear on their waistbands.
This setup, called the photovoltaic retina implant microarray or PRIMA system, uses a video camera in the glasses to capture images of text. The glasses then project that image as infrared light onto the implanted chip. Then, the chip converts the light into electrical signals, which the brain interprets as vision.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
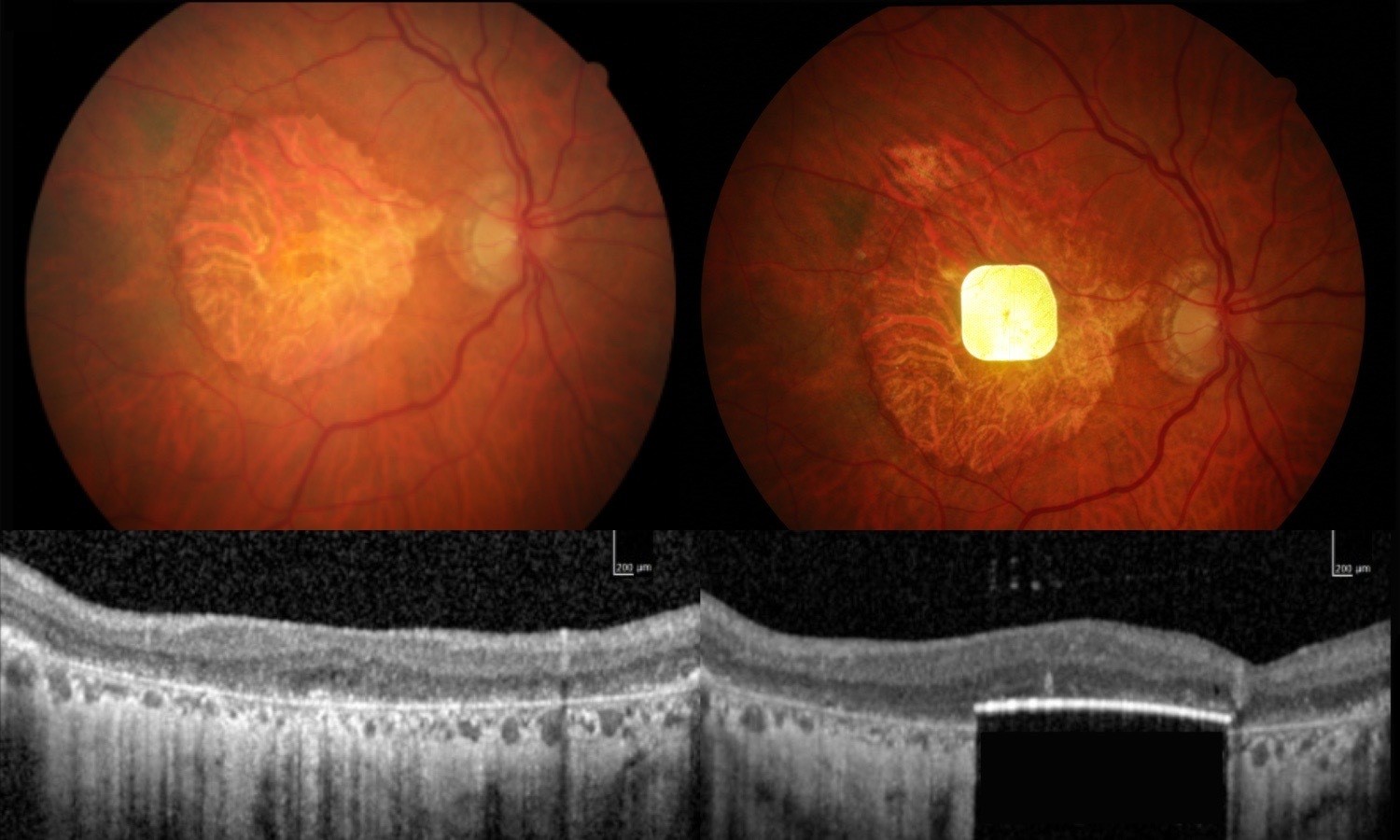
"It's a new way of looking through your eyes, and it was dead exciting when I began seeing a letter," Irvine said in the statement. "It's not simple, learning to read again, but the more hours I put in, the more I pick up."
Participants in the study underwent several months of training to learn to read using the new device. Researchers also encouraged the patients to practice with the device in new ways. Irvine used hers to do crossword puzzles, while another patient used the device to navigate the Paris Metro system. A zoom function on the camera also helps users read fine-print text, such as that on a prescription.
The PRIMA system does have some limitations, Dr. Demetrios Vavvas, director of the retina service at Mass Eye and Ear, who was not involved in the study, told NBC News. In its current form, the device only restores vision in black and white, not color or grayscale, so it can't be used to recognize faces. In addition, it's not yet clear if the device will remain as effective after multiple years of use.
But, "as the iterations of this device become better and better, it could become a real solution for a cohort of patients," Vavvas told NBC.

Skyler Ware is a freelance science journalist covering chemistry, biology, paleontology and Earth science. She was a 2023 AAAS Mass Media Science and Engineering Fellow at Science News. Her work has also appeared in Science News Explores, ZME Science and Chembites, among others. Skyler has a Ph.D. in chemistry from Caltech.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










