Ancient Roman tombstone found beneath undergrowth in New Orleans yard
A New Orleans couple doing yard work behind their house unexpectedly found a Roman headstone of a solider who died 1,900 years ago.
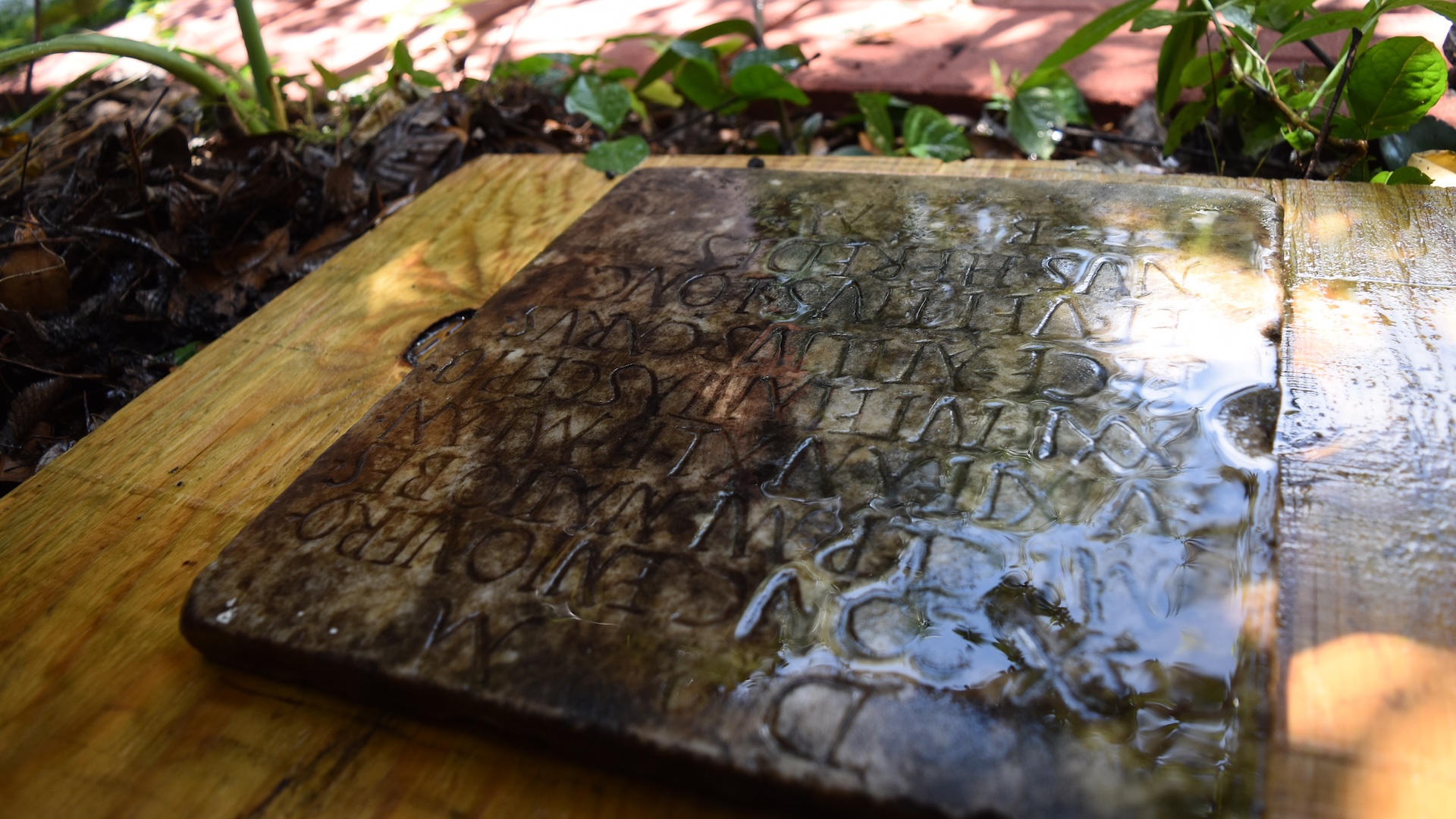
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
When clearing undergrowth in their New Orleans yard one day, a married couple discovered something completely unexpected: a Roman headstone that had once marked the grave of a soldier who lived half the world away in the second century.
Research into the unlikely object indicates that it is genuine, and its discovery hints at an international mystery that dates back to World War II.
"We get calls from the public about odd finds in yards in the area pretty often," University of New Orleans archaeologist D. Ryan Gray, who analyzed the headstone, told Live Science. "Often it turns out to be something natural that just happens to look like an artifact."
In this case, the homeowners were Daniella Santoro, an anthropologist at Tulane University, and her husband Aaron Lorenz, Gray noted in an Oct. 6 online report about the investigations into the stone.
"When Daniella initially described this, I thought maybe it was a 19th-century gravestone that had been scavenged from a New Orleans cemetery and then discarded," Gray said. "However, as soon as I saw the photo of the inscription, I immediately suspected this was something very different."
Ancient gravestone
Santoro had found the unusual marble tablet beneath the undergrowth in the backyard of her "shotgun" house in the city's historic Carrollton neighborhood. The stone is about 12 inches (30 centimeters) wide and slightly longer, and one surface is densely chiseled with Roman text.
Experts say the Latin inscription can be translated to English and reads: "To the Spirits of the Dead for Sextus Congenius Verus, soldier of the praetorian fleet Misenensis, from the tribe of the Bessi [of Thrace], (who) lived 42 years (and) served 22 in the military, on the trireme [warship] Asclepius. Atilius Carus and Vettius Longinus, his heirs, made (this) for him well deserving."
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
It was clear this was the gravestone of a soldier, born in the Thrace region of northern Greece, who had served on a Roman warship. But now there was a new mystery: How did the gravestone end up in New Orleans?

The unexpected Roman gravestone in New Orleans comes from Italy and dates to the second century A.D., about 1,900 years ago.
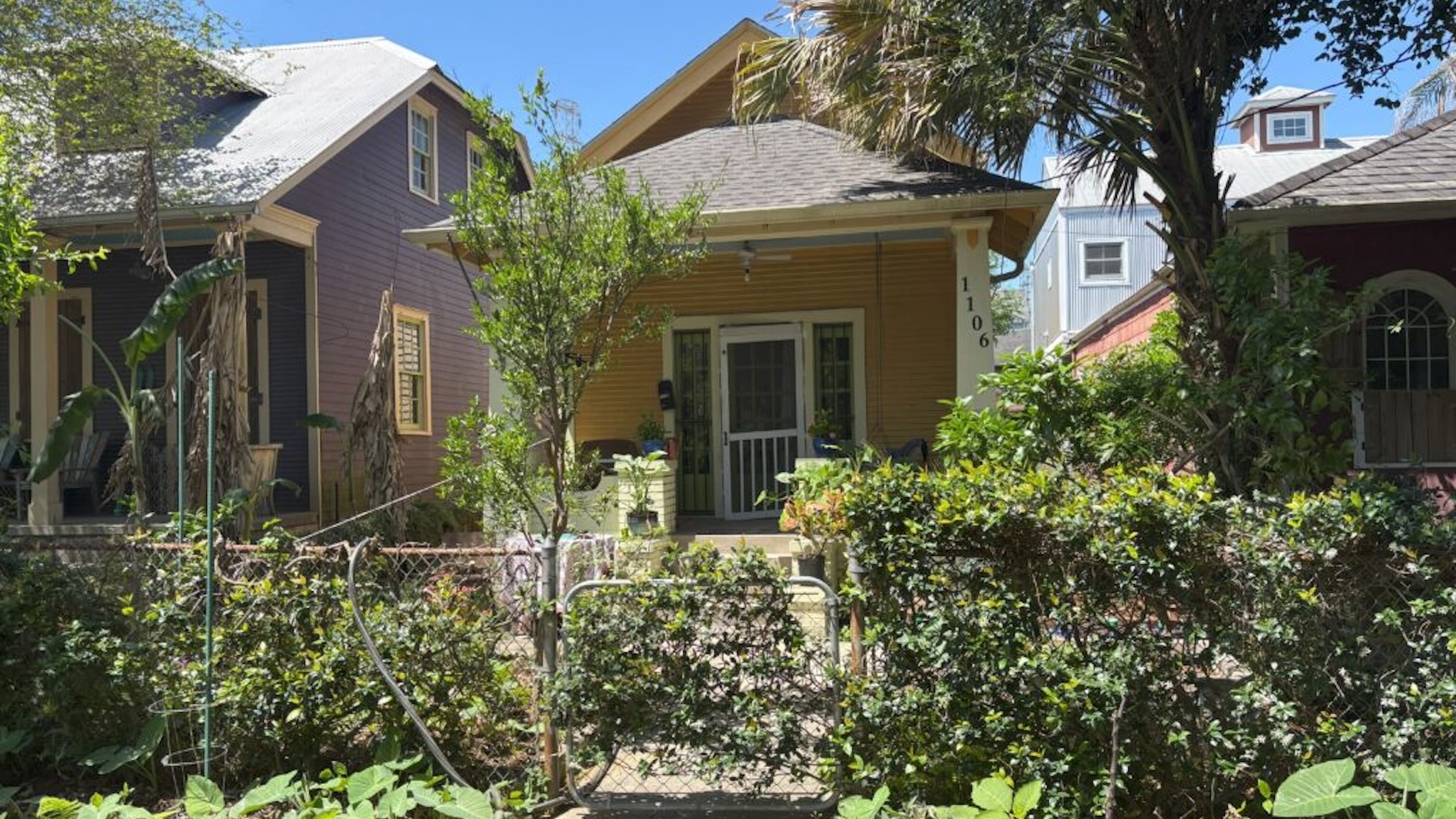

The gravestone was unearthed in the backyard of a "shotgun" house in the city's historic Carrollton neighborhood.
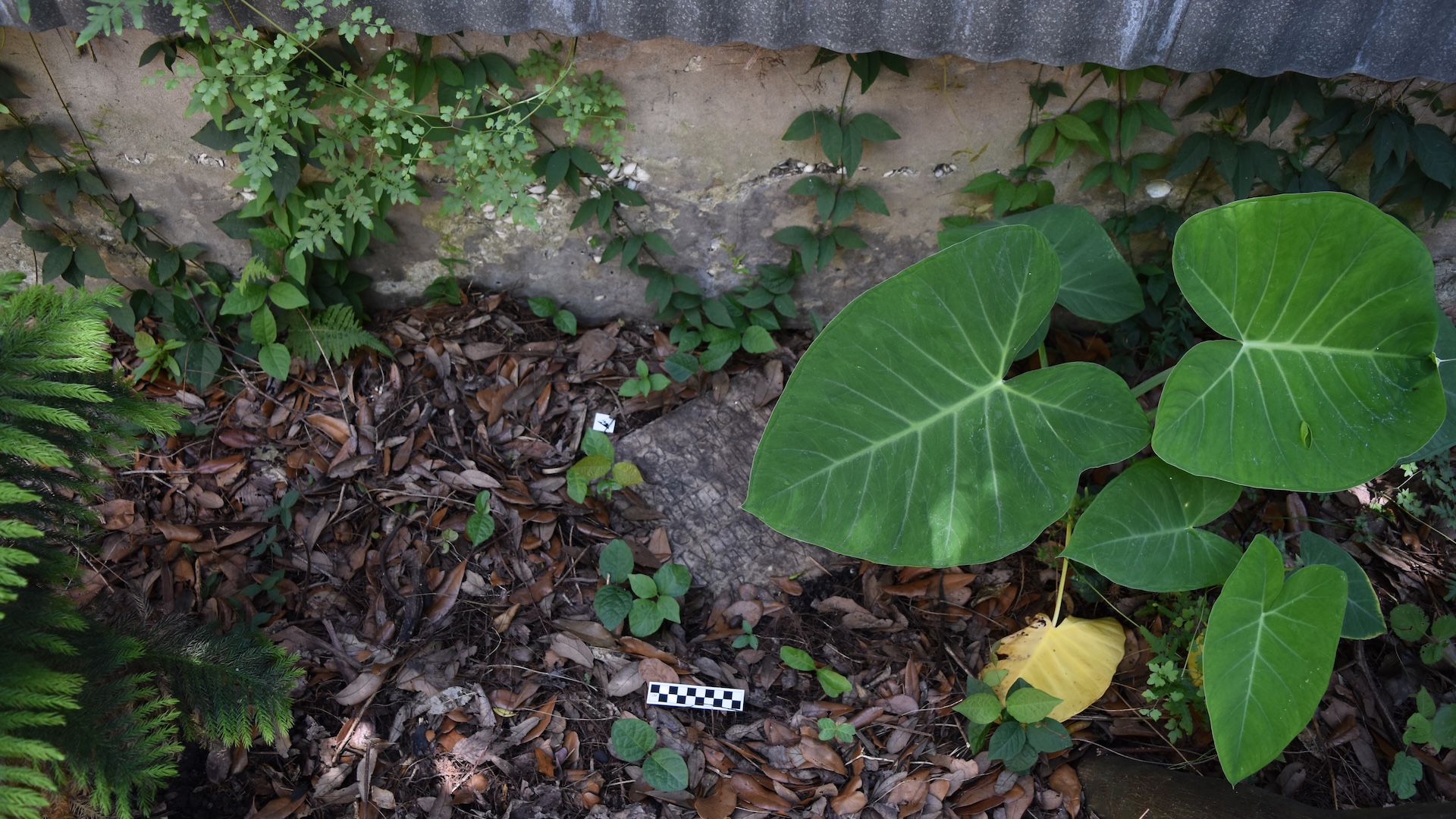

The homeowners found the gravestone beneath undergrowth in a garden in their backyard.
Mystery solved
An investigation revealed that the inscription had already been recorded by archaeologists — but on a second-century grave marker found near Civitavecchia, an ancient city and port about 40 miles (64 kilometers) northwest of Rome. That headstone was reported missing after World War II, however, when Allied bombs destroyed the museum that housed it.
Initially, it wasn't clear how the headstone had ended up in New Orleans. But as news coverage of its discovery spread, its story emerged: The ancient slab had been acquired by a U.S. soldier who fought in Italy during World War II, the man's granddaughter told local news media.
Erin Scott O'Brien reported that her grandfather, Charles Paddock Jr., brought the tombstone home to New Orleans and displayed it in a case in his house before he died in 1986, according to The Guardian. The grave marker was then passed down to O'Brien, and she put it in her garden while living in the Carrollton neighborhood. However, when she sold the house in 2018, O'Brien forgot to take it with her. The couple who bought the house later found the ancient artifact while doing yard work.
Santoro and Lorenz are now working with authorities in the U.S. and Italy to return the gravestone to Civitavecchia.
"For me, this story reflects a wonderful intersection of a homeowner's curiosity ultimately bringing to light something unexpected and historically significant," Gray wrote in his report.
Editor's note: This story was published on Oct. 9, and updated on Oct. 17 with the news from Erin Scott O'Brien that her grandfather had brought the gravestone from Italy to the U.S.
Tom Metcalfe is a freelance journalist and regular Live Science contributor who is based in London in the United Kingdom. Tom writes mainly about science, space, archaeology, the Earth and the oceans. He has also written for the BBC, NBC News, National Geographic, Scientific American, Air & Space, and many others.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










