Facts About Cerium
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
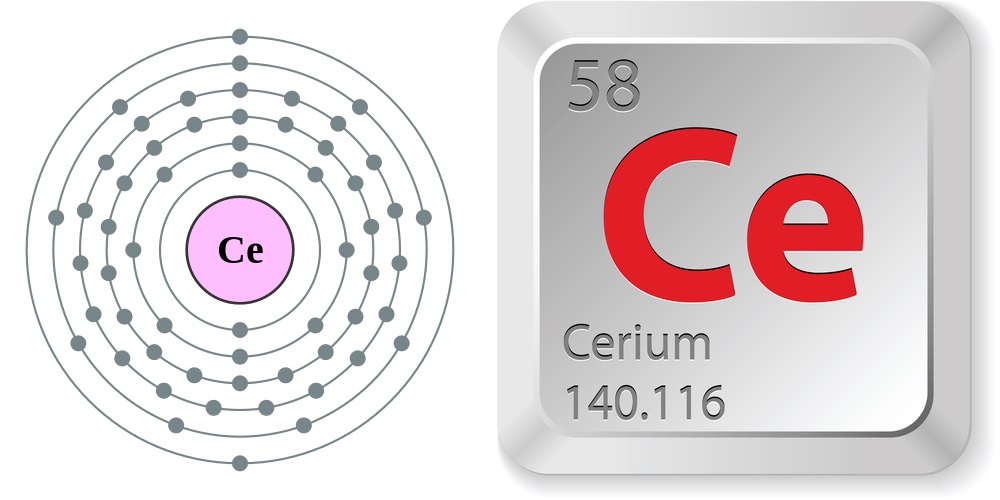
| Atomic Number: 58 Atomic Symbol: Ce Atomic Weight: 140.116 | Melting Point: 1,468.4 F (798 C) Boiling Point: 6,229.4 F (3,443 C) |
Word origin: Cerium is named after the dwarf planet Ceres, which was discovered in 1801, two years before the element.
Discovery: The element was discovered in 1803 by Jöns Jacob Berzelius and Wilhelm Hisinger and independently by Martin Klaproth.
Properties of cerium
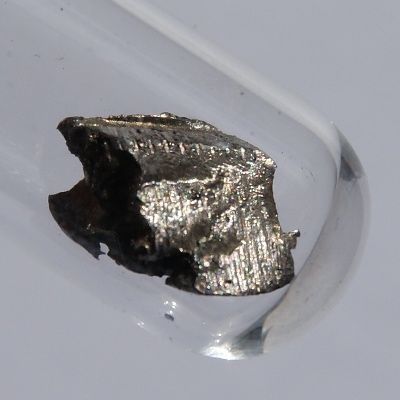
Cerium is a grey lustrous metal that is malleable, and one of the most reactive of the rare-earth metals, also called lanthanides. [See Periodic Table of the Elements]
It oxidizes readily at room temperature. It can decompose slowly in cold water, and very rapidly in hot water. The metal can be attacked by alkaline solutions, dilute and concentrate acids. When scratched with a knife, the pure metal of cerium may ignite.
Sources of cerium
Cerium is one of the most abundant of the rare-earth metals. It is found in several minerals, including allanite or orthrite, monazite, bastnasite, cerite and samarskite. Large deposits of cerium have been found in India, Brazil and in Southern California.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Metallic cerium is obtained through thermal reduction techniques and produces highly pure versions of the element.
Uses of cerium
Cerium is a component of mischmetal, used in the manufacture of alloys for cigarette lighters.
Cerium oxide is used in incandescent gas mantles, as a glass polishing agent and as a catalyst in self-cleaning ovens.
Cerium is also extensively used in the film and television industry in carbon arc lighting for studio lighting and projector lights.
(Source: Los Alamos National Laboratory)
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus