Fire Burns Differently in Space, Space Station Experiment Shows
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
NASA is playing with fire on the International Space Station — literally.
Since March 2009, the space agency's Flame Extinguishment Experiment, or FLEX, has conducted more than 200 tests to better understand how fire behaves in microgravity, which is still not well understood. The research could lead to improved fire suppression systems aboard future spaceships, and it could also have practical benefits here on Earth, scientists said.
"We hope to gain a better knowledge of droplet burning, improved spacecraft fire safety and ideas for more efficient utilization of liquid fuels on Earth," project leader Forman Williams, of the University of California, San Diego, said in a statement. "The experiments will be used to verify numerical models that calculate droplet burning under different conditions."
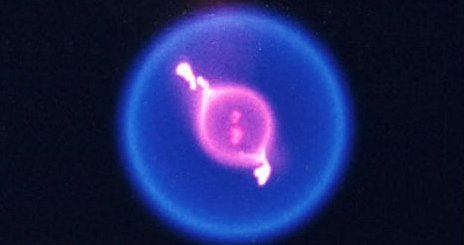
Fire is a different beast in space than it is on the ground. When flames burn on Earth, heated gases rise from the fire, drawing oxygen in and pushing combustion products out. In microgravity, hot gases don't rise. So an entirely different process, called molecular diffusion, drives flame behavior.
"In space, molecular diffusion draws oxygen to the flame and combustion products away from the flame at a rate 100 times slower than the buoyant flow on Earth," said Dan Dietrich, FLEX project scientist at NASA's Glenn Research Center in Ohio.
Space flames can also burn at a lower temperature and with less oxygen than fires on Earth. As a result, the material used to put out space fires must be more concentrated, researchers said.
To study fires in space, FLEX researchers ignite a small drop of heptane or methanol fuel in a special experiment rack aboard the space station. As the droplet burns, a spherical flame engulfs it, and cameras record the whole process.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
So far, researchers have observed some unexpected phenomena.
"Thus far, the most surprising thing we've observed is continued apparent burning of heptane droplets after flame extinction under certain conditions," Williams said. "Currently, this is entirely unexplained."
Williams anticipates many other interesting discoveries to come from the FLEX project. "There are many currently unknown things about combustion processes waiting to be revealed by future scientific experiments," he said.
This story was provided by SPACE.com, a sister site to LiveScience. Follow SPACE.com for the latest in space science and exploration news on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus












