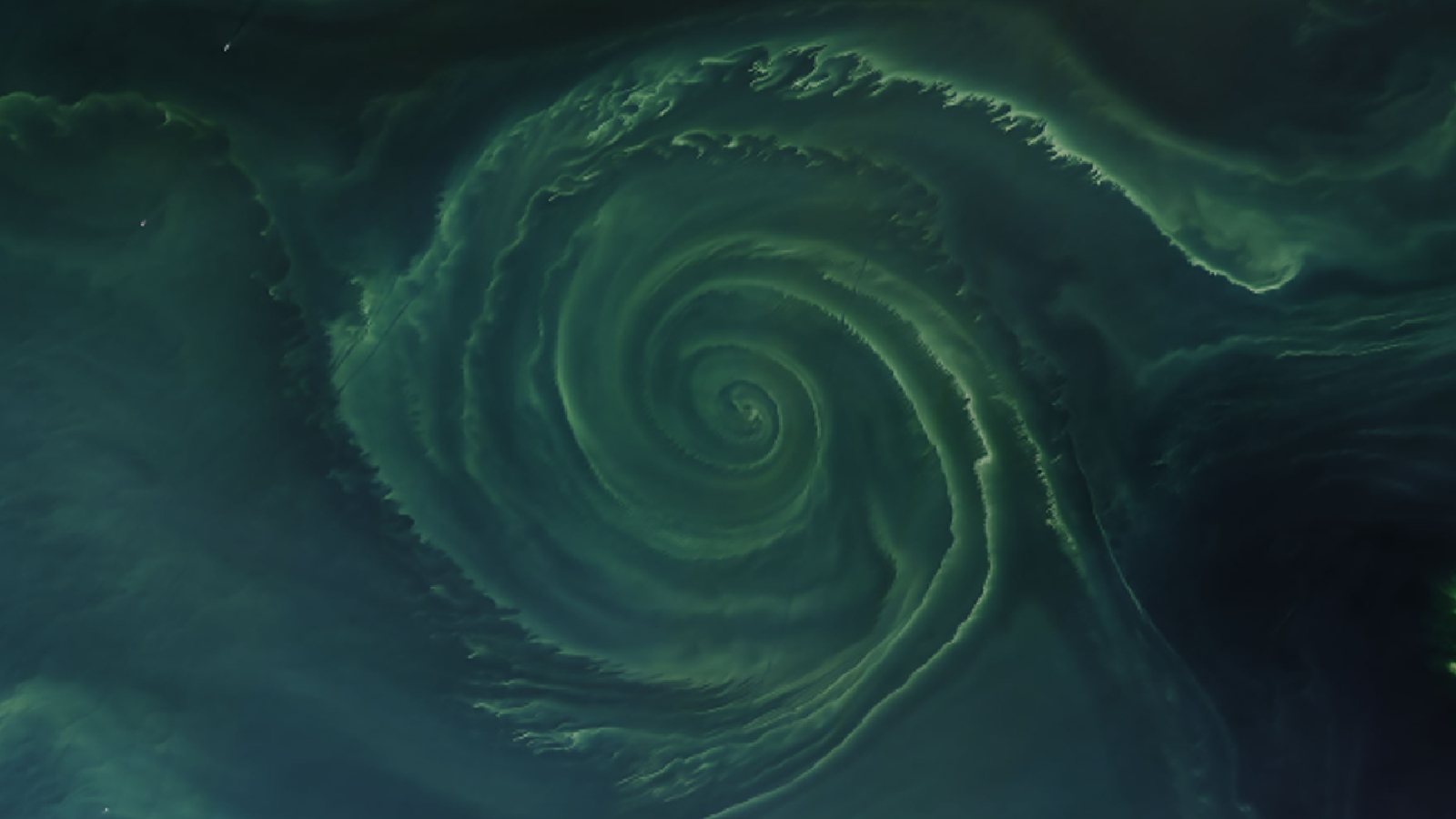
Earth from space: Ethereal algal vortex blooms at the heart of massive Baltic 'dead zone'
In 2018, satellite images captured a stunning spiral of cyanobacteria blooming in the Baltic Sea. The swirling mass of microbes helped to create a massive "dead zone" the size of West Virginia that starved the surrounding water of oxygen.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Where is it? The Gulf of Finland in the Baltic Sea.
What's in the photo? A swirling mass of algae trapped in an ocean vortex.
Which satellite took the photo? Landsat 8.
When was it taken? July 18, 2018.
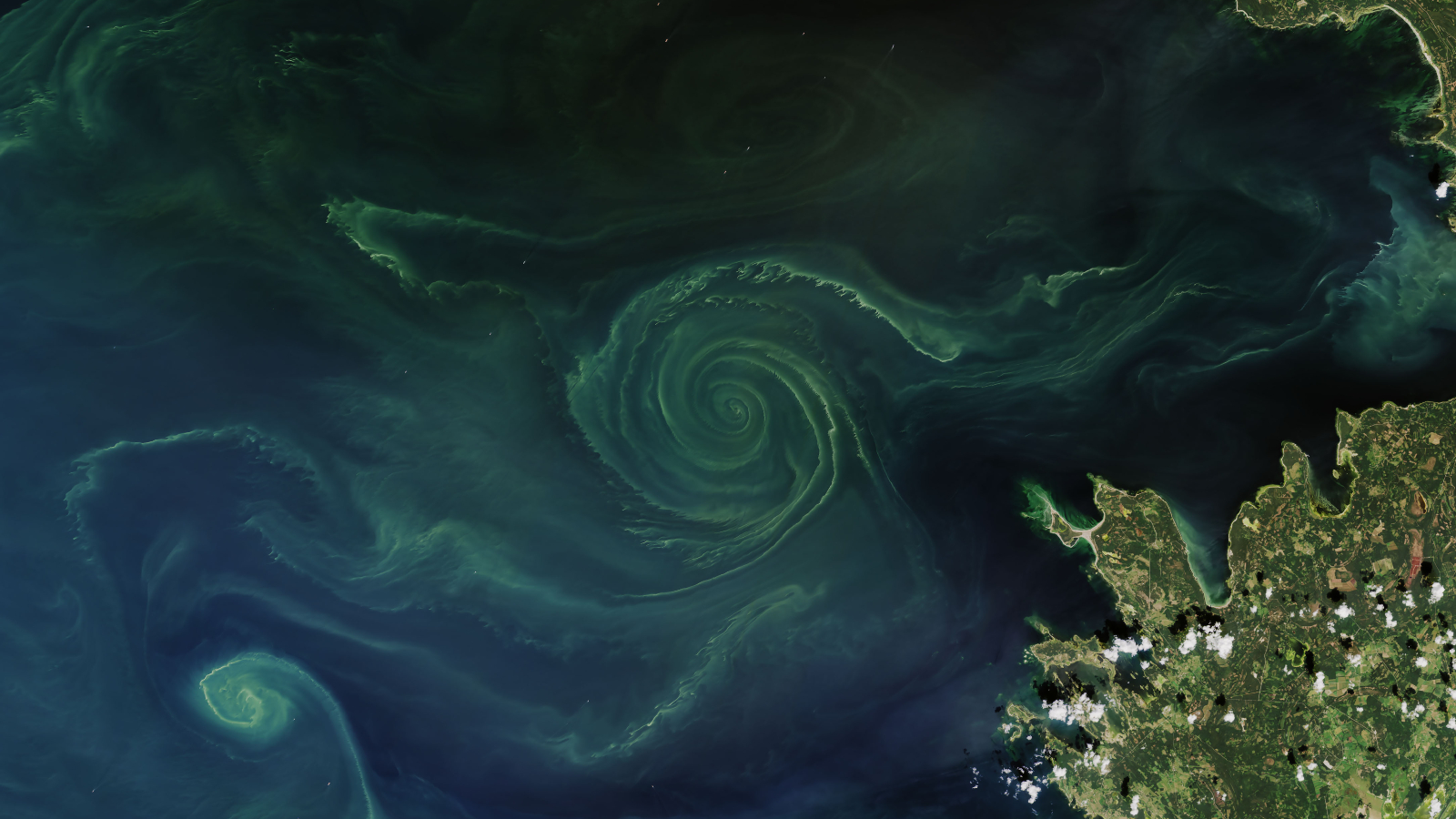
This striking green spiral emerged in the Baltic Sea during a massive algal bloom in 2018. While the swirling microbes have an ethereal beauty in the image, this belies an unseen danger they brought with them as they created a massive, toxic "dead zone."
The large spiral, which was around 15.5 miles (25 kilometers) across at its widest point, appeared in the Gulf of Finland — an arm of the Baltic Sea sandwiched between Finland, Estonia and Russia, according to NASA's Earth Observatory. The swirl mainly consisted of tiny photosynthetic marine bacteria, known as cyanobacteria, as well as some glass-armored plankton, known as diatoms.
The mass of microscopic creatures was trapped in a large vortex, or whirlpool, created by two opposing currents colliding. It is common for algae to be swept up by ocean currents, creating stunning seascapes when viewed from above. However, it is rare to see such a perfectly formed spiral.
Algae naturally bloom in this region of the sea every summer when vertical ocean mixing brings an abundance of nutrients to the surface. However, in recent decades these blooms have exploded in size and frequency as additional nutrients from human activities, such as agricultural run-off, have been dumped into the water.
Between 2003 and 2020, the average size of algal blooms increased by 13% globally, a 2023 study showed.
Related: 12 amazing images of Earth from space
Although algal blooms can be visually stunning, they can also be extremely destructive. When algae amasses near the surface, it temporarily decreases the amount of oxygen in the waters below, potentially suffocating nearby marine creatures, which filter oxygen from the water to breathe, according to the Woods Holes Oceanographic Institution. Scientists often refer to these oxygen-starved areas as "dead zones."
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
As the blooms grow larger, so do the resulting dead zones. When this image was taken in 2018, the dead zone in the Gulf of Finland covered around 27,000 square miles (70,000 square kilometers), around the same size as West Virginia, according to NASA's Earth Observatory.
Not only are the dead zones getting larger, they are also becoming more deadly. Rising sea surface temperatures driven by human-caused climate change mean that the upper oceans can't hold as much oxygen as they used to, which makes it easier for oxygen levels to drop to dangerous levels. A 2018 study revealed that during the last century, oxygen levels in the Baltic Sea dropped to their lowest levels in 1,500 years.
We will likely see more expanded algal blooms worldwide this summer thanks to record sea surface temperatures over the last year, which were partially triggered by the recent El Niño event.

Harry is a U.K.-based senior staff writer at Live Science. He studied marine biology at the University of Exeter before training to become a journalist. He covers a wide range of topics including space exploration, planetary science, space weather, climate change, animal behavior and paleontology. His recent work on the solar maximum won "best space submission" at the 2024 Aerospace Media Awards and was shortlisted in the "top scoop" category at the NCTJ Awards for Excellence in 2023. He also writes Live Science's weekly Earth from space series.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus











