
34,000-Year-Old Organisms Found Buried Alive!
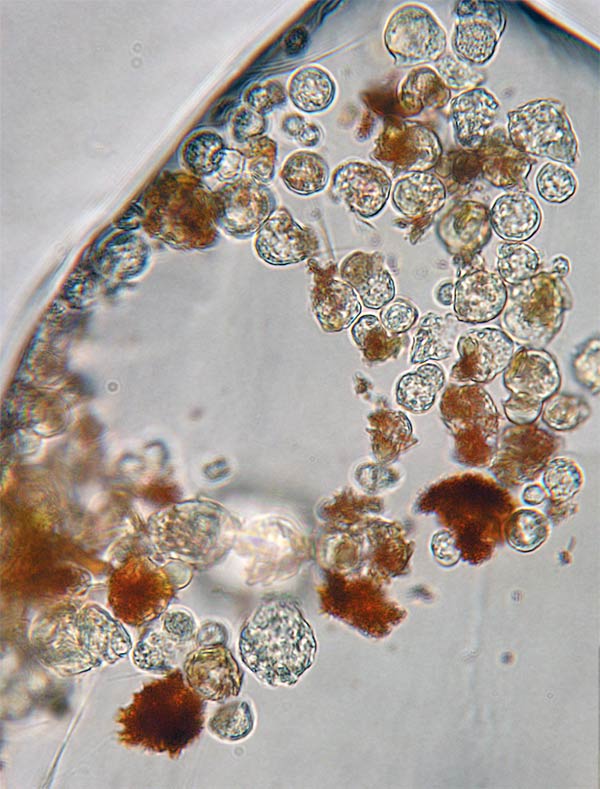
It's a tale that has all the trappings of a cult 1960s sci-fi movie: Scientists bring back ancient salt crystals, dug up from deep below Death Valley for climate research. The sparkling crystals are carefully packed away until, years later, a young, unknown researcher takes a second look at the 34,000-year-old crystals and discovers, trapped inside, something strange. Something … alive.
Thankfully this story doesn't end with the destruction of the human race, but with a satisfied scientist finishing his Ph.D.
"It was actually a very big surprise to me," said Brian Schubert, who discovered ancient bacteria living within tiny, fluid-filled chambers inside the salt crystals.
Salt crystals grow very quickly, imprisoning whatever happens to be floating — or living — nearby inside tiny bubbles just a few microns across, akin to naturally made, miniature snow-globes.
"It's permanently sealed inside the salt, like little time capsules," said Tim Lowenstein, a professor in the geology department at Binghamton University and Schubert's advisor at the time.
Lowenstein said new research indicates this process occurs in modern saline lakes, further backing up Schubert’s astounding discovery, which was first revealed about a year ago. The new findings, along with details of Schubert’s work, are published in the January 2011 edition of GSA Today, the publication of the Geological Society of America.
Schubert, now an assistant researcher at the University of Hawaii, said the bacteria — a salt-loving sort still found on Earth today — were shrunken and small, and suspended in a kind of hibernation state.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"They're alive, but they're not using any energy to swim around, they're not reproducing," Schubert told OurAmazingPlanet. "They're not doing anything at all except maintaining themselves."
The key to the microbes' millennia-long survival may be their fellow captives — algae, of a group called Dunaliella.
"The most exciting part to me was when we were able to identify the Dunaliella cells in there," Schubert said, "because there were hints that could be a food source."
With the discovery of a potential energy source trapped alongside the bacteria, it has begun to emerge that, like an outlandish Dr. Seuss invention (hello, Who-ville), these tiny chambers could house entire, microscopic ecosystems.
Other elderly bacteria?
Schubert and Lowenstein are not the first to uncover organisms that are astonishingly long-lived. About a decade ago, there were claims of discoveries of 250-million-year-old bacteria. The results weren't reproduced, and remain controversial.
Schubert, however, was able to reproduce his results. Not only did he grow the same organisms again in his own lab, he sent crystals to another lab, which then got the same results.
"So this wasn’t something that was just a contaminant from our lab," Schubert said.
Survival strategy
The next step for researchers is to figure out how the microbes, suspended in a starvation-survival mode for so many thousands of years, managed to stay viable.
"We're not sure what's going on," Lowenstein said. "They need to be able to repair DNA, because DNA degrades with time."
Schubert said the microbes took about two-and-a-half months to "wake up" out of their survival state before they started to reproduce, behavior that has been previously documented in bacteria, and a strategy that certainly makes sense.
"It's 34,000 years old and it has a kid," Schubert said. And ironically, once that happens, the new bacteria are, of course, entirely modern.
Of the 900 crystal samples Schubert tested, only five produced living bacteria. However, Schubert said, microbes are picky. Most organisms can't be cultured in the lab, so there could be many living microbes that just didn't like their new home enough to reproduce.
Still, wasn't it exciting to discover what could be one of the oldest living organisms on the planet?
"It worked out very well," Schubert said.
Reach Andrea Mustain at amustain@techmedianetwork.comThis e-mail address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it . Follow her on Twitter @AndreaMustain. This article was provided by OurAmazingPlanet, a sister site to LiveScience.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus





