New Hammerhead Shark Species Found Off South Carolina
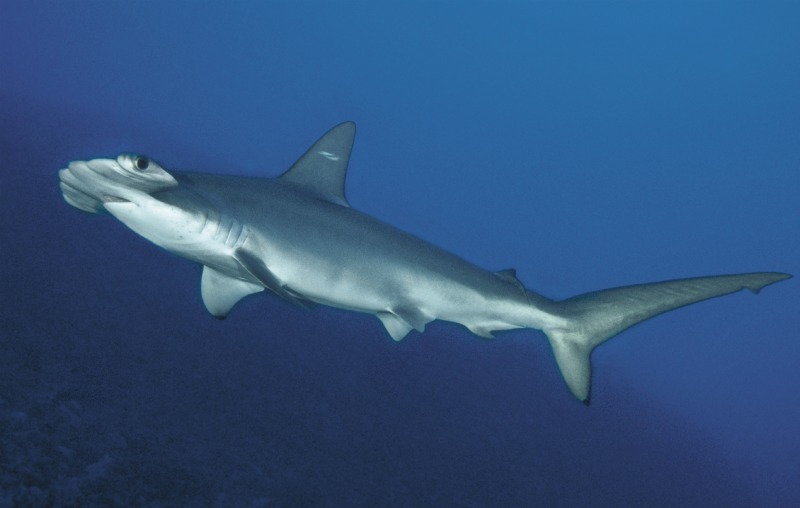

When new species are found near populated areas, they are often small and inconspicuous, not, for example, a hammerhead shark.
But that's exactly what a team of researchers discovered along the coast of South Carolina. The new species looks virtually identical to the scalloped hammerhead, but is genetically distinct, and contains about 10 fewer vertebrae, or segments of backbone, new research shows.
The new species, named the Carolina hammerhead (Sphyrna gilbert), gives birth to shark "pups" in estuaries near the shore off the Carolinas, according to a study published in August in the journal Zootaxa.
To find the shark, scientists led by University of South Carolina fish expert Joe Quattro collected 80 young sharks that looked liked scalloped hammerheads. They then analyzed their DNA, and found that they were distinct from their scalloped cousins. Further analysis found more subtle differences; the new species is slightly smaller, for instance, according to the study. Of these 80 sharks, 54 of them belonged to the new species, the study noted.
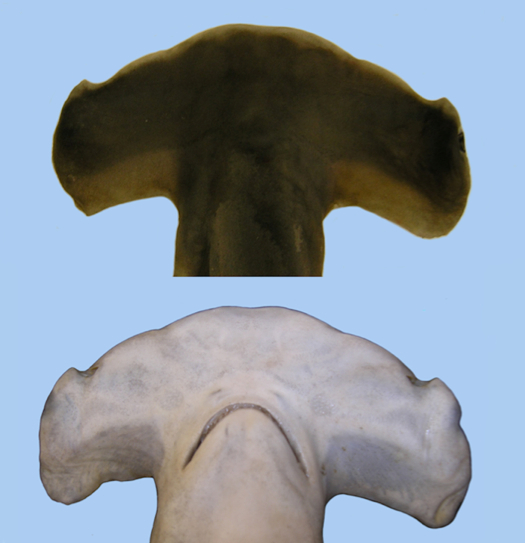
The study shows that the new species is quite rare. "Outside of South Carolina, we've only seen five tissue samples of the cryptic species," Quattro said in a release from the University of South Carolina. "And that's out of three or four hundred specimens."
Populations of scalloped sharks, like those of most other shark species, have plummeted in the past few decades — by up to 90 percent, Quattro said.
"Here, we're showing that the scalloped hammerheads are actually two things," Quattro said. "Since the cryptic species is much rarer than the [more widespread one], God only knows what its population levels have dropped to."
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The decline of sharks has been driven in part by demand for shark fin soup, a Chinese delicacy. About 100 million sharks are killed each year to satisfy this craving, scientists estimate. But there may be some good news — consumption of the soup is down by about 50 percent in China over the past two years, according to the environmental group WildAid.
In more shark news, a new species of "walking shark" was discovered near a remote Indonesian island in August.
Email Douglas Main or follow him on Twitter or Google+. Follow us @OAPlanet, Facebook or Google+. Original article on LiveScience's OurAmazingPlanet.