Facts About Antimony
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
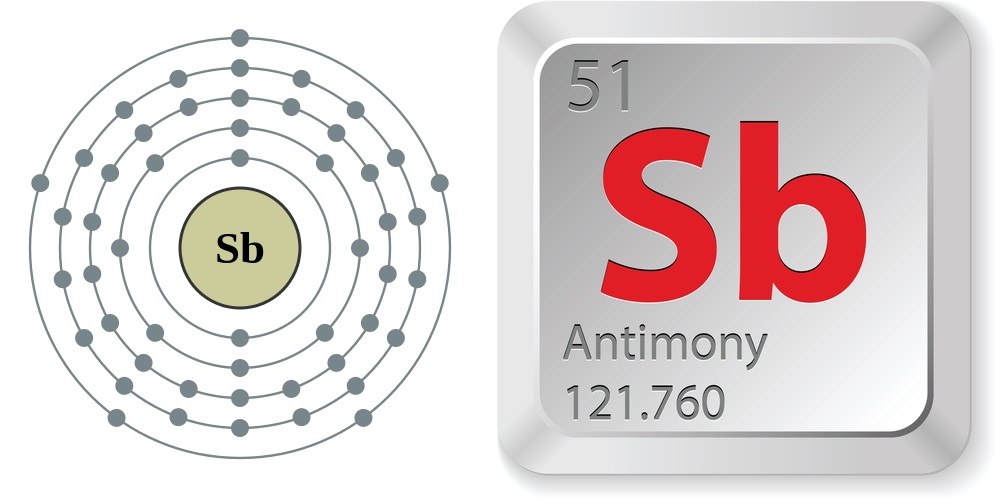
| Atomic Number: 51 Atomic Symbol: Sb Atomic Weight: 121.760 | Melting Point: 1,167.13 F (630.63 C) Boiling Point: 2,888.6 F (1,587 C) |
Word origin: Antimony was named after the Greek words anti and monos to mean “a metal not found alone.” The chemical symbol, Sb, comes from the element's historical name, stibium.
Discovery: Antimony was a known metal in the 17th century and was likely used even earlier.
Properties of antimony
Antimony is a silvery, lustrous gray metal. It is in the metalloid group of elements. It is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. The metal and its compound forms can be toxic. [See Periodic Table of the Elements]
Sources of antimony
Antimony is a rare element but can sometimes be found naturally. However, it’s mostly in the form of its sulfide stibnite.
Uses of antimony
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The pure form of antimony is used to make certain types of semiconductor devices, such as diodes and infrared detectors. An alloy of lead and antimony is used in batteries, low friction metals, small arms and tracer bullets, cable sheathing as well as other products. Other compounds of antimony are also used to make paints, glass, pottery and ceramics.
(Source: Los Alamos National Laboratory)
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus