Robot Legs Mimic How Babies Walk

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
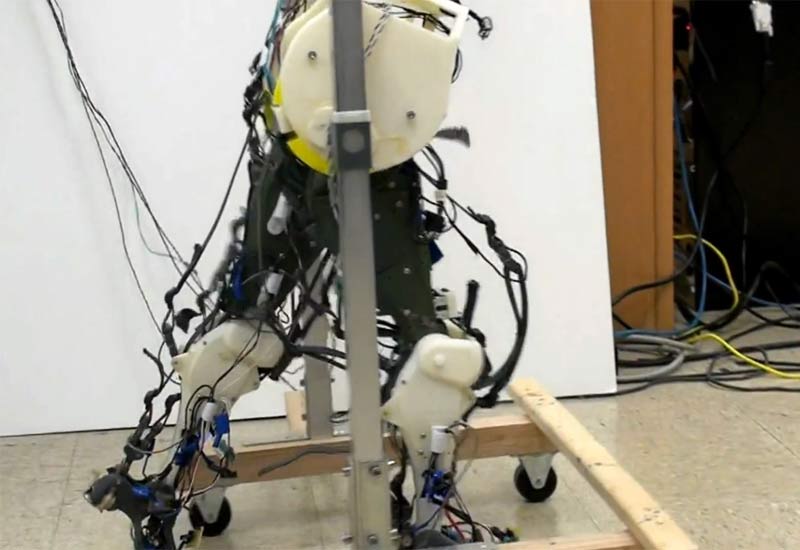
The first pair of biologically accurate robot legs can walk like clumsy human babies placed on a treadmill — placing one foot in front of the other with surprising confidence.
The robot legs work despite having just a simple nervous system to control the hips. That is because the lower legs' reflex responses take over to complete the walking motion — a possible explanation for how human babies can walk on treadmills without an adult's complete sense of coordination and balance.
"Interestingly, we were able to produce a walking gait, without balance, which mimicked human walking with only a simple half-centre controlling the hips and a set of reflex responses controlling the lower limb," said Theresa Klein, a Ph.D. student at the University of Arizona.
That "half-centre" represents a neural network in the human spinal cord that can send out muscle signals. The simplest neural network, the half-centre, fires off alternating signals to create the rhythm of walking.
Past walking robots have never tried including that nervous system feedback and the biological reflexes available to humans. The University of Arizona researchers built their robot with a neural controller — the half-centre — and leg sensors that are able to detect the weight of each step and report back to the neural controller.
The weight sensors join together with the robot's Kevlar straps that mimic leg muscles — another fairly unique aspect of the walking robot. Mechanical control comes from four motors in the hip segment, three motors in the thigh and just one motor in the calf.
Such baby steps for robot walking could lead to better understanding of how human babies and patients with spinal cord injuries learn to walk. But they could also improve bipedal humanoid robots that the U.S. military wants on tomorrow's battlefields, or that rescue workers could deploy in disaster zones.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The research is detailed in the July 6 issue of the Journal of Neural Engineering.
This story was provided by InnovationNewsDaily, a sister site to LiveScience. Follow InnovationNewsDaily on Twitter @News_Innovation, or on Facebook.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus