The Life of a Baby Tardigrade
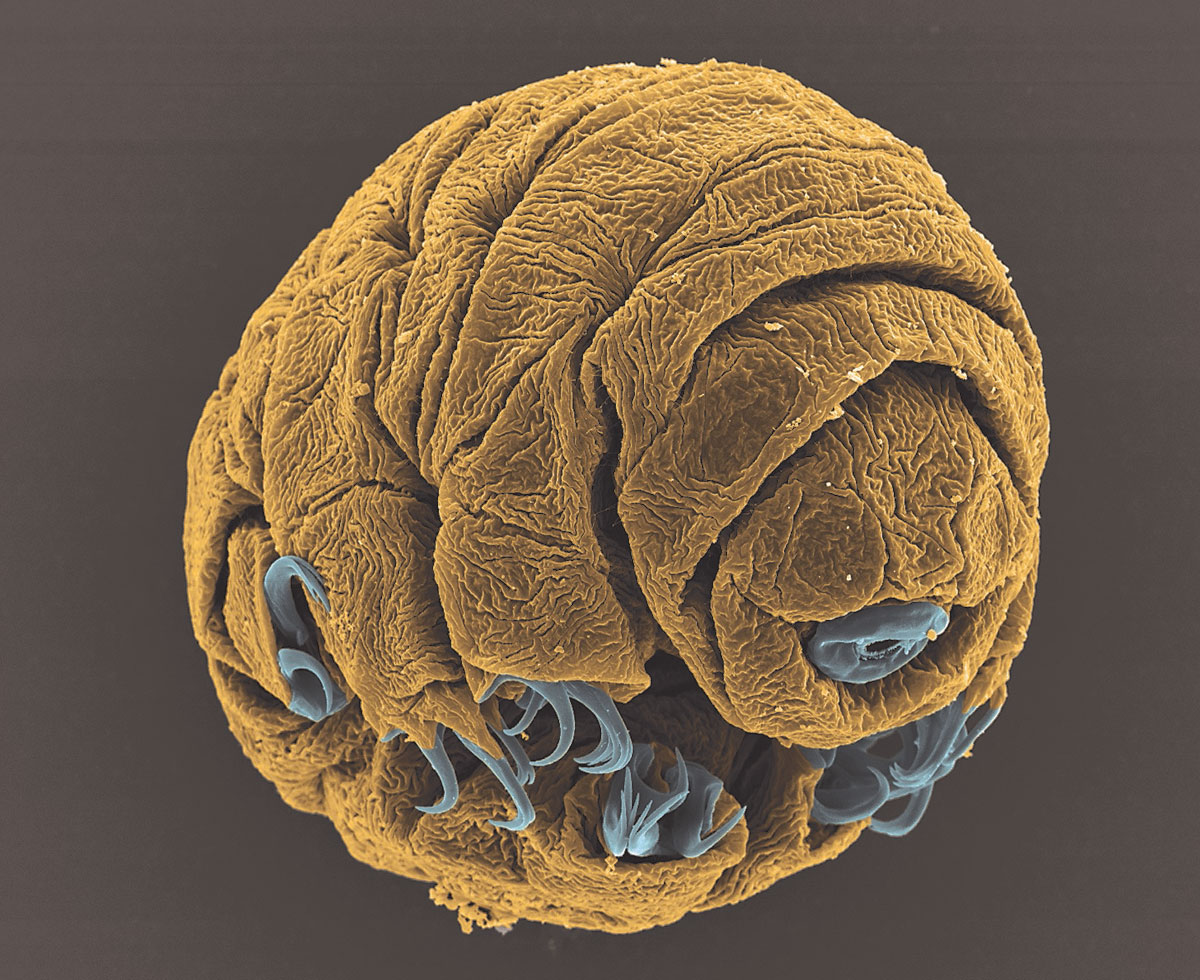
It started as a speck of a speck, a bundle of nerves and immature tissues curled up inside an egg, bunched up against its siblings. The small clutch of embryonic water bears was immobile, silent, unseeing and possibly unfeeling. Locked away inside their mother's ovaries, they waited to be born.
One of nearly 1,000 species of hardy tardigrades, the Hypsibius dijardini embryo pictured above may have been the product of a sexless act of reproduction, its mother squirting her genetic material directly into eggs without bothering with any of the handful of males of her species for fertilization, according to the Encyclopedia of Life. That reproductive ability (called parthenogenesis), a genetic heritage largely unchanged through the generations, was her birthright and one she would likely have passed down to her children.
Tardigrades are among the hardiest animals on planet Earth, resistant to heat and cold, radiation and extreme dehydration. This H. dijardini embryo would have eventually emerged from its egg fully formed, and as ready to take on those horrors as her mother had been. Tardigrades, as researchers studying them way back in 1938 for a paper in American Midland Naturalist discovered, have no childhood. They pierce through their eggs small, but fully formed.
The embryo captured by photographer Vladimir Gross is 50 hours old, nearing readiness to emerge. All of her limbs, mouth parts and most of her organs developed over the course of those hours, before and after her mother squeezed her out into the world. (Gross snagged runner-up in the Royal Society Publishing Photography Competition's Microimaging category.)
When the egg-enclosed baby was ready, the 1938 researchers discovered, she would have driven her mouthparts into the wall of her egg, carved a small hole, and wriggled through it into her new life. Her organs, streamlined for digestion and reproduction, would already be churning. She wouldn't swim through her wet world, but would instead get around on her eight stubby, clawed legs.
If she were in the wild, she would have gotten to work munching on the wet mosses and small plants where she would have made her home. And with all the food she would take in, she would grow. Over the course of her lifetime, she could expect to cast off her outer skin several times to make room for her growing body, according to a study published in 2015 in the journal Polar Biology.
According to The Encyclopedia of Life, she would have been ready to give birth to her first batch of eggs within two weeks of her own birth — between one and 30 tardigrade embryos, depending on how much food she'd had available. Some species of tardigrade lay eggs inside their cast-off skins. Some wait for males to fertilize them, but not H. dijardini. Except in unusual circumstances, which scientists still do not fully understand, she would create eggs with near-exact copies of her genetic code, just like her mother had with her.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
She could expect to birth several more clutches of eggs in her life, which would last another 70 or so days — unless, of course, she were frozen or dehydrated, in which case she might live on in a dormant state for months, years, decades or longer, until the world was ready for her again. Then she would wake up, and get right back to the business of being a water bear.
Originally published on Live Science.

