The World’s Smallest Robot
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
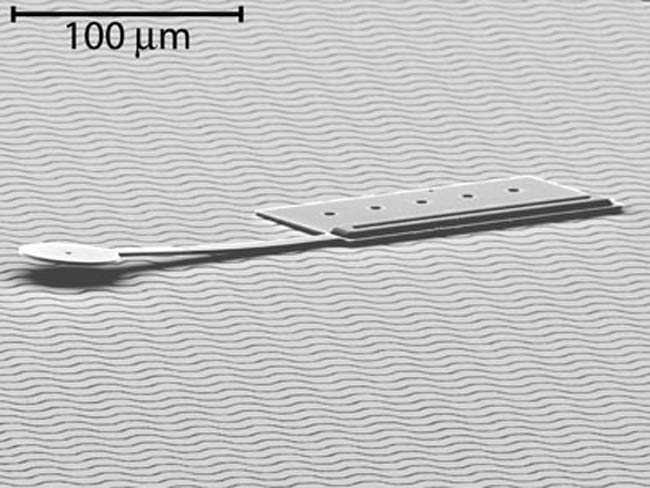
Researchers have built an inchworm-like robot so small you need a microscope just to see it.
In fact about 200 hundred of them could line up and do the conga across a plain M&M.
The tiny bot measures about 60 micrometers wide (about the width of a human hair) by 250 micrometers long, making it the smallest untethered, controllable microrobot ever.
"It's tens of times smaller in length, and thousands of times smaller in mass than previous untethered microrobots that are controllable," said designer Bruce Donald of Dartmouth University. "When we say ‘controllable,' it means it's like a car; you can steer it anywhere on a flat surface, and drive it wherever you want to go. It doesn't drive on wheels, but crawls like a silicon inchworm, making tens of thousands of 10-nanometer steps every second. It turns by putting a silicon 'foot' out and pivoting like a motorcyclist skidding around a tight turn."
Because it makes use of this innovative bending movement and is untethered, it can move freely across a surface without the wires or rails that restricted the mobility of previously developed microrobots. The caterpillar strategy also helped the researchers avoid a common problem in microrobotics.
"Machines this small tend to stick to everything they touch, the way sand sticks to your feet after a day at the beach," said Craig McGray of the National Institute of Standards and Technology. "So we built these microrobots without any wheels or hinged joints, which must slide smoothly on their bearings. Instead, these robots move by bending their bodies like caterpillars. At very small scales, this machine is surprisingly fast."
To get around, the robot makes use of two independent microactuators – the robot's "muscles." One is for forward motion and the other for turning.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
It doesn't have pre-programmed directions. Instead, it reacts to electric changes in the grid of electrodes it moves on. This grid also supplies the microrobot with the power needed to make these movements.
This microrobot and similar versions that could be developed might eventually ensure information security, inspect and make repairs to integrated circuits, explore hazardous environments, or even manipulate human cells or tissues.
This research will be presented in October at the International Symposium of Robotics Research in San Francisco. It will also be detailed in an upcoming issue of the Journal of Microelectrochemical Systems.
- The World's Smallest Motor
- Bragging Rights: The Smallest Fish Ever
- The World's Smallest Refrigerator
- U.S. Losing Robotics Edge
Small Stuff
Micromachines
Microscopic Art
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus