Get Ready for Invading Asian Tiger Mosquitoes
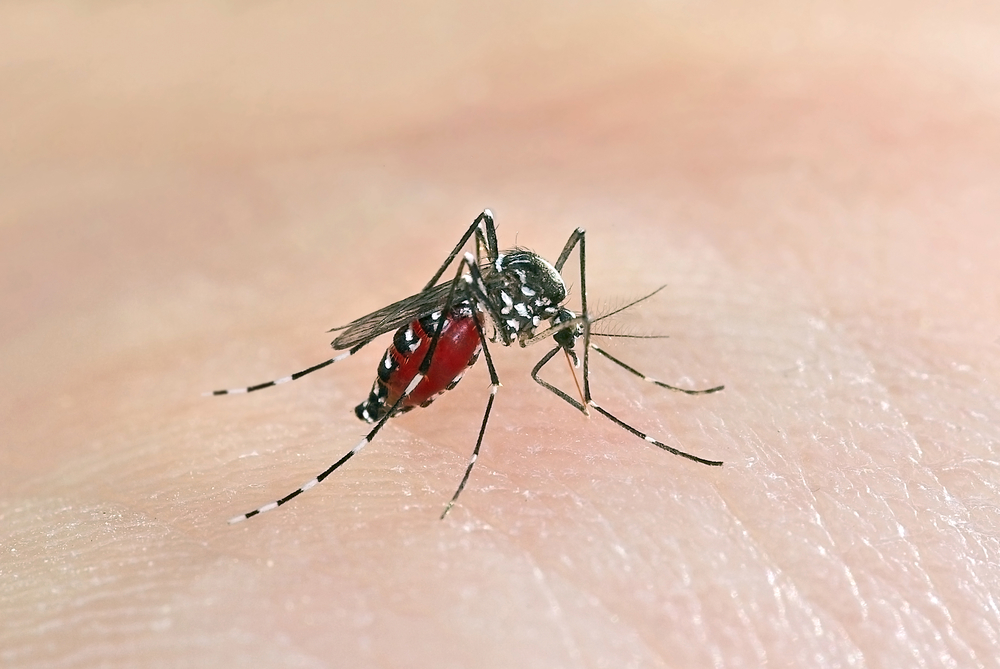

There's a new pest invading many American towns, and it's about as menacing as it sounds: the Asian tiger mosquito.
Named for the black-and-white stripes on its body, the Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) was first brought to Texas in a shipment of tires (which are notorious for holding the standing water that mosquitoes require for breeding), the Wall Street Journal reports.
The bug is worrisome for several reasons: Unlike other mosquitoes, the aggressive Asian tiger bites all day long, from morning until night. It has a real bloodlust for humans, but also attacks dogs, cats, birds and other animals. [Sting, Bite, Destroy: Nature's 10 Biggest Pests]
"Part of the reason it is called 'tiger' is also because it is very aggressive," Dina Fonseca, associate professor of entomology at Rutgers University, told the Journal. "You can try and swat it all you want, but once it's on you, it doesn't let go."
The Asian tiger mosquito joins other insects now threatening U.S. residents. Gallinippers (Psorophora ciliata), for example, are a type of shaggy-haired mosquito whose bite reportedly feels like being stabbed; they're currently found throughout much of Florida.
But few insects are as effective at spreading illness as the Asian tiger mosquito. The pest transmits more than 20 diseases, according to the Cornell Chronicle, including West Nile fever, dengue fever, yellow fever and two types of encephalitis.
Additionally, the mosquitoes transmit the chikungunya virus, the Chronicle reports. Though the disease is rarely fatal, chikungunya causes debilitating symptoms, including severe joint pain, fever, achiness, headache, nausea, vomiting, rash and fatigue.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
There's no vaccine to prevent chikungunya and no treatment; people usually recover in a few weeks. But while they're infected with the virus, they can be bitten again by another mosquito, which could then spread the disease to someone else, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Since its introduction to the United States in the 1980s, the Asian tiger mosquito has spread to 26 states, primarily in the eastern United States, the CDC reports. The bug is also established in South and Central America, southern Europe and several Pacific islands.
Part of its success at spreading throughout the world is due to a warming climate, but the Asian tiger mosquito has one other pesky adaptation: Its eggs are tough enough to survive a cold winter, according to Science News.
If there's a silver lining to this story, it might be this: The Asian tiger mosquito is displacing another disease-carrying mosquito species, Aedes aegypti. Every time a male Asian tiger mosquito mates with a female A. aegypti, chemicals in his semen make her sterile, Science News reports.
But this also means Asian tiger mosquitoes are expanding their territory. Experts recommend removing all sources of standing water, wearing insect repellent and covering up with long sleeves and pants to avoid the bloodthirsty mosquitoes — and the diseases they spread.
Follow Marc Lallanilla on Twitter and Google+. Follow us @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on LiveScience.com.

 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus