Mollusks to Hungry Lobsters: Snot Gonna Happen!

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
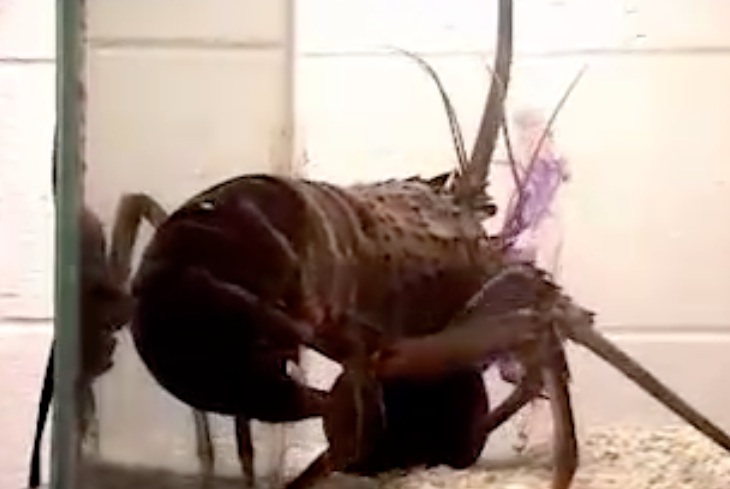
Spiny lobsters have hard shells and strong jaws easily capable of turning the soft-bodied, sluglike sea hare into an easy meal. But new research finds that sea hares have a snotty solution: Clog up potential lobster predators' nostrils.
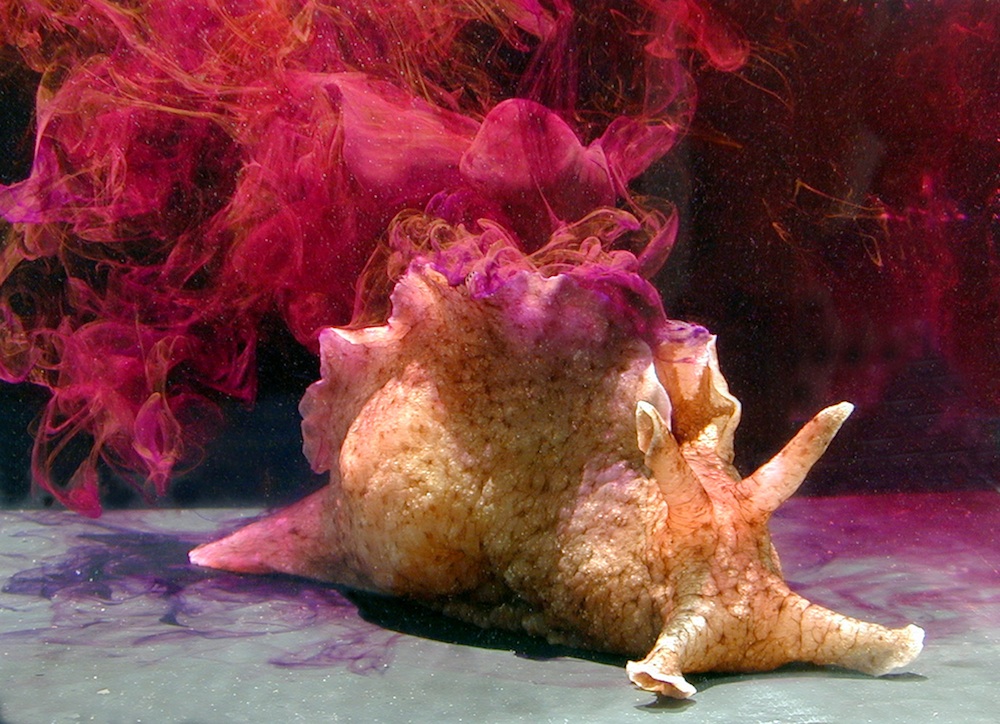
When threatened, the sea hares excrete a white, sticky substance called opaline that stuffs up the lobsters' sensory organs. While the lobster struggles to deal with this sudden lack of smell, the sea hare can often escape its clutches.
Sea hares (Aplysia) are marine mollusks that get their name from two long, earlike projections on their heads. The largest species can grow up to 4.4 pounds (2 kilograms).
Chemical protection
Size offers some protection from potential predators, but sea hares' main defenses are chemical. Like squid, they release purplish ink when threatened, but also excrete opaline.
Georgia State University researchers knew that these chemicals could save sea hares from becoming a meal to spiny lobsters, but it wasn't clear whether the substances simply blocked the lobster sensory organs (which are on its antennae) or whether they actually induced chemical signals that prevented the crustaceans from smelling food.
To find out, the researchers used Caribbean spiny lobsters (Panulirus argus) and sea hares (Aplysia californica). They extracted the water-soluble part of the sea hares' opaline, which left them with all of the stickiness but none of the amino acids and other chemicals that might have affected the lobsters' chemosensory receptors. They painted the opaline abstract on the lobsters' antennae and then exposed the crustaceans to "shrimp juice," which was made by soaking shredded shrimp in water for an hour.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The researchers repeated the same experiment with three other substances: carboxymethylcellulose, which is sticky but lacks opaline's amino acids; a mixture of only the amino acids found in opaline, without the stickiness; and a combination of carboxymethylcellulose and the opaline amino acids. A final group of lobsters got to smell the shrimp juice with nothing blocking their antennae.
As the lobsters responded to the shrimp juice in each condition, the researchers measured the activity of their chemosensory neurons.
Sticky defense
The results revealed that even without neuron-affecting chemicals, opaline's stickiness alone is enough to save sea hares from spiny lobsters. The amino acid-free carboxymethylcellulose had the same effect as opaline, the researchers report today (March 27) in the Journal of Experimental Biology. The opaline amino acids alone, however, did not stop the lobster neurons from responding to smells, perhaps in part because they were easily washed away by sea water.
Spiny lobsters have chemical sensory organs all over their head and legs, and the researchers suspect sea hares can clog them all.
"Typically, a sea hare is in the grasp of a spiny lobster before the sea hare inks," they wrote. "Our observations are that the ink sticks to all of the sensory appendages in the anterior end, including the antennules, mouthparts and anterior legs. We would expect an effect on these other chemoreceptors similar to that we have demonstrated for antennular chemoreceptors."
Follow Stephanie Pappas on Twitter and Google+. Follow us @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on Live Science.

Stephanie Pappas is a contributing writer for Live Science, covering topics ranging from geoscience to archaeology to the human brain and behavior. She was previously a senior writer for Live Science but is now a freelancer based in Denver, Colorado, and regularly contributes to Scientific American and The Monitor, the monthly magazine of the American Psychological Association. Stephanie received a bachelor's degree in psychology from the University of South Carolina and a graduate certificate in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus