Koalas Have Human-like Fingerprints

What's a forensic investigator's worst nightmare? Hint: It's a whole lot cuter than whatever you were imagining.
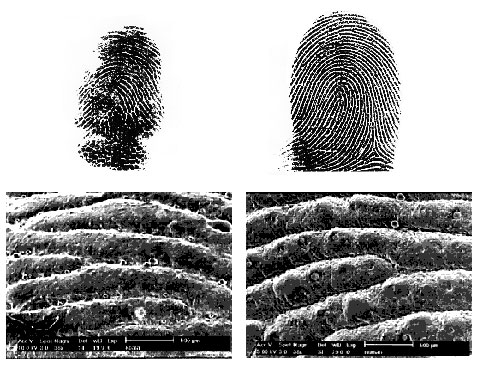
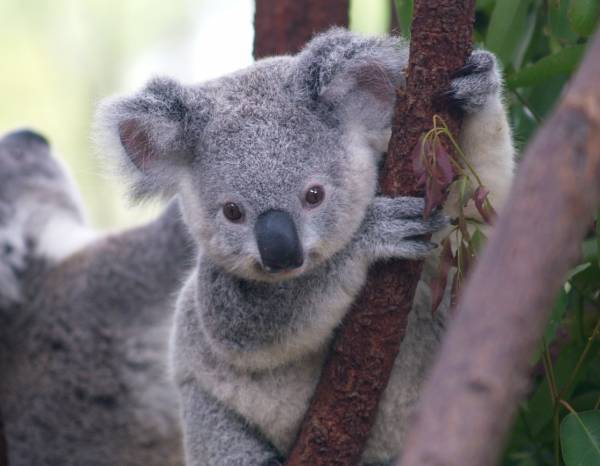
A crime in a zoo's koala cage would probably confound the efforts of even the best detectives. Why? Because koalas, doll-sized marsupials that climb trees with babies on their backs, have fingerprints that are almost identical to human ones. Not even careful analysis under a microscope can easily distinguish the loopy, whirling ridges on koalas' fingers from our own.
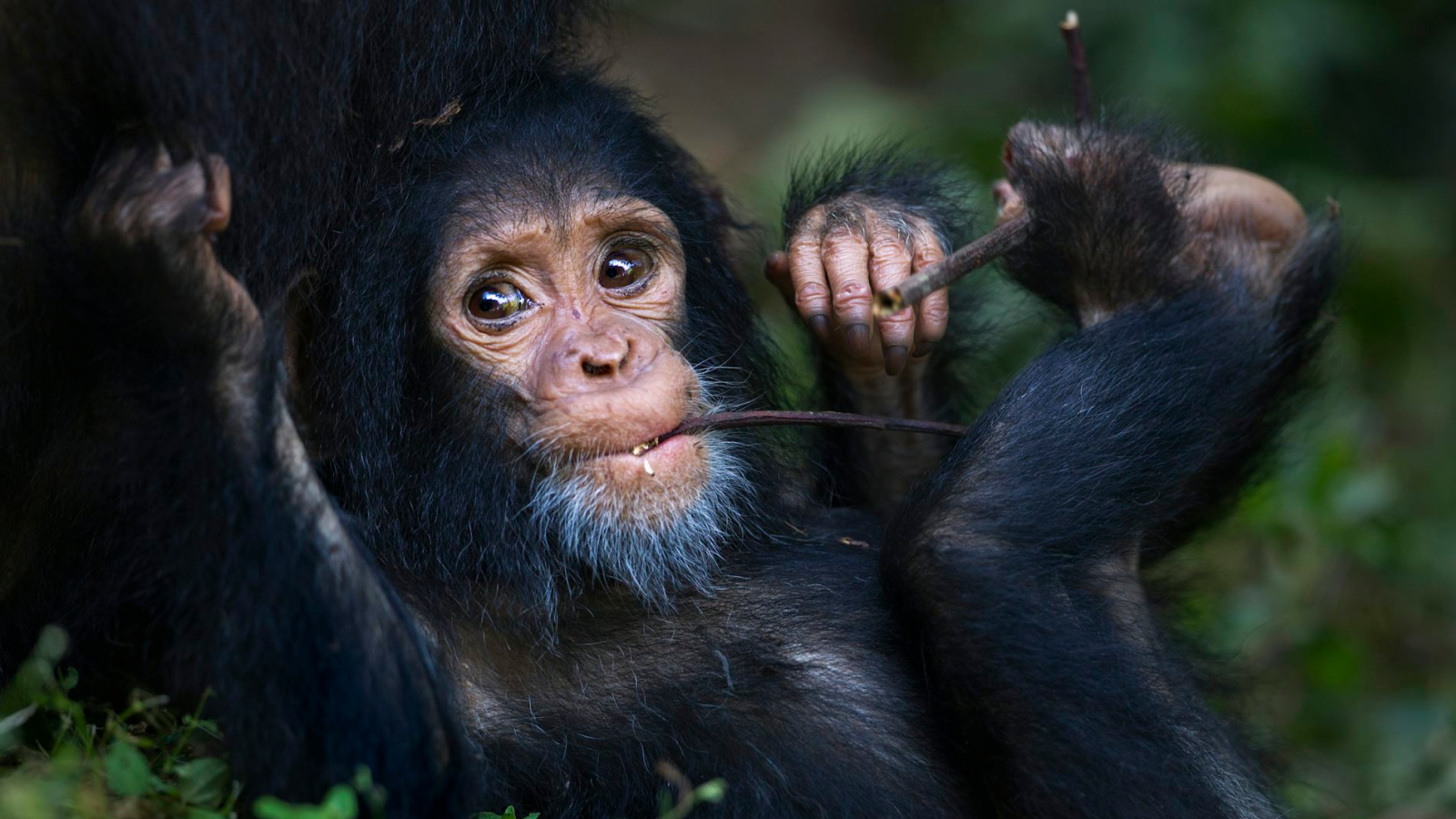
Koalas aren't the only non-humans with fingerprints: Close human relatives such as chimps and gorillas have them as well. The remarkable thing about koala prints is that they seem to have evolved independently. On the evolutionary tree of life, primates and modern koalas' marsupial ancestors branched apart 70 million years ago. Scientists think the koala's fingertip features developed much more recently in its evolutionary history, because most of its close relatives (such as wombats and kangaroos) lack them.
For centuries, anatomists have intensely debated the purpose of fingerprints. According to the team of anatomists at the University of Adelaide in Australia who discovered koala fingerprints in 1996, koala prints may help explain the features' purpose. The clue lies in our shared way of grasping.
"Koalas … feed by climbing vertically onto the smaller branches of eucalyptus trees, reaching out, grasping handfuls of leaves and bringing them to the mouth," the researchers wrote in their landmark paper. "Therefore the origin of dermatoglyphes [fingerprints] is best explained as the biomechanical adaptation to grasping, which produces multidirectional mechanical influences on the skin. These forces must be precisely felt for fine control of movement and static pressures and hence require orderly organization of the skin surface."
Humans and chimps grasp; koalas grasp -- to do so, it helps to have fingerprints.
This article was provided by Life's Little Mysteries, a sister site to LiveScience. Follow Natalie Wolchover on Twitter @nattyover.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Natalie Wolchover was a staff writer for Live Science from 2010 to 2012 and is currently a senior physics writer and editor for Quanta Magazine. She holds a bachelor's degree in physics from Tufts University and has studied physics at the University of California, Berkeley. Along with the staff of Quanta, Wolchover won the 2022 Pulitzer Prize for explanatory writing for her work on the building of the James Webb Space Telescope. Her work has also appeared in the The Best American Science and Nature Writing and The Best Writing on Mathematics, Nature, The New Yorker and Popular Science. She was the 2016 winner of the Evert Clark/Seth Payne Award, an annual prize for young science journalists, as well as the winner of the 2017 Science Communication Award for the American Institute of Physics.