New Antarctic Evidence Reveals Past Melting

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
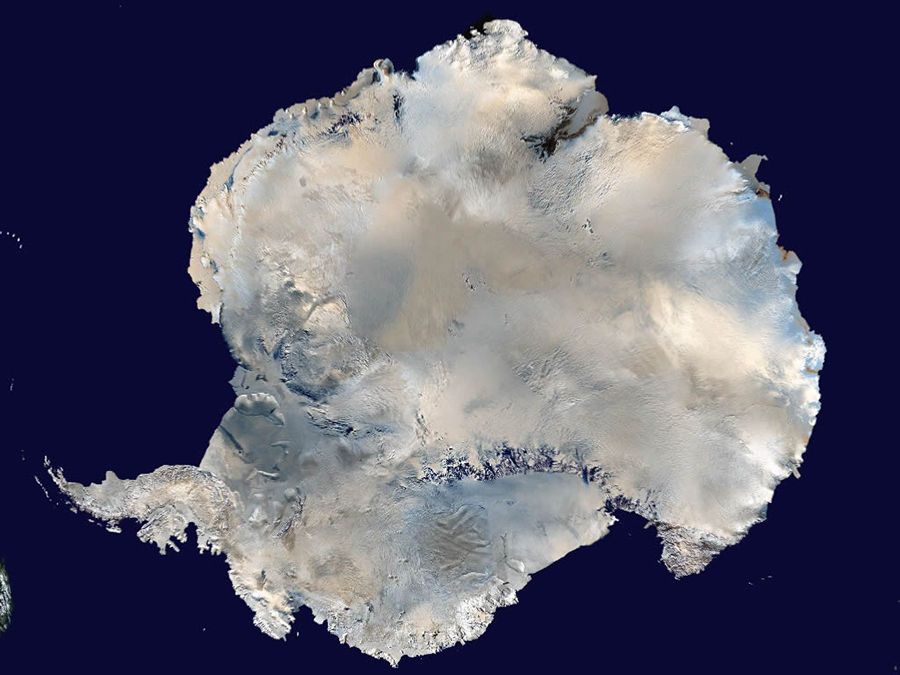
One of the wild cards in estimating future sea level rise from global warming is the enormous East Antarctic Ice Sheet, which holds more freshwater in its icy expanse than the whole of Greenland.
Some climate models predict the giant ice sheet will undergo relatively little change as the planet warms in coming decades, while others forecast significant melting. Now, a new study suggests parts of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet underwent significant melting during the Pliocene, a recent geologic epoch when climate conditions were similar to those of today.
"Scientists previously considered the East Antarctic Ice Sheet to be more stable than the much smaller ice sheets in West Antarctica and Greenland, even though very few studies of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet have been carried out," Carys Cook, lead study author, said in a statement. "Our work now shows that the East Antarctic Ice Sheet has been much more sensitive to climate change in the past than previously realized," said Cook, a doctoral student at Imperial College London.
During the Pliocene epoch between 5.3 million to 2.6 million years ago, geologic evidence indicates atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide were similar to modern levels of 400 parts per million (meaning that for every million air particles, 400 of them are carbon dioxide molecules) and global temperatures were 2 to 3 degrees Celsius (about 3.6 to 5.4 degrees Fahrenheit) higher than they are now. Sea levels stood about 66 feet (20 meters) higher, according to ancient preserved shorelines.
To raise sea level that much, all of Greenland and West Antarctica had to be ice-free and parts of East Antarctica may have melted, modeling studies show. (The Antarctic ice sheet first started forming 34 million years ago.)
Cook and her colleagues looked for evidence of past ice melting by drilling into deep-sea sediments offshore of East Antarctica. The ancient mud contains a unique geochemical fingerprint that matches bedrock in the Wilkes Subglacial Basin, which is now thickly covered with ice. The sediments were deposited between about 5 million to 3 million years ago, indicating the ice sheet retreated several hundred kilometers (about 200 miles) inland, exposing the bedrock, the researchers conclude. Erosion carried the sediments offshore.
The findings were published July 21 in the journal Nature Geoscience.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The researchers plan to conduct additional studies to determine whether the ice sheet melted all at once or in pulses, and how quickly melting took place.
Editor's note: This story was updated July 22 to reflect the correct definition of parts per million.
Email Becky Oskin or follow her @beckyoskin. Follow us @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on LiveScience.com.

 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus