Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Editor's Note: This story was updated at 10:15 a.m. on Nov. 18
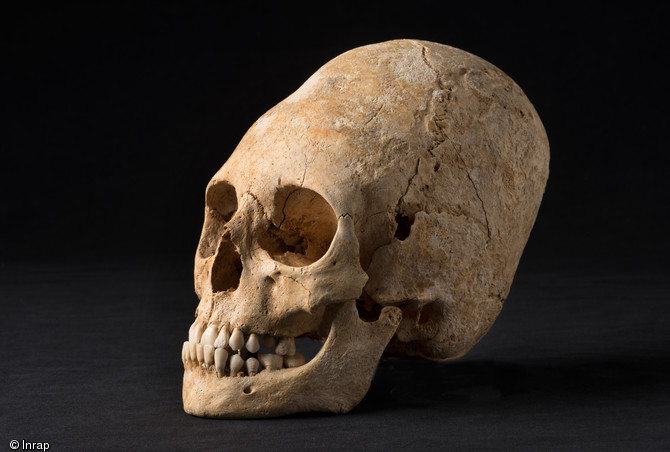
The skeleton of an ancient aristocratic woman whose head was warped into a deformed, pointy shape has been unearthed in a necropolis in France.
The necropolis, found in the Alsace region of France, contains 38 tombs that span more than 4,000 years, from the Stone Age to the Dark Ages.
Rich valley
The Obernai region where the remains were found contains a river and rich, fertile soil, which has attracted people for thousands of years, Philippe Lefranc, an archaeologist who excavated the Stone Age burials, wrote in an email.
Archaeologists first found the tombs in 2011 while doing a preliminary excavation of the area prior to the start of a big industrial building project. This year, Lefranc and his colleagues went back to do a more in-depth excavation.
They found that the tombs were well preserved by the limestone rock in which they were buried. One of the burials contained 20 tombs of men, women and children. [See Images of the Tombs & Deformed Skull]
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"The corpses are lying on their backs, with outstretched legs and heads turned westwards," Lefranc said.
The tombs, which date to between 4900 B.C. and 4750 B.C., also contained a few stone vases and tools, along with ornaments such as mother-of-pearl elbow bracelets and collars. The small group may have been a family from a Neolithic farming and animal-herding culture that lived in long houses and buried their dead in cemeteries, Lefranc said.
Eastern transplants
In the second burial, which was in a separate area, they found 18 tombs from either the late Roman period or the early Dark Ages, about 1,650 years ago. One of the tombs held a woman, likely an aristocrat, who had a deformed, flattened forehead.
"The deformation of the skull with the help of bandages (narrow strips of cloth) and small boards is a practice coming from central Asia," Lefranc said in an email. "It was popularized by the Huns and adopted by many German people."
In those times, the deformed, alienlike skull was a privilege reserved for the aristocracy.
"In France, Germany and eastern Europe, these deformed skulls appear in tombs rich in objects," Lefranc said.
The wealthy lady's tomb also contained gold pins, belts known as chatelaines, pearls, a comb made of a stag antler, and a bronze mirror that likely came from the Caucasus region or central Asia, he said.
The team speculates that the 1,650-year-old graves held mercenary soldiers from the East and their families, who were employed by the Roman Army during the waning days of the Roman empire.
Editor's Note: This story was updated to clarify that the skull was not deformed after death, and that the Caucasus Region is not part of Central Asia.
Follow Tia Ghose on Twitter and Google+. Follow LiveScience @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on LiveScience.

Tia is the editor-in-chief (premium) and was formerly managing editor and senior writer for Live Science. Her work has appeared in Scientific American, Wired.com, Science News and other outlets. She holds a master's degree in bioengineering from the University of Washington, a graduate certificate in science writing from UC Santa Cruz and a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Texas at Austin. Tia was part of a team at the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel that published the Empty Cradles series on preterm births, which won multiple awards, including the 2012 Casey Medal for Meritorious Journalism.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus