Aliens could be hiding in 'terminator zones' on planets with eternal night
Alien life could thrive in terminator zones, the edges between the light and dark sides of planets that are tidally locked with their host stars.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
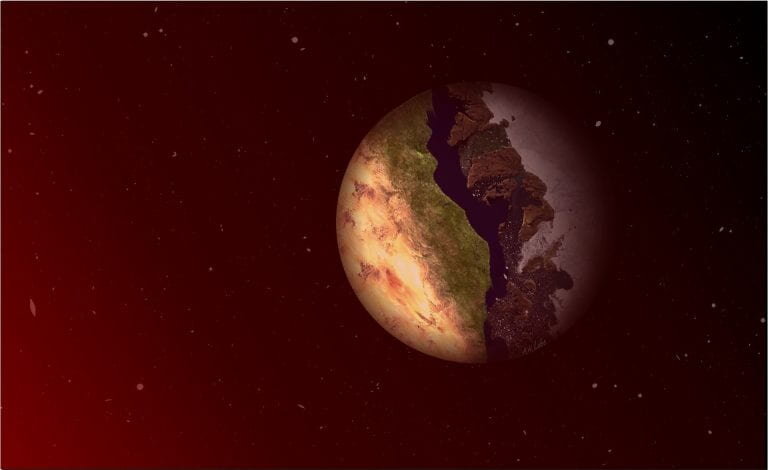
Imagine if one side of the Earth always faced the sun. Half of the planet would be stuck in perpetual daylight, the other shrouded in permanent night.
But for aliens in other solar systems, our doomsday scenario may be their everyday — and life might get along just fine. In a new study published March 10 in The Astrophysical Journal, astronomers propose that extraterrestrial life could exist in so-called terminator zones, the border between light and dark halves of an exoplanet.
"These planets have a permanent day side and a permanent night side," Ana Lobo, University of California, Irvine (UCI) astrophysicist and lead author of the new work, said in a statement. "This is a planet where the dayside can be scorching hot, well beyond habitability, and the night side is going to be freezing, potentially covered in ice. You could have large glaciers on the night side."
This seemingly strange kind of planet is actually quite common, particularly around the dim small M dwarf stars that make up nearly 70% of all stars. Around these smaller stars, exoplanets often become tidally locked, a gravitational phenomenon in which one side of the planet always faces the star. (Similarly, tidal locking is why Earth only sees one side of the moon.)
Related: 9 strange, scientific excuses for why humans haven't met aliens yet
Astrobiologists often focus on ocean worlds since water is such a key ingredient for life. Lobo and collaborators, however, wanted to find new niches where life may be able to survive. "We are trying to draw attention to more water-limited planets, which despite not having widespread oceans, could have lakes or other smaller bodies of liquid water, and these climates could actually be very promising," Lobo said.
Through computer simulations, Lobo showed that terminator zones on planets with a significant amount of land — versus those covered entirely in oceans — could, in fact, support liquid water and therefore life. With too much water, however, everything evaporates, covering the surface in a thick cloud of vapor.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
A slew of upcoming planet-hunting telescopes could search such terminator zones for signs of life, from the famed James Webb Space Telescope to the future Habitable Worlds Observatory, slated to take to the skies in the 2040s.

Briley Lewis (she/her) is a freelance science writer and Ph.D. Candidate/NSF Fellow at the University of California, Los Angeles studying Astronomy & Astrophysics. Follow her on Twitter @briles_34 or visit her website www.briley-lewis.com.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus





