Diagram of the Human Integumentary System (Infographic)
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
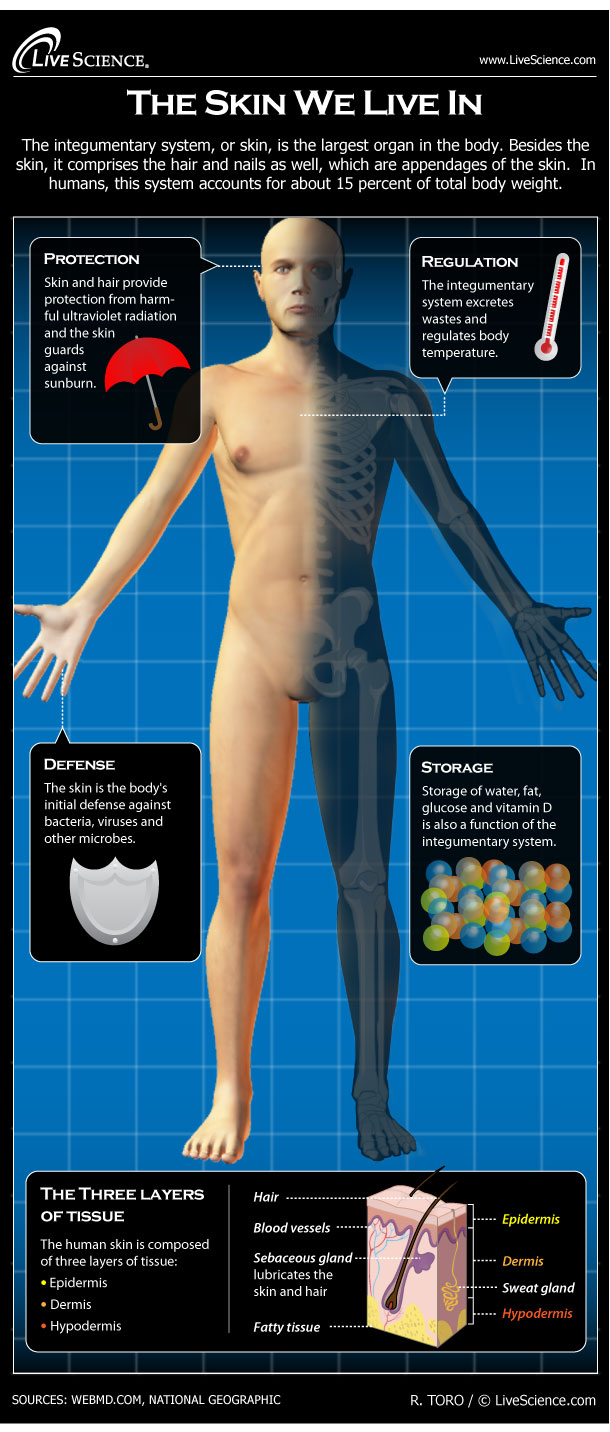
The integumentary system, or skin, is the largest organ in the body. Besides the skin, it comprises the hair and nails as well, which are appendages of the skin. In humans, this system accounts for about 15 percent of total body weight. Skin and hair provide protection from harmful ultraviolet radiation and the skin guards against sunburn. It also waterproofs, cushions and protects the body from infection. The integumentary system excretes wastes and regulates body temperature. The skin is the body's initial defense against bacteria, viruses and other microbes. Human skin color is determined by the interaction of melanin, carotene and hemoglobin.
((VideoProviderTag|jwplayer|Ams60mDN|100%|100%))
Storage of water, fat, glucose and vitamin D is also a function of the integumentary system. The human skin is composed of three layers of tissue: • Epidermis: the top layer of skin. It does not contain blood vessels. The epidermis is about one-tenth of a millimeter thick. • Dermis: the middle layer of skin is composed of the Papillary layer and the Reticular layer. These layers provide elasticity. • Hypodermis: the deepest layer of skin helps insulate the body and cushion internal organs. The hypodermis is composed of adipose tissue that stores excess energy as fat.
Related:
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










