'New star' as bright as the North Star will ignite in the sky this year. Here's how to see it.
A nova outburst visible to the naked eye is expected to decorate the night sky this year with a "new star" that will briefly become as bright as the North Star, offering a once-in-a-lifetime stargazing opportunity.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
A nova outburst visible to the naked eye is expected to decorate the night sky this year, offering a rare skywatching opportunity.
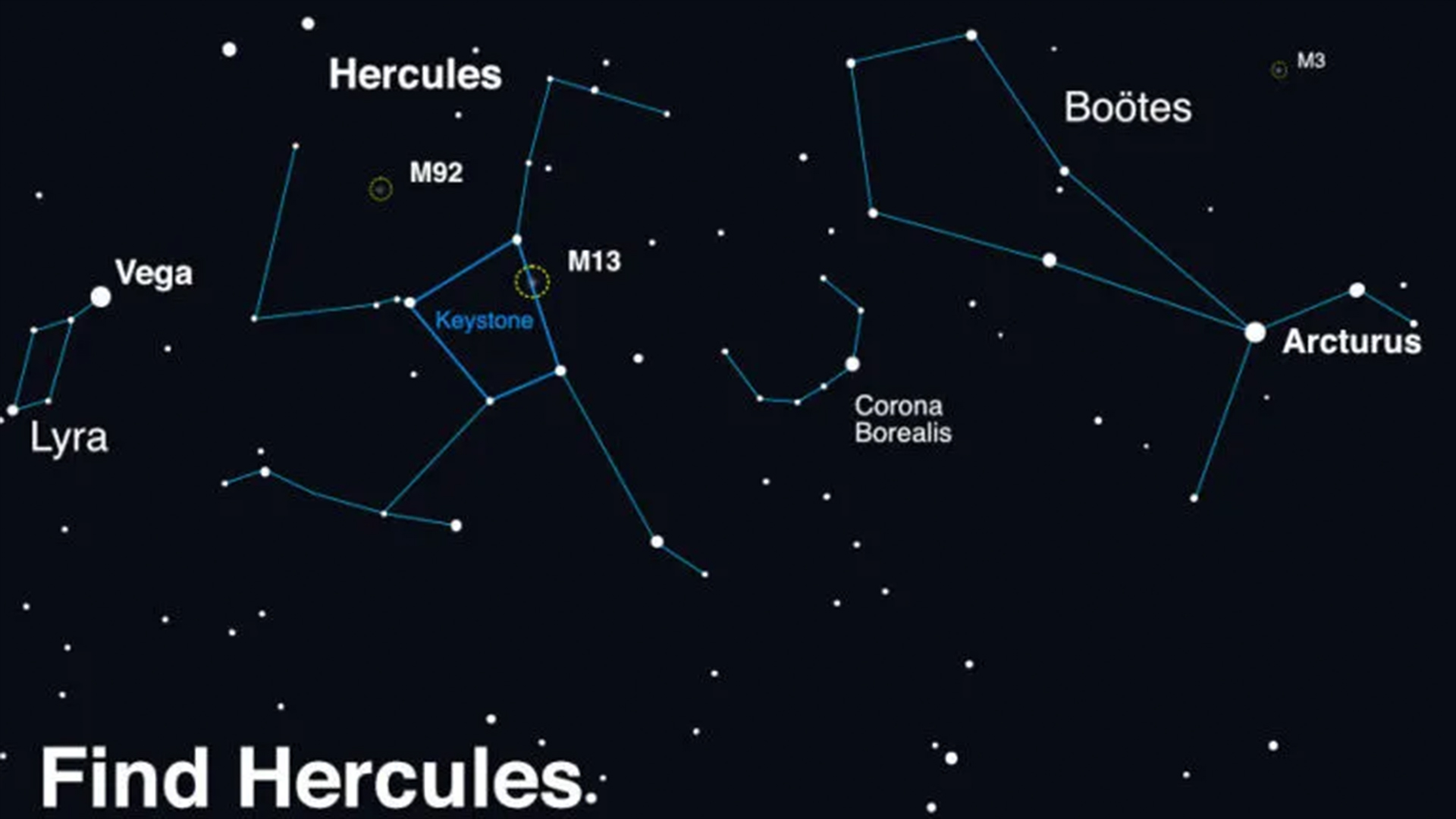
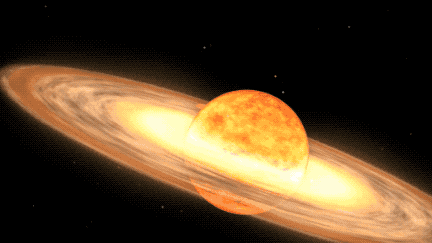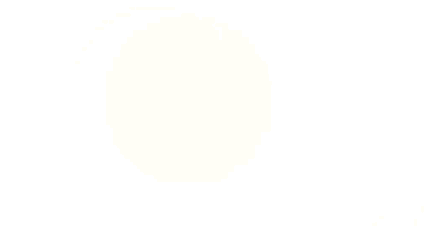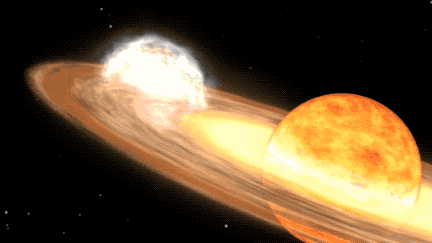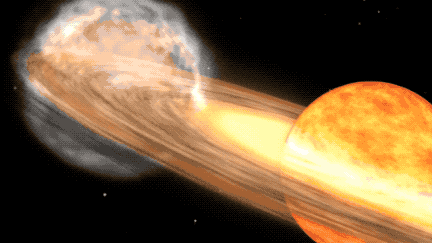
The star system offering us this opportunity is known as T Coronae Borealis (T CrB). It's located some 3,000 light-years away from Earth and consists of a red giant star and a white dwarf that orbit each other. When the white dwarf steals enough stellar material from its red giant companion, it ignites a brief flash of nuclear fusion on its surface, triggering what is known as a nova outburst.
The outburst will be visible in the constellation Corona Borealis, also known as the Northern Crown, which forms a semicircle of stars. The outburst is expected to occur between February and September 2024 and appear as bright as the North Star in our night sky for no longer than a week before fading again, NASA officials said in a statement.
"This could be a once-in-a-lifetime viewing opportunity as the nova outburst only occurs about every 80 years," NASA officials said in the statement.
This recurrent nova, which last exploded in 1946, is just one of five observed within the Milky Way galaxy. To spot the outburst, viewers should point their gaze to Corona Borealis, which lies between the constellations Boötes and Hercules. The outburst will appear as a bright "new" star in the night sky.
Generally, these binary stars have a magnitude of +10, which is far too dim to see with the unaided eye. However, during the outburst, the stellar system will have a magnitude of +2, which is comparable to the brightness of the North Star, Polaris, according to the statement.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"Once its brightness peaks, it should be visible to the unaided eye for several days and just over a week with binoculars before it dims again, possibly for another 80 years," NASA officials said.
The explosive stellar pair consists of a white dwarf — a relatively small, dense stellar remnant — and a larger red giant star in the late stages of stellar evolution, meaning its outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous. The gravitationally-bound stars are close enough that, as the red giant grows unstable from its increasing temperature and pressure, it ejects its outer layers onto the white dwarf.
The accumulation of matter heats the white dwarf's dense atmosphere enough to trigger a thermonuclear reaction that produces the nova we see from Earth. This cycle will continue once the nova dims as well, with the white dwarf collecting enough matter to create another outburst.
Originally posted on Space.com.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus