Ruins of Lost City May Lurk Deep in Honduras Rain Forest
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
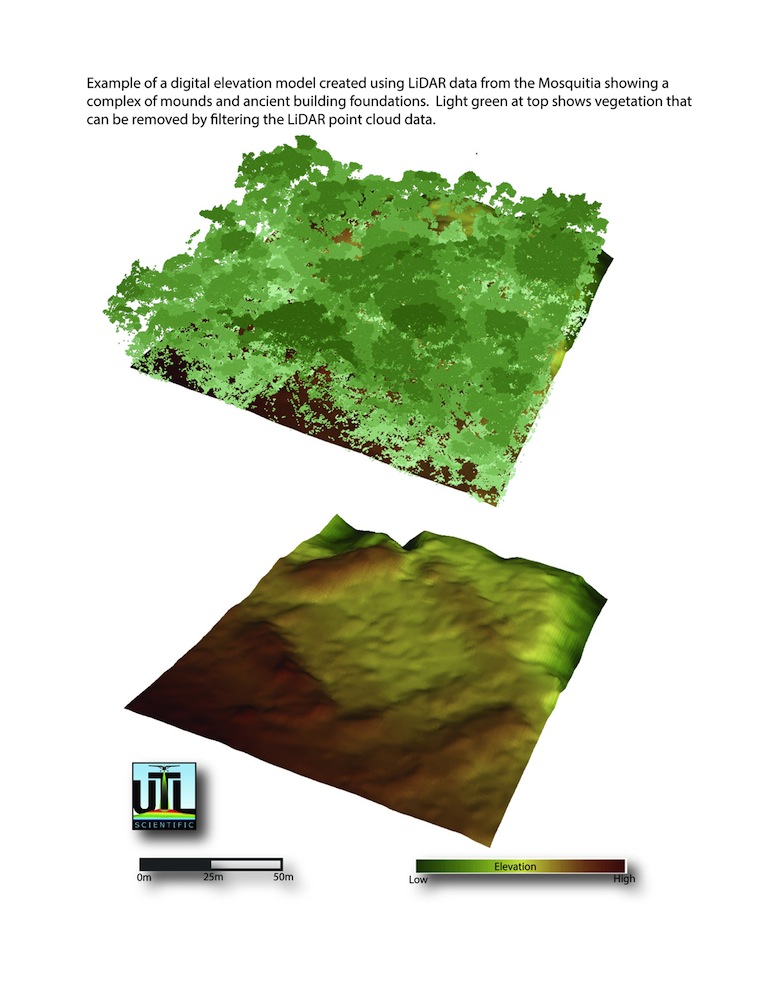
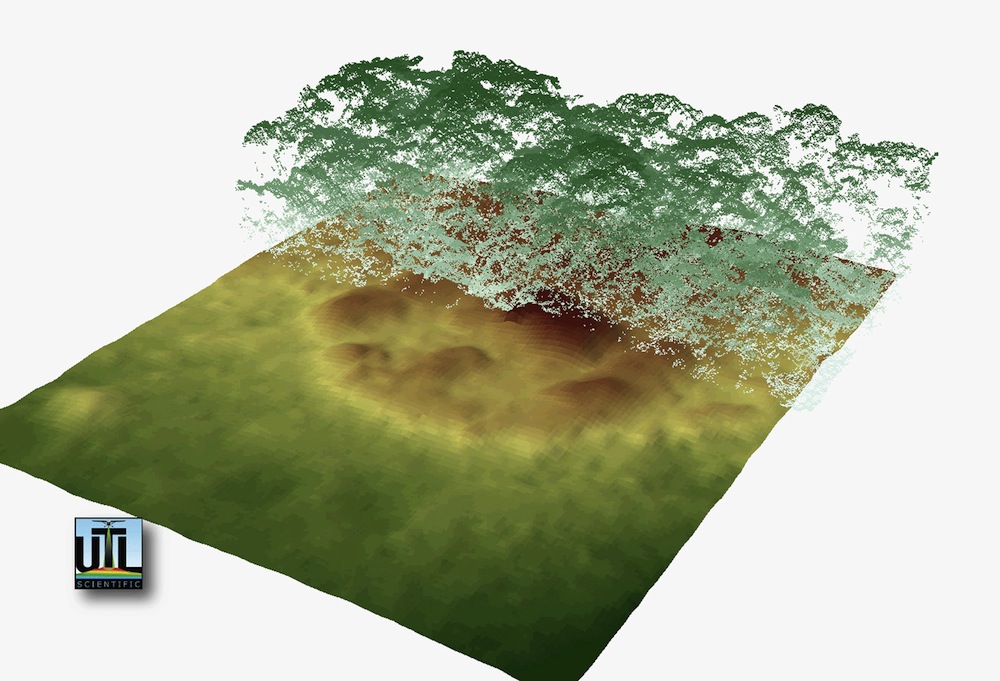
New images of a possible lost city hidden by Honduran rain forests show what might be the building foundations and mounds of Ciudad Blanca, a never-confirmed legendary metropolis.
Archaeologists and filmmakers Steven Elkins and Bill Benenson announced last year that they had discovered possible ruins in Honduras' Mosquitia region using lidar, or light detection and ranging. Essentially, slow-flying planes send constant laser pulses groundward as they pass over the rain forest, imaging the topography below the thick forest canopy.
What the archaeologists found — and what the new images reveal — are features that could be ancient ruins, including canals, roads, building foundations and terraced agricultural land. The University of Houston archaeologists who led the expedition will reveal their new images and discuss them today (May 15) at the American Geophysical Union Meeting of the Americas in Cancun.
Ciudad Blanca, or "The White City," has been a legend since the days of the conquistadors, who believed the Mosquitia rain forests hid a metropolis full of gold and searched for it in the 1500s. Throughout the 1900s, archaeologists documented mounds and other signs of ancient civilization in the Mosquitias region, but the shining golden city of legend has yet to make an appearance.
Whether or not the lidar-weilding archaeologists have discovered the same city the conquistadors were looking for is up for debate, but the images suggest some signs of an ancient lost civilization.
"We use lidar to pinpoint where human structures are by looking for linear shapes and rectangles," Colorado State University research Stephen Leisz, who uses lidar in Mexico, said in a statement. "Nature doesn't work in straight lines."
The archaeologists plan to get their feet on the ground this year to investigate the mysterious features seen in the new images.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Follow Stephanie Pappas on Twitter and Google+. Follow us @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on LiveScience.com.

Stephanie Pappas is a contributing writer for Live Science, covering topics ranging from geoscience to archaeology to the human brain and behavior. She was previously a senior writer for Live Science but is now a freelancer based in Denver, Colorado, and regularly contributes to Scientific American and The Monitor, the monthly magazine of the American Psychological Association. Stephanie received a bachelor's degree in psychology from the University of South Carolina and a graduate certificate in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus