Inventors: Solar Dish Could Revolutionize Energy Production

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
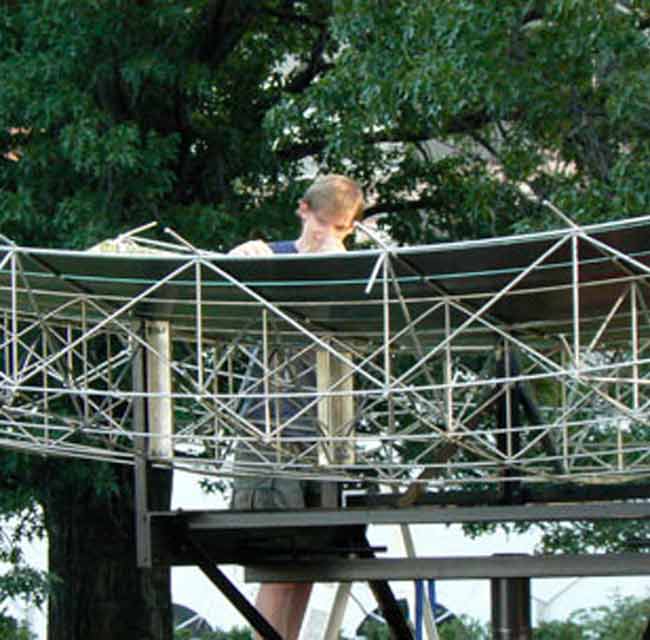
A new type of solar energy collector concentrates the sun into a beam that could melt steel. Researchers say the device could revolutionize global energy production.
The prototype is a 12-foot-wide mirrored dish was made from a lightweight frame of thin, inexpensive aluminum tubing and strips of mirror. It concentrates sunlight by a factor of 1,000 to produce steam.
"This is actually the most efficient solar collector in existence," said Doug Wood, an inventor based in Washington state who patented key parts of the dish's design — the rights to which he has signed over to a team of students at MIT.
To test the prototype this week, MIT mechanical engineering Spencer Ahrens put a plank of wood in the beam an generated an almost instant puff of smoke.
The thing does more than burn wood, of course. At the end of a 12-foot aluminum tube rising from the center of the dish is a black-painted coil of tubing that has water running through it. When the dish is pointing directly at the sun, the water in the coil flashes immediately into steam.
Ahrens and his teammates have started a company, RawSolar, to hopefully mass produce the dishes. They could be set up in huge arrays to provide steam for industrial processing, or for heating or cooling buildings, as well as to hook up to steam turbines and generate electricity, according to an MIT statement. Once in mass production, such arrays should pay for themselves within two years or so with the energy they produce, the students figure.
Wood, the inventor, said the students built the dish and improved on his design.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"They really have simplified this and made it user-friendly, so anybody can build it," he said.
Wood said small dishes work best because it requires much less support structure and costs less for a given amount of collection area.
"I've looked for years at a variety of solar approaches, and this is the cheapest I've seen," said MIT Sloan School of Management lecturer David Pelly, in whose class the project first took shape last fall. "And the key thing in scaling it globally is that all of the materials are inexpensive and accessible anywhere in the world."
- Video: The Solar Collector Explained
- More Solar: How Satellites Could Power the Future
- Top 10 Disruptive Technologies
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus