Hitachi Creates Brain 'Remote Control'
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
HATOYAMA, Japan (AP) -- Forget the clicker: A new technology in Japan could let you control electronic devices without lifting a finger simply by reading brain activity.
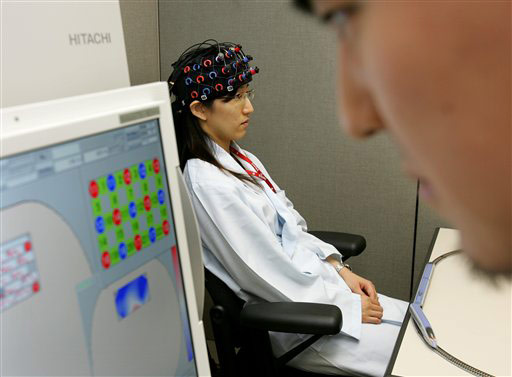
The “brain-machine interface'' developed by Hitachi Inc. analyzes slight changes in the brain's blood flow and translates brain motion into electric signals.
A cap connects by optical fibers to a mapping device, which links, in turn, to a toy train set via a control computer and motor during one recent demonstration at Hitachi's Advanced Research Laboratory in Hatoyama, just outside Tokyo.
“Take a deep breath and relax,'' said Kei Utsugi, a researcher, while demonstrating the device on Wednesday.
At his prompting, a reporter did simple calculations in her head, and the train sprang forward -- apparently indicating activity in the brain's frontal cortex, which handles problem solving.
Activating that region of the brain -- by doing sums or singing a song -- is what makes the train run, according to Utsugi. When one stops the calculations, the train stops, too.
Underlying Hitachi's brain-machine interface is a technology called optical topography, which sends a small amount of infrared light through the brain's surface to map out changes in blood flow.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Although brain-machine interface technology has traditionally focused on medical uses, makers like Hitachi and Japanese automaker Honda Motor Co. have been racing to refine the technology for commercial application.
Hitachi's scientists are set to develop a brain TV remote controller letting users turn a TV on and off or switch channels by only thinking.
Honda, whose interface monitors the brain with an MRI machine like those used in hospitals, is keen to apply the interface to intelligent, next-generation automobiles.
The technology could one day replace remote controls and keyboards and perhaps help disabled people operate electric wheelchairs, beds or artificial limbs.
Initial uses would be helping people with paralyzing diseases communicate even after they have lost all control of their muscles.
Since 2005, Hitachi has sold a device based on optical topography that monitors brain activity in paralyzed patients so they can answer simple questions -- for example, by doing mental calculations to indicate “yes'' or thinking of nothing in particular to indicate “no.''
“We are thinking of various kinds of applications,'' project leader Hideaki Koizumi said. “Locked-in patients can speak to other people by using this kind of brain machine interface.''
A key advantage to Hitachi's technology is that sensors don't have to physically enter the brain. Earlier technologies developed by U.S. companies like Neural Signals Inc. required implanting a chip under the skull.
Still, major stumbling blocks remain.
Size is one issue, though Hitachi has developed a prototype compact headband and mapping machine that together weigh only about two pounds.
Another would be to tweak the interface to more accurately pick up on the correct signals while ignoring background brain activity.
Any brain-machine interface device for widespread use would be “a little further down the road,'' Koizumi said.
He added, however, that the technology is entertaining in itself and could easily be applied to toys.
“It's really fun to move a model train just by thinking,'' he said.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










