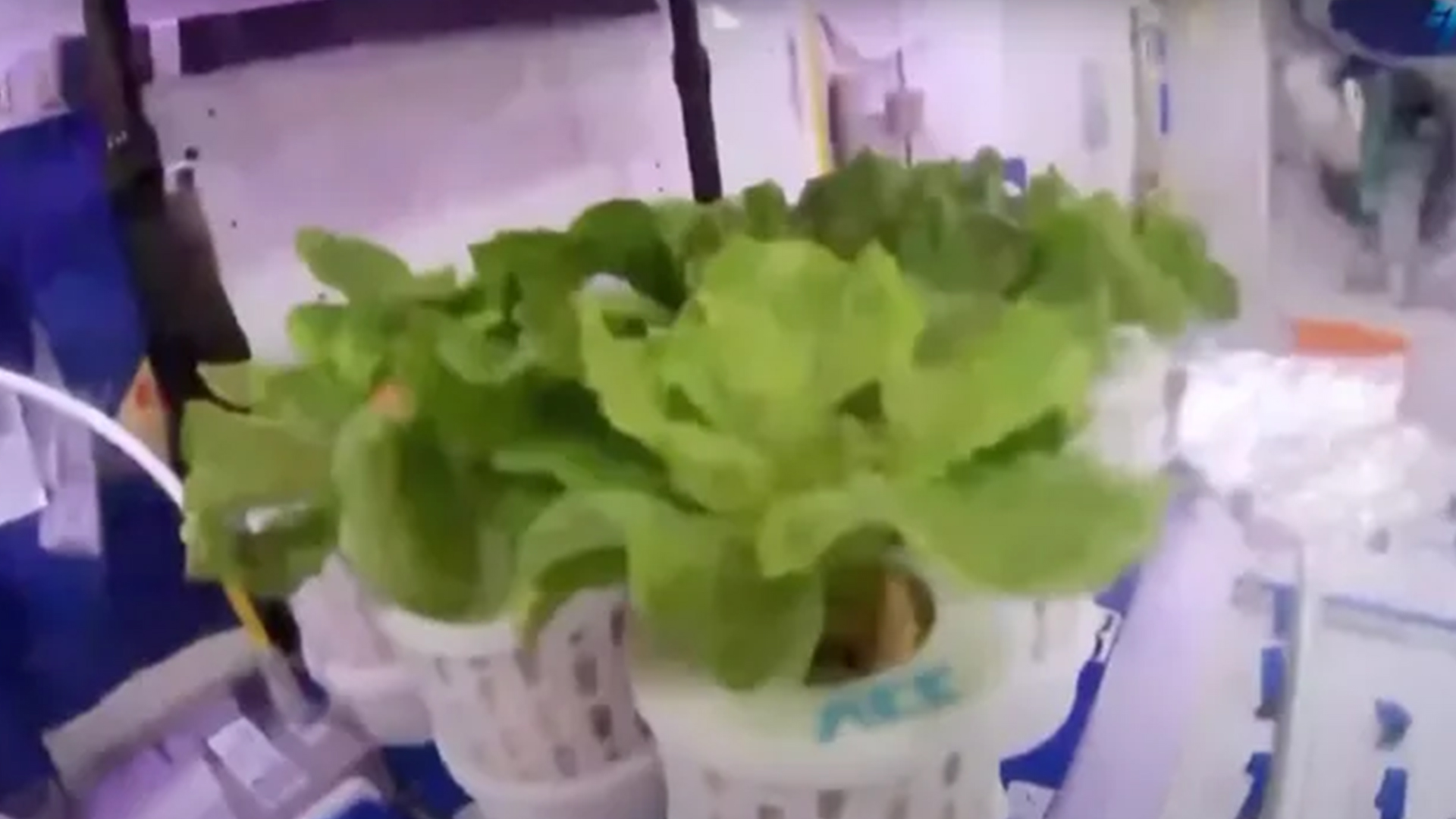
China successfully grows lettuce and tomatoes aboard Tiangong space station
Lettuce, cherry tomatoes and more are sprouting in space aboard China's Tiangong space station.

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
China's Shenzhou 16 astronauts have been growing vegetables aboard the Tiangong space station, as part of plans for future deep space exploration.
Mission commander Jing Haipeng and rookie astros Zhu Yangzhu and Gui Haichao have been aboard Tiangong since late May and are due to return to Earth on Oct. 31, after handing over control of the station to the newly arrived Shenzhou 17 mission crew.
Jing and company have spent time cultivating veggies using two sets of specialized equipment. The first started operation in June and has reaped four batches of lettuce. The second one was put into operation in August for growing cherry tomatoes and green onions.
The China Astronaut Research and Training Center has also set up replicas on Earth, allowing researchers to compare results and more accurately analyze divergences in how plants grow in space and on the ground. This, researchers say, is part of a long-term plan to aid deep space exploration.
"This vegetable cultivation apparatus is a key part of the whole Environmental Control and Life Support System [ECLSS], and it is used in space to verify the relevant technologies. In the future, we will focus on rapid and large-scale cultivation," Yang Renze, a researcher from China Astronaut Research and Training Center, told CCTV.
"The system can be applied to the field of deep space exploration, including our crewed lunar and Mars landing missions," Yang said.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"As a key part of the ECLSS, the plants grown from the cultivation apparatus can absorb carbon dioxide in the air to generate oxygen with the photosynthesis, and then regenerate and purify water with transpiration."
China is working to put a pair of astronauts on the moon before 2030. It is also planning to build a moon base, called the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS), in the next decade. A crewed Mars landing is much further off, but the Red Planet has been noted as a future destination for Chinese spaceflight.
Originally posted on Space.com.

Andrew is a freelance space journalist with a focus on reporting on China's rapidly growing space sector. He began writing for Live Science sister site Space.com in 2019, and he also writes for SpaceNews, IEEE Spectrum, National Geographic, Sky & Telescope, New Scientist and others. Andrew first caught the space bug when, as a youngster, he saw Voyager images of other worlds in our solar system for the first time. Away from space, Andrew enjoys trail running in the forests of Finland.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus