In Images: The Insect Family Tree
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
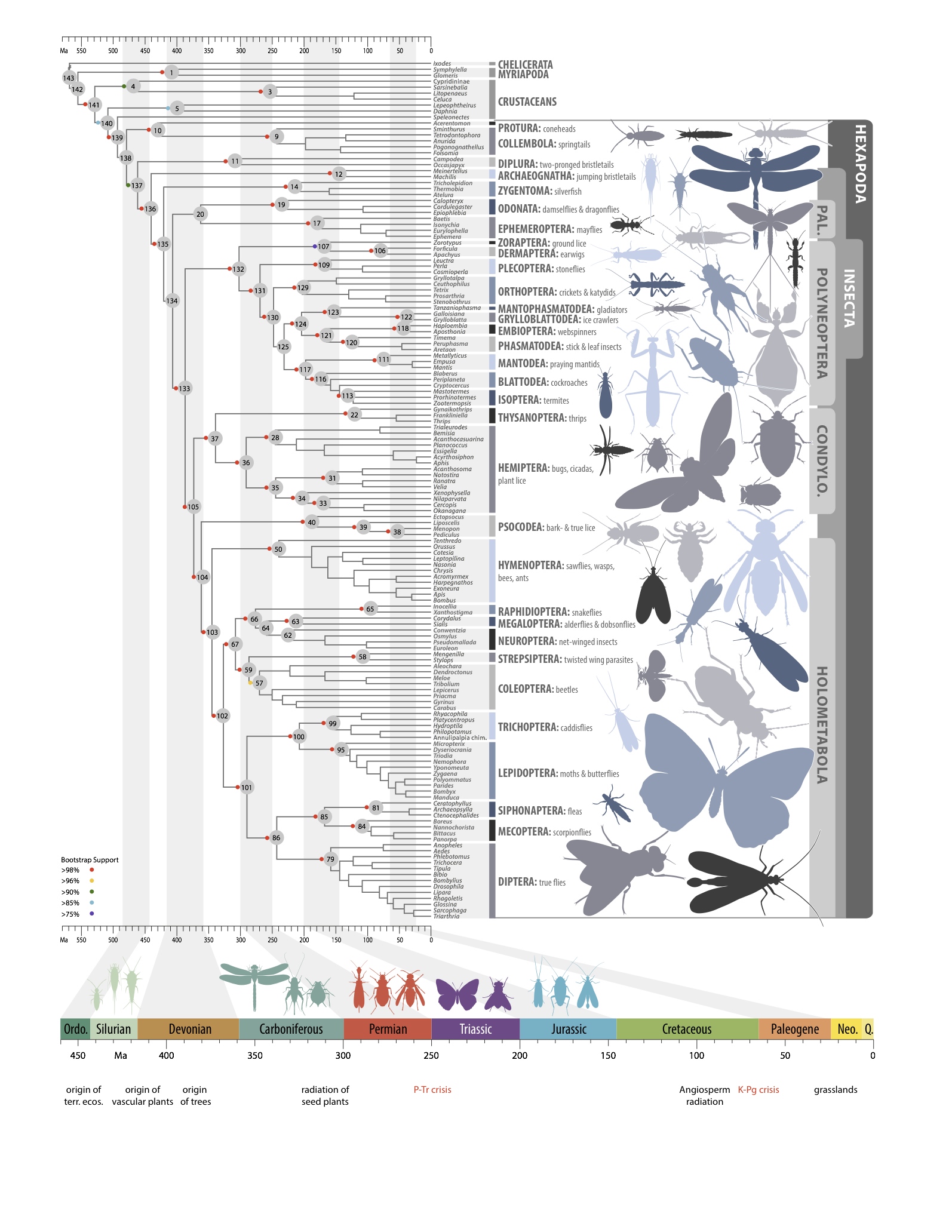
Researchers from around the world recently came together to answer a question that has been bugging the scientific community for some time: How old are insects? Using 1,478 protein-coding genes from all of the major insect orders, the researchers constructed an enormous dataset that detailed the genetic makeup of all the major insect groups in existence today. Then they compared this dataset to existing fossil record for insects to pinpoint when different species evolved. The result is what scientists call a phylogenetic tree, and it's the most comprehensive guide to insect evolution ever created: [Read more about the insect evolution study]
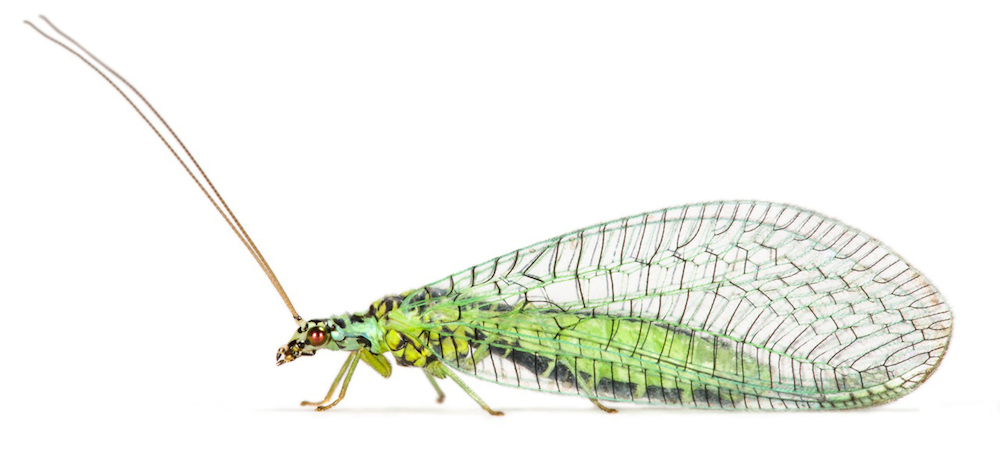
Neuroptera
The green lacewing (Chrysopa perla) pictured here belongs to the order Neuroptera, which is comprised of insects that have complex vein patterns in their wings, giving them a lace-like appearance. Also known as net-wings, these insects undergo complete metamorphism, or holometabolism, during their lifecycle. The earliest members of the Neuroptera order evolved between 200 and 250 million years ago, during the Triassic period, according to the researchers. (Credit: Dr. Oliver Niehuis, ZFMK, Bonn)
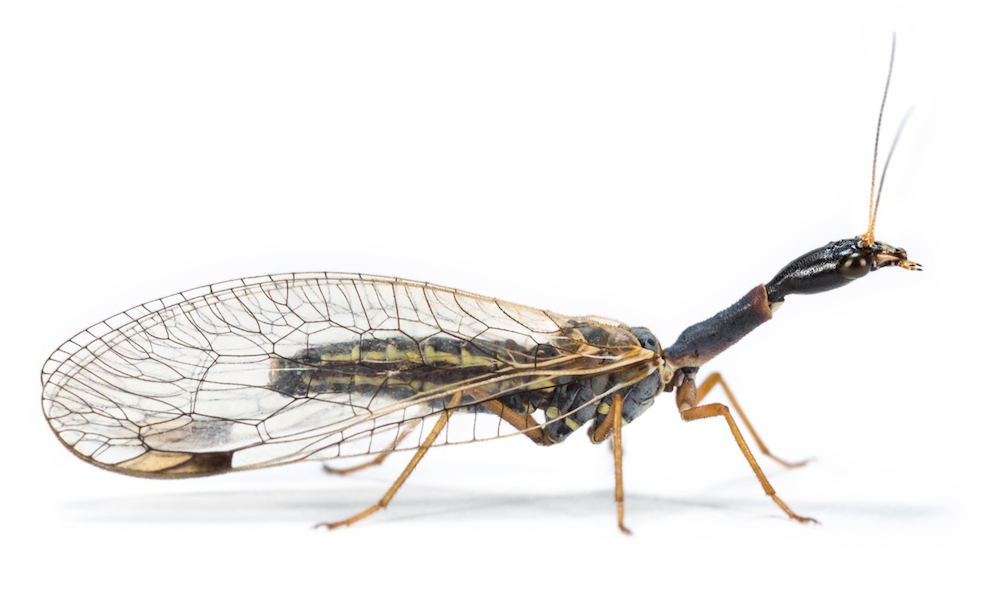
Article continues belowRaphidioptera
This snakefly (Dichrostigma flavipes) is one of over 200 species belonging to the order Raphidioptera. Snakeflies are closely related to species in the order Neuroptera, though they evolved slightly earlier, 250 to 300 million years ago, during the Permian period, according to the researchers. (Credit: Dr. Oliver Niehuis, ZFMK, Bonn)
Coleoptera
The red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum) is a member of the order Coleoptera. The family this beetle belongs to, Tribolium, evolved about 100 million years ago, during the Crustaceous period, the researchers found. (Credit: Dr. Oliver Niehuis, ZFMK, Bonn)
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Hymenoptera
This gold wasp (Hedychrum nobile) belongs to the order Hymenoptera, which also includes bees and ants. While the acenstors of today's wasps evolved some 200 to 250 million years ago during the Triassic period, the diversification of this order did not kick off until 100 million years later, during the Cretaceous period, the researchers discovered. (Credit: Dr. Oliver Niehuis, ZFMK, Bonn)
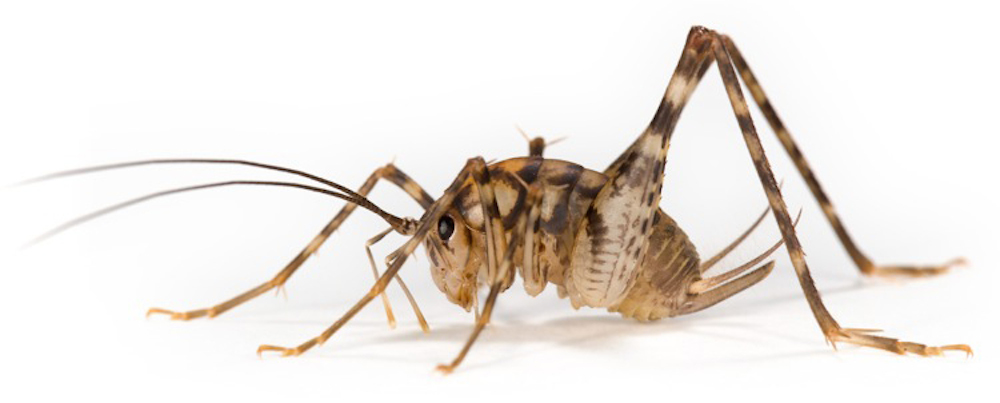
Orthoptera
The crickets and katydids that make up the order Orthoptera first came on the scene over 300 million years ago, during the Carboniferous period, according to the researchers. Pictured here is a greenhouse camel cricket (Diestrammena asynamora). (Credit: Dr. Oliver Niehuis, ZFMK, Bonn)
Plecoptera
This stonefly (Perla marginata) belongs to the order Plecoptera. Its ancestors evolved during the Devonian period, about 400 million years ago, the researchers found. (Credit: Dr. Oliver Niehuis, ZFMK, Bonn)
Insect family tree
More than 100 international scientists helped construct this comprehensive phylogenetic tree. The enormous molecular dataset used in the project included genetic information from 144 carefully chosen insect species. (Credit: 1KITE, 1K Insect Transcriptome Evolution)
Follow Elizabeth Palermo @techEpalermo. Follow Live Science @livescience, Facebook & Google+.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus