Why Has It Been So Cold This Spring?

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
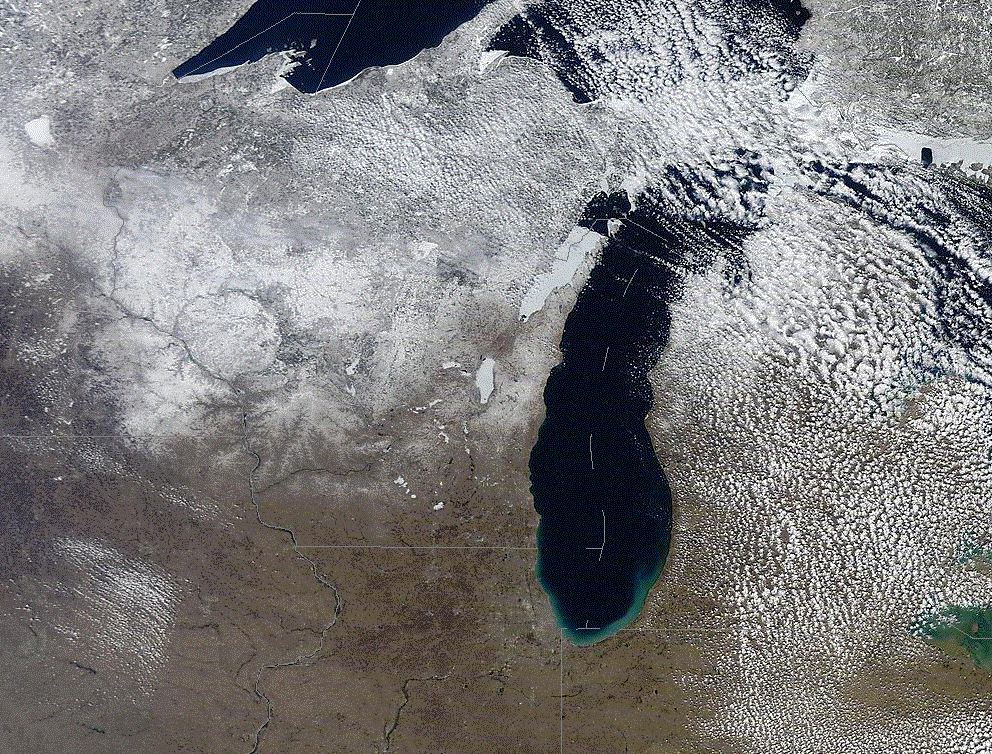
Although spring has arrived, it may not feel that way for many in the United States and Canada who have had to put up with unusually cold temperatures.
Last month was a chilly one, ranking as the second-coldest March in the continental United States since 2000, according to the National Weather Service (NWS). The average temperature across the United States this March was also 13 degrees Fahrenheit (7.2 degrees Celsius) lower than in March 2012, and a late-winter blizzard broke snowfall records in many areas.
So, why has it been so cold?
The culprit is a stubborn, stationary mass of warm air over Greenland and the North Atlantic that has blocked the normal flow of air from west to east and south to north, said Greg Carbin, a meteorologist with the NWS' Storm Prediction Center. This flow of air, known as the jet stream, usually brings more warm air from the South as the Northern Hemisphere begins to heat up in the spring.
Obstinate air masses
This March, however, the mass of warm air — a high-pressure system that repels incoming weather systems — has redirected air currents and created a pattern of winds coming from the Northwest, blasting the eastern two-thirds of the United States with Arctic air, Carbin said.
"This obstinate mass of warm air over Greenland has redirected air currents like a rock in a stream," Carbin said.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
However, the spring season hasn't been cold everywhere. In fact, the southwestern United States has been warmer than average, as the region has been unaffected by the blocking system in the North Atlantic, said Bob Henson, a meteorologist and science writer with the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colo.
Due, in part, to the cold, there have been fewer than 20 tornadoes in the United States this March, Carbin said. On average, March will see 76 twisters across the United States. Tornadoes depend on warm, moist air, which was scarce this past March, Carbin added. [Infographic: Tornado! How, When & Where Twisters Form]
Climate change?
Some research has suggested a link between a retreat of Arctic sea ice in a warming world and these high-pressure blocking systems, Carbin said.
As cold as March seemed, it was only the 59th coldest March since 1871, according to the Washington Post's Capital Weather Gang blog. In other words, the month's frigid temperatures do not disprove the observation that the world is heating up — and climate change could be playing a role in the development of the high-pressure system that has fueled the unusually cool month, Carbin said.
This March’s temperatures contrasted sharply with those seen in March 2012, which was the warmest March on record. In 2012, a mass of hot air developed over the middle of the country, causing unusually high temperatures and fueling an outbreak of tornadoes.
"They were almost like — no pun intended — polar opposites," Henson said.
The cold will not stick around forever, though, Carbin said. the high-pressure blocking system over Greenland is already beginning to weaken and looks likely to dissipate by the beginning of next week (April 7). This will bring temperatures back into the average range, he said — which means it may finally start to feel like spring.
Email Douglas Main or follow him @Douglas_Main. Follow us @OAPlanet, Facebook or Google+. Original article on LiveScience's OurAmazingPlanet.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus