Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
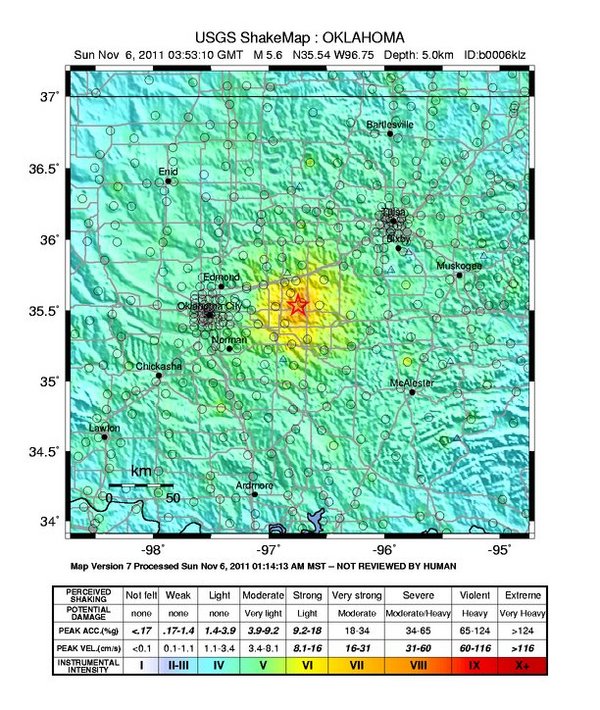
The largest-ever recorded quake in Oklahoma was caused by the injection of wastewater, a byproduct of oil extraction, into the ground, new research confirms.
On Nov. 6, 2011, a series of earthquakes, including a 5.6-magnitude temblor, struck the rural town of Prague, about 37 miles (60 kilometers) east of Oklahoma City, crumbling homes in the area and damaging a federal highway. The quake could be felt as far away as Milwaukee.
"We don't normally feel earthquakes, it was shocking," said study co-author Katie Keranen, a seismologist at Oklahoma University.
Now, a new study published March 26 in the journal Geology confirms that wastewater injected into the ground after oil extraction caused the quake. The quake is the largest wastewater-induced earthquake ever recorded. The wastewater was from traditional drilling, not the controversial hydraulic fracturing method.
Ever since wastewater injection was linked to a series of small quakes around Denver, Colo., in the 1960s, scientists have known that oil extraction could trigger temblors. When oil is extracted from the ground, lots of water, dubbed "wastewater," comes up as well. So oil companies sometimes pump the water back into the well, where it fills porous spaces within the rocks, Keranen said.
"It's almost a lubrication, it can push the fault apart," Keranen told LiveScience. "When you do that you lower the stress that's holding a fault together and you can cause it to slip."
But in the past, scientist thought the resulting quakes would be fairly benign: most of these triggered temblors are typically a 3 or 4 on the moment magnitude scale, Keranen said.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
In theory, however, these man-made earthquakes could get even bigger — an especially worrisome possibility if they occur near population centers. [Image Gallery: Deadly Earthquakes]
"We don't know what the maximum size of earthquakes could be that we could trigger from disposal," Keranen said.
Whether or not an area is prone to such tremblers depends on the permeability of the local rock: If water can't seep through the rock easily, meaning it's not very permeable, pressure builds up and makes an earthquake more likely. Earthquake risk also depends on the presence and angle of faults in relation to the water-injection site.
Though the process that caused the Oklahoma earthquake didn't involve hydraulic fracturing, fracking often involves injecting spent water into the ground, which carries the same risks. In fracking, water, sand and other substances are injected into a well under high pressure in order to fracture the rock, creating fissures that help natural gas flow out.
There hasn't been much oil extraction on the East Coast, but as fracking takes off in areas like Pennsylvania, the risk of big quakes in the region needs to be considered, Keranen said.
Editor's Note: This article has been corrected to reflect the fact that earthquake strength is now measured on the moment magnitude scale, not the Richter scale.
Follow Tia Ghose on Twitter @tiaghose. Follow LiveScience @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on LiveScience.com.

Tia is the editor-in-chief (premium) and was formerly managing editor and senior writer for Live Science. Her work has appeared in Scientific American, Wired.com, Science News and other outlets. She holds a master's degree in bioengineering from the University of Washington, a graduate certificate in science writing from UC Santa Cruz and a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Texas at Austin. Tia was part of a team at the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel that published the Empty Cradles series on preterm births, which won multiple awards, including the 2012 Casey Medal for Meritorious Journalism.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus