'Fast-moving' E. coli outbreak prompts CDC investigation
The food source of the outbreak is unknown.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
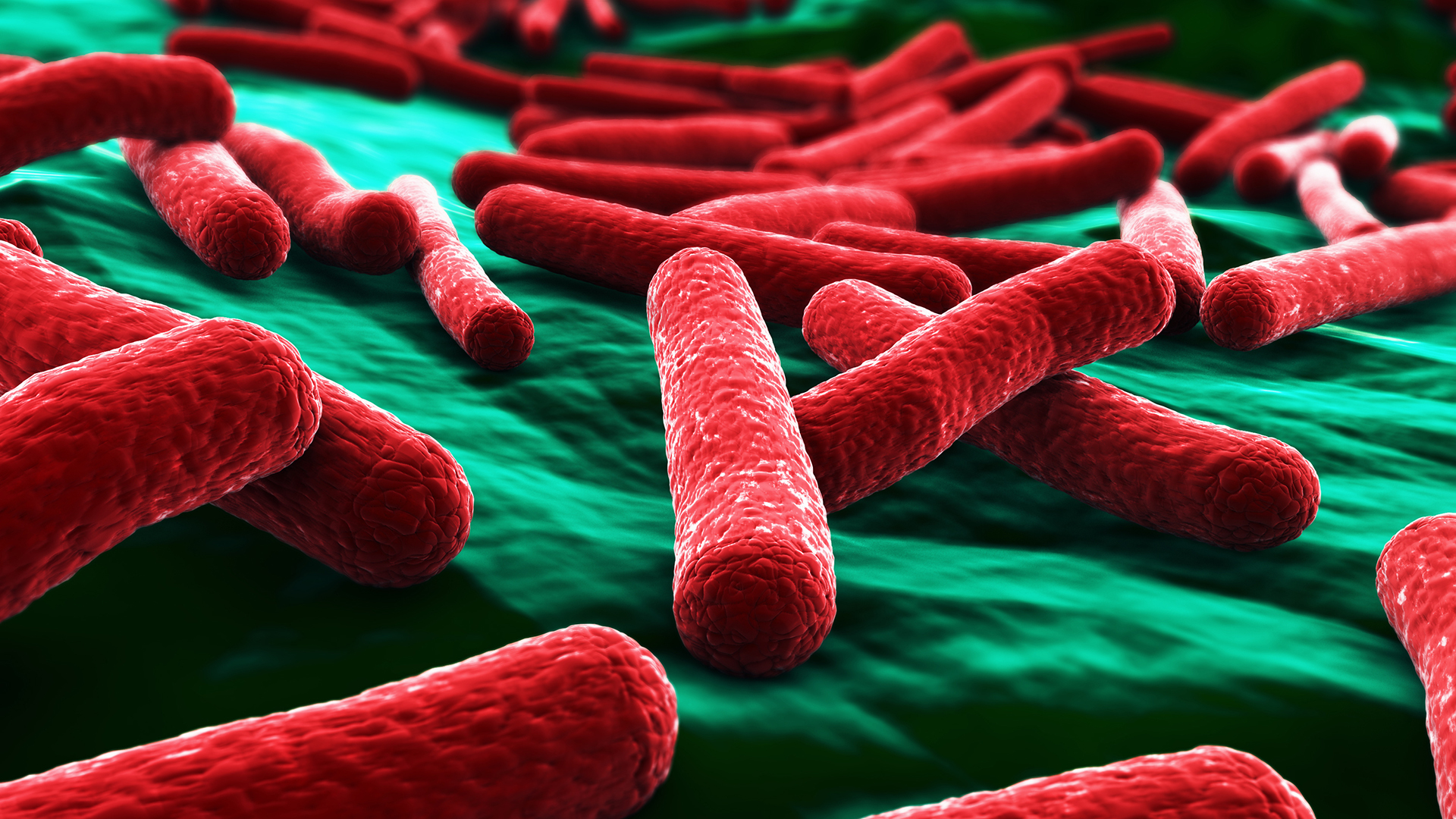
Public health officials are investigating a "fast-moving" outbreak of Escherichia coli, or E. coli, that has sickened at least 15 people in Michigan and 14 in Ohio, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced Wednesday (Aug. 17).
So far, nine people out of the 29 infected have required hospitalization but no one has died.
The strain of E. coli that appears to be driving the outbreak is known as E. coli O157:H7. This type of bacteria produces a poison called Shiga toxin that can cause severe gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal cramps, vomiting and bloody diarrhea, the CDC stated. In some cases, E. coli O157:H7 infections can lead to a serious complication called hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), which damages the red blood cells and kidneys and can result in kidney failure and death, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine. Children and elderly people have an elevated risk of HUS.
Public health officials are now working to identify any additional cases of illness linked to the outbreak, while also interviewing people about the foods they ate in the week before they got sick. The food source of the outbreak has yet to be identified, but based on the DNA of E. coli sampled from infected individuals, it's likely that they all became ill from eating the same food because the bacterial strains appear very closely related, the CDC stated.
Related: These volunteers drank E. coli-laced water and got diarrhea, for science
Some recent E. coli cases in Michigan and Ohio have yet to be added to the CDC's PulseNet system, a national database of DNA fingerprints of bacteria that cause foodborne illnesses, so the CDC's tally is expected to increase soon. The Michigan Department of Health and Human Services (MDHHS) has received 98 reports of E. coli infection this August, as compared to only 20 cases reported during the same time period in 2021, according to a statement.
"While reports of E. coli illness typically increase during the warmer summer months, this significant jump in cases is alarming," Dr. Natasha Bagdasarian, chief medical executive of MDHHS, said in the statement. "This is a reminder to make sure to follow best practices when it comes to hand hygiene and food handling to prevent these kinds of foodborne illness."
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The CDC advises calling your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these severe E. coli symptoms:
- Diarrhea and a fever higher than 102 degrees Fahrenheit (38.9 degrees Celsius)
- Diarrhea for more than 3 days that is not improving
- Bloody diarrhea
- So much vomiting that you cannot keep liquids down
- Signs of dehydration, such as not peeing much; dry mouth and throat; or feeling dizzy when standing up
Symptoms of E. coli tend to appear within one to 10 days of exposure, with most people falling ill within three to four days of swallowing the bacteria, according to the CDC. The majority of people recover in five to seven days without the need for treatment, but those with severe infections and complications like HUS may require hospitalization.
The following safety tips can help prevent E. coli infections:
- Clean: Wash your hands, utensils and surfaces often. Rinse fruits and vegetables under running water before eating, cutting or peeling.
- Separate: Keep food that won’t be cooked separate from raw meat, poultry and seafood.
- Cook: Use a food thermometer to make sure you have cooked your food to a temperature high enough to kill germs.
- Chill: Refrigerate perishable food (food that goes bad) within 2 hours. If the food is exposed to temperatures above 90 F (32 C), for instance in a hot car or at a picnic, refrigerate within 1 hour. Thaw food in the refrigerator, not on the counter.
"If a [contaminated] food item is identified, investigators will issue advice for people and businesses," the CDC says.
Originally published on Live Science.

Nicoletta Lanese is the health channel editor at Live Science and was previously a news editor and staff writer at the site. She holds a graduate certificate in science communication from UC Santa Cruz and degrees in neuroscience and dance from the University of Florida. Her work has appeared in The Scientist, Science News, the Mercury News, Mongabay and Stanford Medicine Magazine, among other outlets. Based in NYC, she also remains heavily involved in dance and performs in local choreographers' work.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










