Emily Cooke
Emily is a health news writer based in London, United Kingdom. She holds a bachelor's degree in biology from Durham University and a master's degree in clinical and therapeutic neuroscience from Oxford University. She has worked in science communication, medical writing and as a local news reporter while undertaking NCTJ journalism training with News Associates. In 2018, she was named one of MHP Communications' 30 journalists to watch under 30.
Latest articles by Emily Cooke

Acromegaly: A disease that causes adults to grow uncontrollably
By Emily Cooke published
Patients with acromegaly make too much growth hormone, which causes them to grow disproportionately large bones, organs and tissues.

Babies' brain activity changes dramatically before and after birth, groundbreaking study finds
By Emily Cooke published
New brain scans have shown that neurons in several regions of the brain become significantly more active across birth.
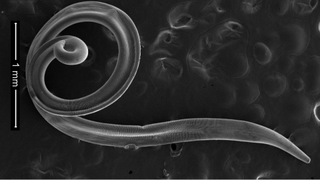
Doctors discover live worms growing under a woman's eyelid in China
By Emily Cooke published
An office worker in Beijing developed a parasitic infection that caused worms to grow under her right eyelid.

'Electronic' scalp tattoos could be next big thing in brain monitoring
By Emily Cooke published
Electrodes can now be printed onto the scalp to measure brain activity.
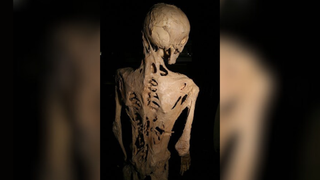
Stone man disease: A rare condition that causes a person to grow a second skeleton
By Emily Cooke published
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) is an extremely rare congenital condition that causes the body to grow a second skeleton, rendering patients immobile.

Is playing in the dirt good for kids' immune systems?
By Emily Cooke last updated
Experts explain why it's healthy to let your children occasionally play in the dirt — and it may not be for the reasons you assume.
Cervical cancer deaths have plummeted among young women, US study finds
By Emily Cooke published
A new study has revealed that cervical cancer deaths have strongly declined in the U.S. since 2016, likely due to increased rates of HPV vaccination.

Your skin color may affect how well a medication works for you — but the research is way behind
By Emily Cooke published
As a new analysis highlights the impact of skin tone on drug safety and efficacy, experts outline what can be done to make medical research more inclusive.

Ancient hunter-gatherer DNA linked to higher BMI in modern Japanese people
By Emily Cooke published
A new study suggests that the DNA some modern Japanese people have inherited from ancient hunter-gatherers may increase BMI.

Butterfly disease: A disorder that makes skin as delicate as butterfly wings
By Emily Cooke published
Epidermolysis bullosa is a potentially fatal, inherited disorder that causes patients to blister very easily.
'Dengue is coming': Climate-fueled rise in cases will affect the US, scientists warn
By Emily Cooke published
New research suggests that climate change is currently driving a surge in global dengue infections and that case rates could increase by 60% by 2050.

Necrotizing fasciitis: The 'flesh-eating' infection that bores holes in the body
By Emily Cooke published
Necrotizing fasciitis is a rare, life-threatening illness caused by bacteria that aggressively attack the soft tissue of the body.

Migraine molecules may drive endometriosis pain. Existing drugs might help.
By Emily Cooke published
Pain-sensing neurons exchange signals with immune cells that drive endometriosis, sparking the pain associated with the condition, new research suggests.

BRCA only explains a fraction of breast cancers — genes tied to metabolism may also up risk
By Emily Cooke published
Scientists pinpointed 80 gene variants, including eight tied to fatty acid metabolism, that may cause breast cancer in some people, new research suggests.

These 3 neurons may underlie the drive to eat food
By Emily Cooke published
A brain circuit made up of three types of neurons may regulate appetite, a mouse study finds.

Natural selection is unfolding right now in these remote villages in Nepal
By Emily Cooke published
Physiological traits that help Tibetan women survive at high altitudes are being selected for within the population, meaning they may be becoming more common, new research hints.
Trigger for deadly neurodegenerative disorder identified
By Emily Cooke published
The discovery of an important enzyme involved in Huntington's disease may pave the way for future treatments to prevent the condition, researchers say.

How to get better faster when you have the flu, according to science
By Emily Cooke published
Experts explain how to shorten a flu infection.
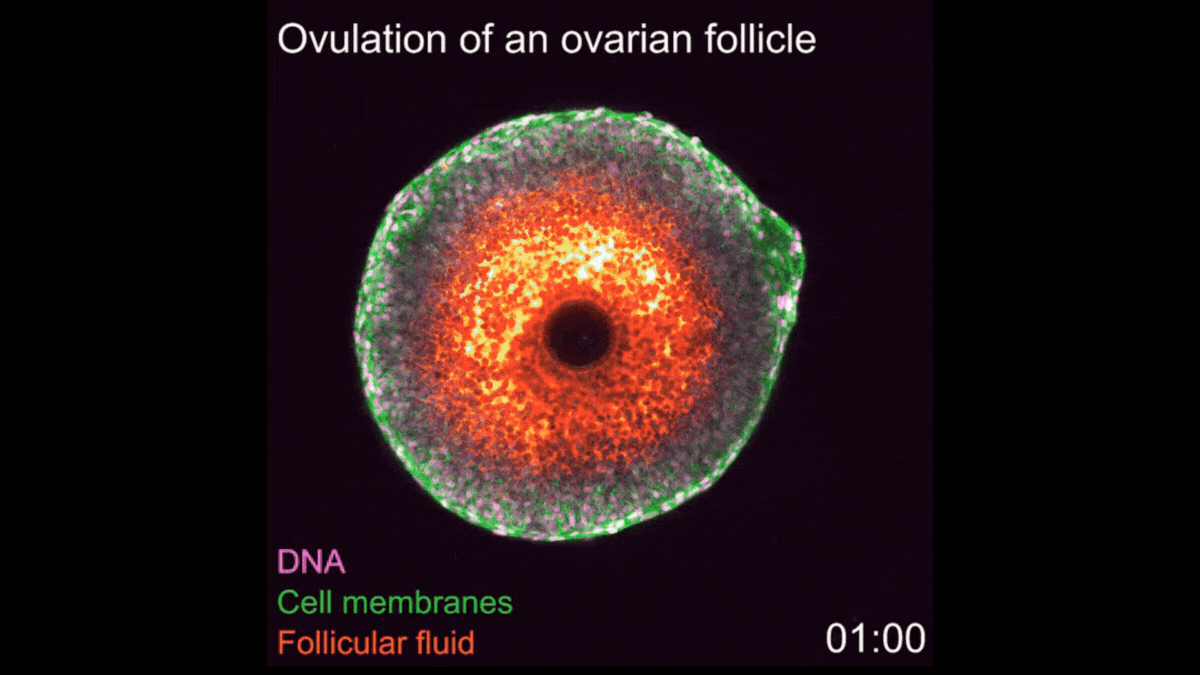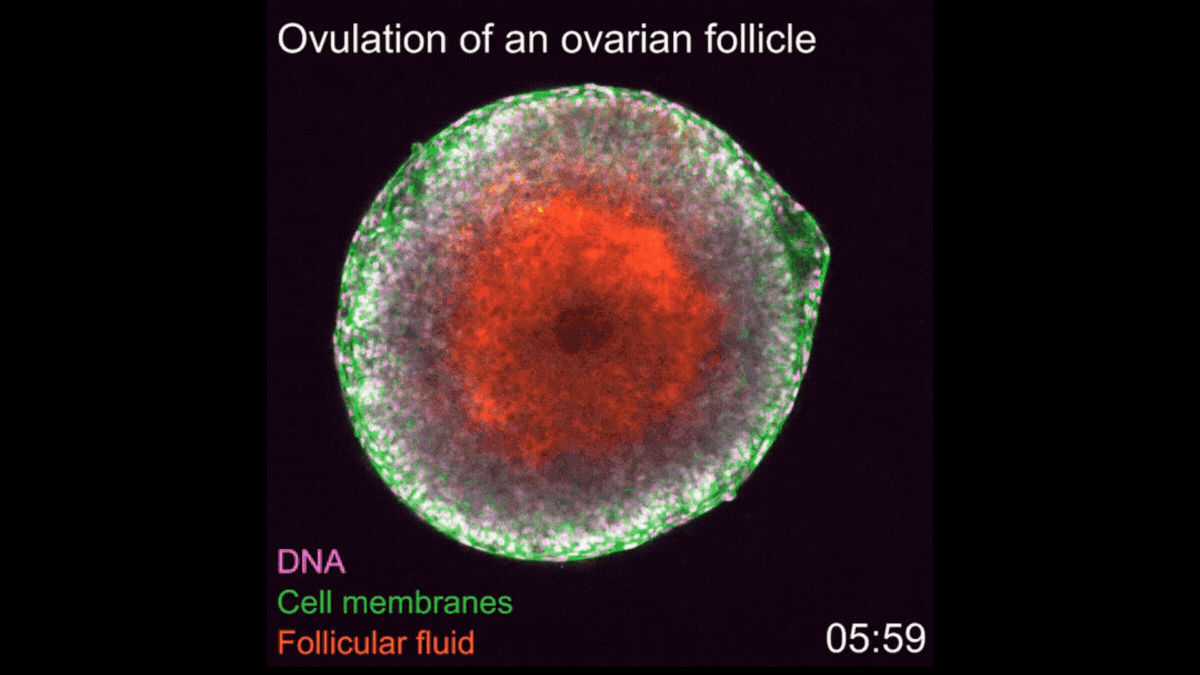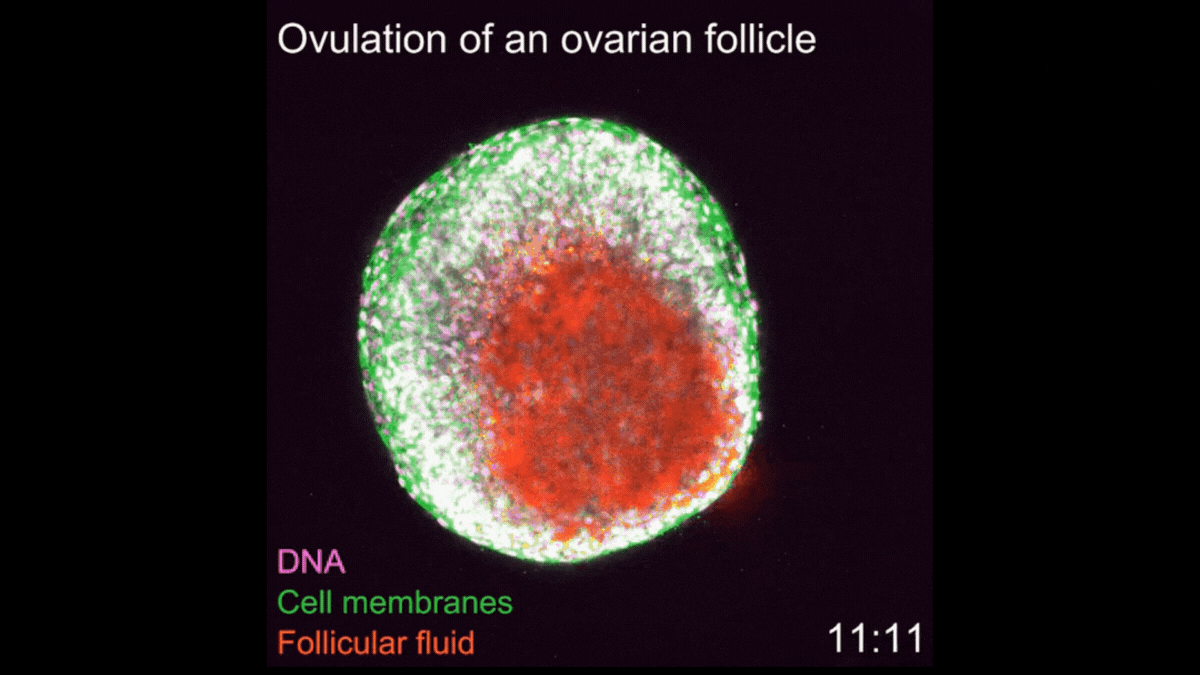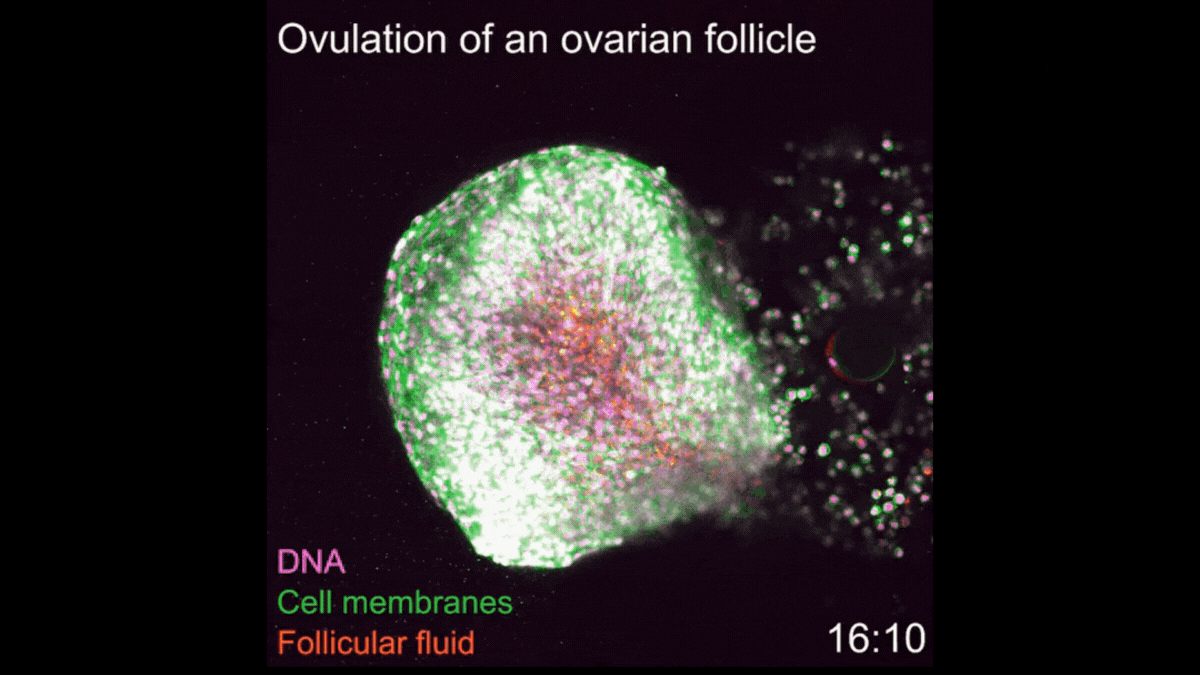
Watch 1st-ever video of ovulation occurring in real-time
By Emily Cooke published
A new imaging technique enabled scientists to film every step of ovulation as it unfolds in mouse cells.

New device 'zaps' bacteria on the skin, potentially preventing infections
By Emily Cooke published
Early experiments suggest a patch that delivers harmless electric currents into the skin can thwart certain bacterial infections. However, it has not yet been tested in humans.

Parents who have this gene may be more likely to have a girl
By Emily Cooke published
A large new analysis suggests that some people carry genetic variants that make them more likely to have female than male offspring.

Melatonin disruption tied to early-onset osteoporosis, new study suggests
By Emily Cooke published
A genetic analysis suggests that rare cases of early onset osteoporosis may be partly caused by disruptions to the function of the hormone melatonin.

At-home brain stimulation could be promising depression treatment, trial hints
By Emily Cooke published
A new trial suggests that at-home brain stimulation could potentially be a first-line treatment for depression. However, some experts are skeptical.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.