Creatures Reunite After Ancient Divorce
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
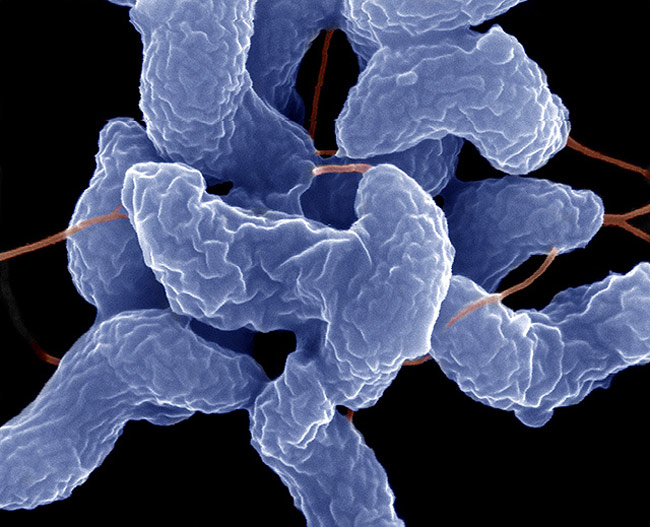
Like lovers reunited after a cruel world tore them apart, two species of bacteria have found each other in the guts of domestic livestock and are becoming one.
Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli, as the intestinal organisms are known, aren't just consummating their microscopic love by exchanging genes — they're merging into a single species, scientists say.
The researchers think the marriage of the creatures represents a profound example of how people can affect evolution.
"What we're seeing here is hybridization, and it's only been recently acknowledged as an important part of evolution," said Samuel Sheppard, an evolutionary microbiologist at Oxford University in the United Kingdom. "It's really exciting stuff."
Sheppard and his colleagues detail their findings today in an advance online version of the April 11 issue of the journal Science. The team reached their conclusions by analyzing DNA, or genetic information, from the bacteria found inside both wild and farm animals.
Ancient split
C. jejuni and C. coli are thought to have shared a common ancestor, or parent, in the ancient past. When the microbial descendent split up and evolutionary pressures stepped in, two new species began to take shape and fill different niches within the guts of wild chickens, pigs and other animals.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Although the definition of a species is one of the most hotly debated topics among biologists, Sheppard said the two microbes are strikingly different, despite sharing about 85 percent of their genetic code.
"Chimpanzees and humans are known to be about 98 percent genetically similar, so the bacteria's converging toward becoming a single species, as we think, is pretty impressive," Sheppard told LiveScience. "That's a big genetic gulf to leap. Maybe like a lobster mating with a fly."
Sheppard said the bacteria likely began reversing their growing divergence, or genetic separation, when human agriculture came along.
Under pressure
He thinks the bacterial merger has accelerated in recent years, as the world has become more industrialized and the demand for food has prompted crowded farms.
"We're now really packing a bunch of livestock together, and so the bacterial environment is changed," Sheppard said.
He noted that chickens often mistake their feathered friends' poop for food — and that creates a consistent, rapid way of mixing of two intestinal organisms that were once ecologically separated. "By altering their environment, we're altering the bacteria, their very being," he said.
Sheppard explained that bacteria try and most often fail to trade genes, but when two descendants from the same parent meet and then mate, he said, the chance of successfully trading genes gets a big boost. He couldn't say when the two life forms might finally merge, but thinks evolutionary pressures created by humans will surely speed things up.
"The big message here is that we're directly messing with species by messing with their natural environments," Sheppard said. "This is a strong, thumping example where man's influence can have a profound effect on evolution."
The team's work was funded by the UK Department of Environment, Food and Rural Affairs and the Food Standards Agency.
- Gallery: Microscopic Images as Art
- Greatest Mysteries: What Drives Evolution?
- Image Gallery: Darwin on Display
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










