Gigantic Apes Coexisted with Early Humans, Study Finds
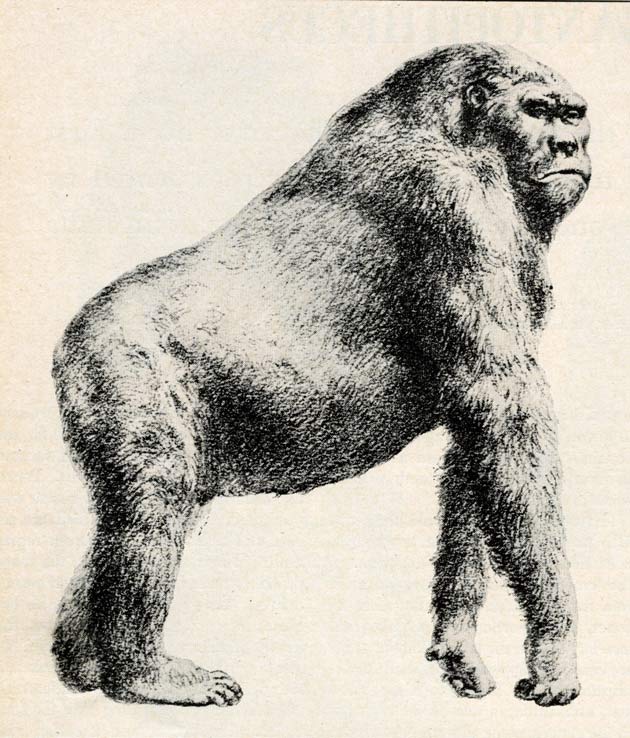
A gigantic ape standing 10 feet tall and weighing up to 1,200 pounds lived alongside humans for over a million years, according to a new study.
Fortunately for the early humans, the huge primate's diet consisted mainly of bamboo.
Scientists have known about Gigantopithecus blackii since the accidental discovery of some of its teeth on sale in a Hong Kong pharmacy about 80 years ago. While the idea of a giant ape piqued the interest of scientists – and bigfoot hunters – around the world, it was unclear how long ago this beast went extinct.
Precise dating
Now Jack Rink, a geochronologist at McMaster University in Ontario, has used a high-precision absolute-dating method to determine that this ape – the largest primate ever – roamed Southeast Asia for nearly a million years before the species died out 100,000 years ago during the Pleistocene period. By this time, humans had existed for a million years.
"A missing piece of the puzzle has always focused on pin-pointing when Gigantopithecus existed," Rink said. "This is a primate that co-existed with humans at a time when humans were undergoing a major evolutionary change. Guangxhi province in southern China, where some of the Gigantopithecus fossils were found, is the same region where some believe the modern human race originated."
Since the original discovery, scientists have been able to piece together a description of Gigantopithecus using just a handful of teeth and a set of jawbones. It may not be much, but the unusually large size of these teeth indicates they belonged to one big ape.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"The size of these specimens – the crown of the molar, for instance, measures about an inch across – helped us understand the extraordinary size of the primate," Rink said.
What happened?
Humans may have helped destroy the ape.
Further studies of the teeth revealed that the ape was an herbivore, and bamboo was probably its favorite meal. Some scientists believe that an appetite focused on bamboo combined with increasing competition from more nimble humans eventually led to the extinction of Gigantopithecus.
While most scientists agree that Gigantopithecus died out long ago, some people – Bigfoot, Sasquatch, and Yeti enthusiasts in particular – believe that this ape is the source of tales of giant, hairy beasts roaming the woods. These claims are not considered credible by mainstream scientists. There have been cases in which creatures are first known first by their fossil remains and later found living, such as the coelacanth – a type of fish thought to have died out millions of years ago until it was discovered swimming off the coast of Africa in 1938.
Researchers do not have a full skeleton for Gigantopithecus. But they can fill in the gaps and estimate its size and shape by comparing it to other primates – those that came before it, coexisted with it, and also modern apes. Currently, scientists are debating over how Gigantopithecus got around – was it bipedal or did it use its arms to help it walk, like modern chimpanzees and orangutans? The only way to answer this is to collect more bones.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus





