Conflict-Scarred Temple Uncovered Near Jerusalem

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
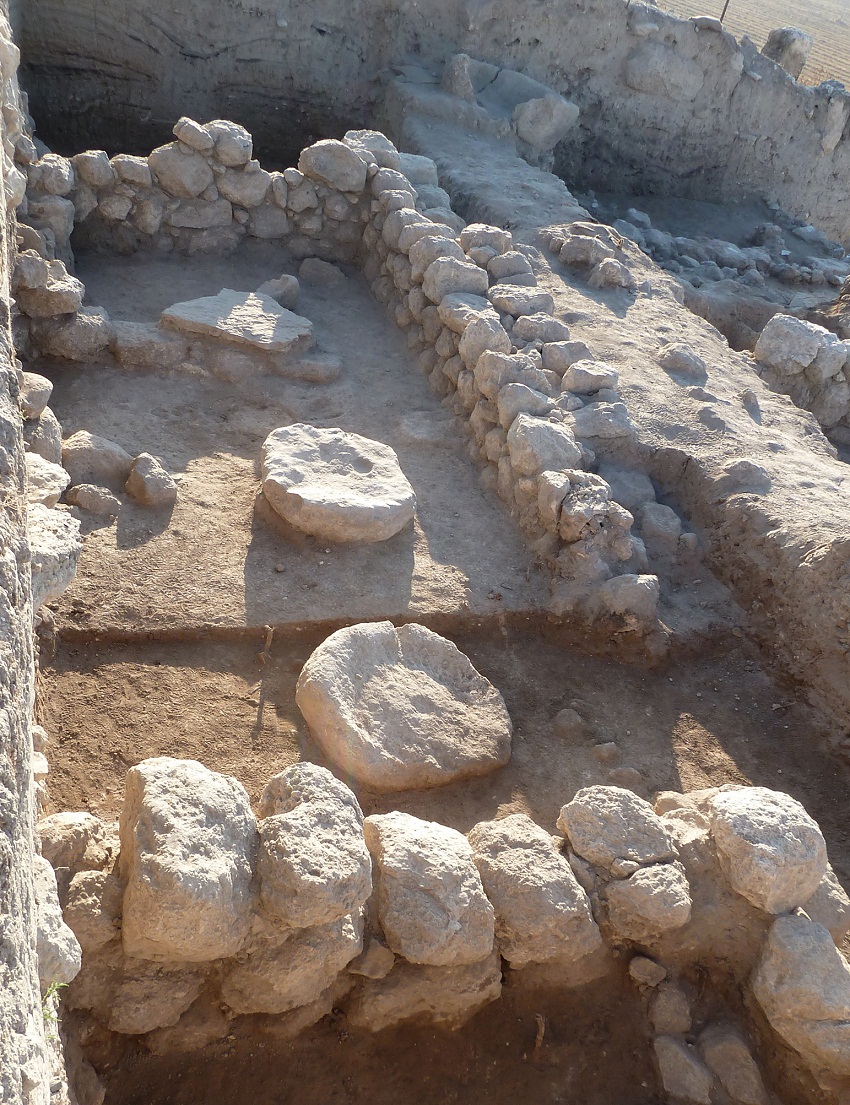
At a biblical border city outside of Jerusalem, archaeologists have uncovered a temple from the 11th century B.C. that they say bears evidence of conflict among the ancient Israelites, Canaanites and Philistines.
Spread across what would have been the floor at the complex at Tel Beth-Shemesh, an ancient village about 12 miles (20 kilometers) west of Jerusalem, excavators found shards of painted chalices and goblets — not the type of containers that would have been used for daily household activities. They also found animal bones surrounding a flat stone inside the building and discovered two more flat stones seemingly designed to direct liquids. Lacking the typical traces of domestic use, the excavators believe the building served as a place of worship that was possibly connected to an Israelite cult.
But the complex didn't stay holy for long. The archaeologists found evidence that the temple was destroyed. What's more, an analysis of dirt at the site turned up microscopic remains of plants commonly eaten by livestock as well as the remnants of poop from grass-eating animals, suggesting the site was appropriated as a livestock pen.
The excavators believe the animal takeover of the temple might represent a deliberate desecration by the Philistines, who lived alongside, though hardly peacefully, with the Israelites and Canaanites. The ancient village of Beth-Shemesh, located at the crossroads of the three groups, frequently changed hands between the Philistines and the Canaanite and Israelite populations that resisted them. The researchers say the Philistines likely gained temporary control of Beth-Shemesh and then brought in livestock to reside on what they knew had been a holy place for their enemies.
Related: Canaanites Live: DNA Reveals Fate of Biblical People
But further evidence suggests the ancestors of the worshippers may have eventually returned. The archaeologists found several round clay ovens known as "tabuns" in the layer of soil excavated above the temple's ruins. These food-prepping features are usually found near ancient living quarters, not sacred sites, but the researchers may have an explanation for the ovens.
"We believe that ancestors of those who had built the original complex came back to rebuild the site," archaeologist Zvi Lederman, of Tel Aviv University, said in a statement, adding that the ovens may have been used to cook feasts to honor the memory of the old temple after the Philistines pulled out of the area.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The researchers are planning further excavations at the site and their findings will be presented this month at the annual meeting of the American Schools of Oriental Research in Chicago.
Follow LiveScience on Twitter @livescience. We're also on Facebook & Google+.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus