Permafrost Could Be Climate's Ticking Time Bomb
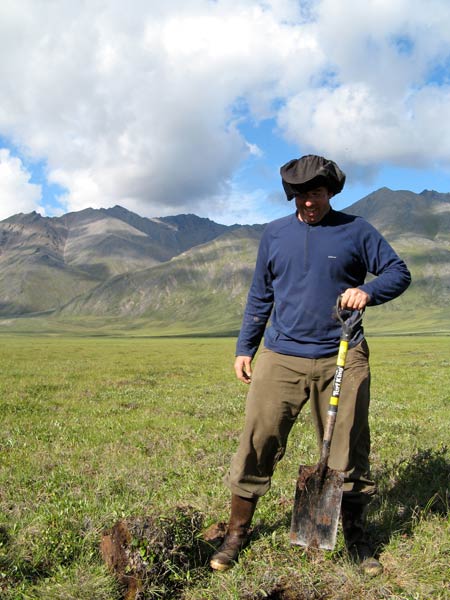

This Behind the Scenes article was provided to LiveScience in partnership with the National Science Foundation. The terrain of the North Slope of Alaska is not steep, but Andrew Jacobson still has difficulty as he hikes along the spongy tundra, which is riddled with rocks and masks multitudes of mosquitoes. Jacobson, a professor of earth and planetary sciences at Northwestern University, extracts soil and water samples in search of clues to one of global warming's biggest ticking time bombs: the melting of permafrost. Permafrost, or frozen ground, covers approximately 20 to 25 percent of the land-surface area in the northern hemisphere, and is estimated to contain up to 1,600 gigatons of carbon, primarily in the form of organic matter. (One gigaton is equivalent to one billion tons.) By comparison, the atmosphere now contains around 825 gigatons of the element as carbon dioxide. "Permafrost historically has served as a carbon sink, largely isolating carbon from participating in the carbon cycle," says Jacobson, whose research is funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the David and Lucile Packard Foundation. "However, global warming could transform the Arctic into a new carbon source by accelerating the rate of permafrost melting. This undoubtedly would have a dramatic effect on the global carbon cycle." Jacobson says the key concern is that permafrost carbon will oxidize to carbon dioxide as melting accelerates, causing a positive feedback to global warming. A vicious cycle is created as a warmer climate facilitates more carbon release, which in turn favors more warming. So Jacobson and his colleagues collect river water and soil samples near NSF’s Toolik Long-Term Ecological Research station, approximately 250 km north of the Arctic Circle. The Dalton Highway — built as a supply road to support the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System — provides the only access to the site. "Planning constitutes a large part of our day — looking at maps, figuring out where to go and how to get there," he laughs. "Fieldwork is typically fraught with vehicle problems, poor roads and bad weather. One thing you can always count on is that every expedition is exciting." While a logical first step for modeling global warming is quantifying carbon flow, unresolved complexities surrounding the Arctic carbon cycle make it difficult to create models for that element. Jacobson and his team take a complementary approach by analyzing naturally occurring isotopes of other elements, such as calcium and strontium, which track permafrost melting and therefore provide insight into carbon release. Initial data show that rivers and permafrost have distinctly different calcium and strontium isotope compositions. When permafrost thaws during the summer and melts into rivers, the rivers show calcium and strontium isotope compositions that approach those for permafrost. Jacobson hypothesizes that in a warmer world, the permafrost signature in rivers will be more pronounced for longer periods of time. Changes in the isotope composition of rivers can relate to changes in the release of carbon. So the calcium and strontium isotope composition of Arctic rivers can track the impact of warming on permafrost stability and carbon dioxide release. "The ultimate goal is to establish a baseline to which future changes can be compared," Jacobson says. "Several years from now, we can compare real changes to model predictions and improve our understanding of how the system works.” The sampling season lasts for only a short time when permafrost thaws in the spring until it refreezes in the fall. Although he visited Alaska in May and will return in October, Jacobson has a team of colleagues and students who will conduct fieldwork throughout the season and again next year. Samples are shipped from the field to Jacobson’s laboratory in Evanston, Ill., where he analyzes them in the off-season. He received NSF funding in 2007 to acquire a multi-collector thermal ionization mass spectrometer for measuring isotopes of calcium, strontium and other elements. Northwestern currently is building a state-of-the-art “metal free” clean laboratory that will house the instrument and support Jacobson’s research. For more on his research, visit Jacobson’s laboratory website here.
- Top 10 Surpring Results of Global Warming
- Global Warming Could Release Permafrost Carbon
- Ten Ways You Can Improve the Earth's Health
Editor's Note: This research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF), the federal agency charged with funding basic research and education across all fields of science and engineering. See the Behind the Scenes Archive.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus