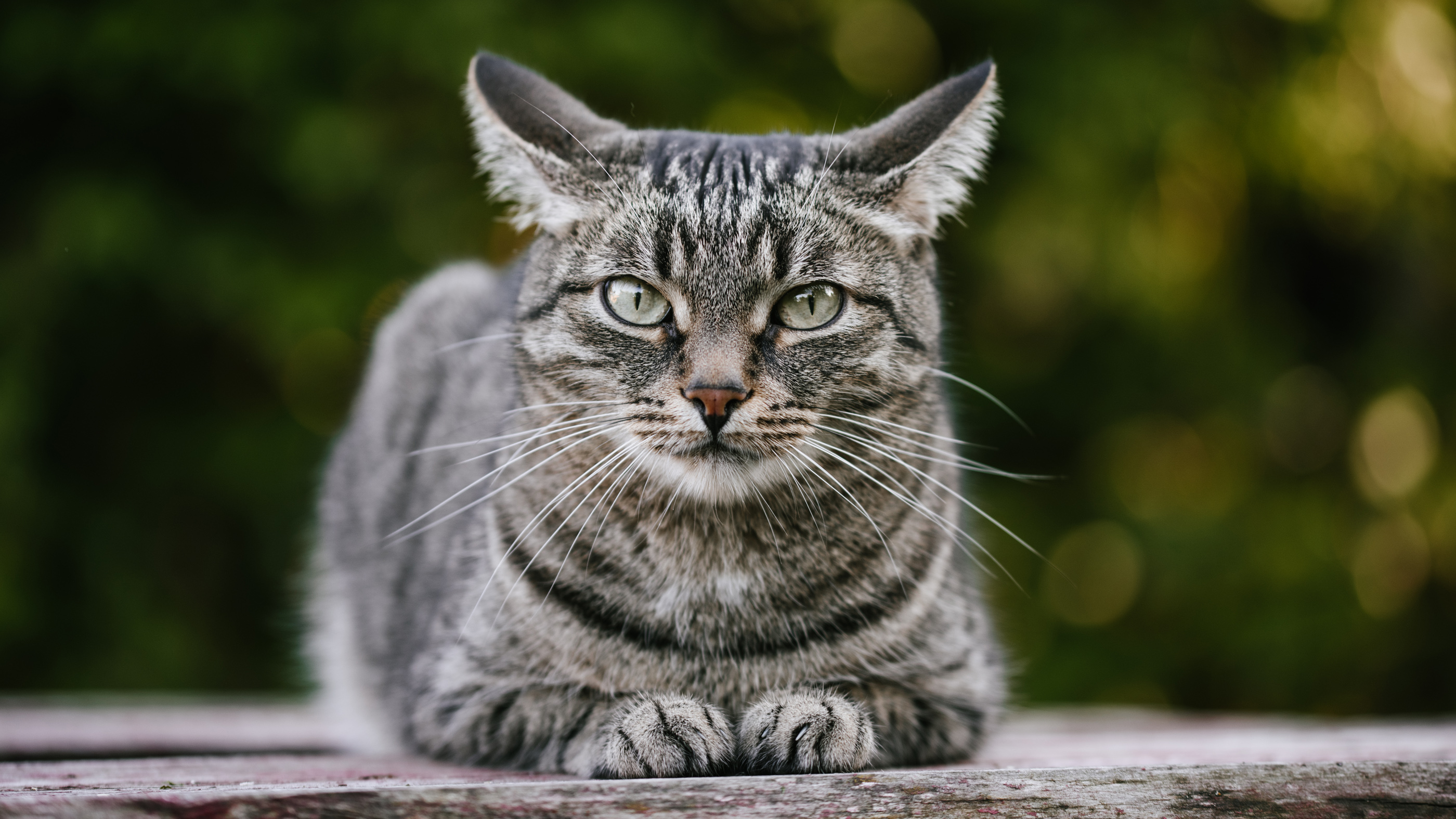
Cat infected with COVID-19 from owner in Belgium
This is the first case of human-to-cat transmission of the novel coronavirus.

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
A domestic cat in Belgium has been infected with COVID-19, the disease caused by the new coronavirus that's spreading across the globe, the government's FPS Public Health, Food Chain Safety and Environment announced March 27, according to news reports.
This is the first human-to-cat transmission of the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). About a week after its owner got sick with COVID-19, after returning from a trip to Northern Italy, the cat developed coronavirus symptoms: diarrhea, vomiting and respiratory issues, Steven Van Gucht, virologist and federal spokesperson for the coronavirus epidemic in Belgium, told Live Science.
The owner sent samples of vomit and feces to Dr. Daniel Desmecht's lab at the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine of Liège. Genetic tests showed high levels of SARS-CoV-2 in those samples, he said. "The cat recovered after 9 days," Van Gucht said.
Related: 13 Coronavirus myths busted by science
Cats and humans appear to have a similar "doorknob" on the surfaces of respiratory cells that lets the SARS-CoV-2 virus get inside, according to Van Gucht.
In humans, scientists have figured out that the SARS-CoV-2 virus attaches to a receptor protein called ACE2 that's on the outside of respiratory cells. Once inside of these cells, the virus hijacks certain machinery so it can replicate.
"The feline ACE2 protein resembles the human ACE2 homologue, which is most likely the cellular receptor which is being used by Sars-CoV-2 for cell entry," Van Gucht said.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
During the 2003 SARS outbreak, cats were infected with a coronavirus as well, Van Gucht said.
The only other pets thought to have "caught" the novel coronavirus from owners were two dogs in Hong Kong. The first dog, a 17-year-old Pomeranian, tested a weak positive for the virus at the end of February, Live Science reported. The dog died in mid-March, though the exact cause of death is not known, as the owner didn't allow an autopsy. A second dog, a German shepherd, tested positive but showed no symptoms of the disease, Bloomberg reported.
During the outbreak of another coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), dogs and cats contracted low levels of that virus, animal health expert Vanessa Barrs from City University told the South China Morning Post.
There have been no reports of pets passing the virus to their human owners, and Van Gucht stressed that even human-to-pet transmission is not a significant path of viral spread.
"We think the cat is a side victim of the ongoing epidemic in humans and does not play a significant role in the propagation of the virus," he said.
To prove definitively that the cat was infected with SARS-CoV-2, scientists will need a blood test to look for antibodies specific to this virus, Van Gucht said. Those tests will happen once the cat is no longer under quarantine.
Coronavirus science and news
- Coronavirus: Live updates
- What are coronavirus symptoms?
- How deadly is the new coronavirus?
- How long does coronavirus last on surfaces?
- Is there a cure for COVID-19?
- How does coronavirus compare with seasonal flu?
- How does the coronavirus spread?
- Can people spread the coronavirus after they recover?
Originally published on Live Science.
The one-month trial gives you access to all of the educational site's 9,000 activities in reading, science, math and art. Keep your child busy and learning while we are all stuck indoors.
Jeanna Bryner is managing editor of Scientific American. Previously she was editor in chief of Live Science and, prior to that, an editor at Scholastic's Science World magazine. Bryner has an English degree from Salisbury University, a master's degree in biogeochemistry and environmental sciences from the University of Maryland and a graduate science journalism degree from New York University. She has worked as a biologist in Florida, where she monitored wetlands and did field surveys for endangered species, including the gorgeous Florida Scrub Jay. She also received an ocean sciences journalism fellowship from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. She is a firm believer that science is for everyone and that just about everything can be viewed through the lens of science.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus