How Does 'Kinetic' Sand Work?

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
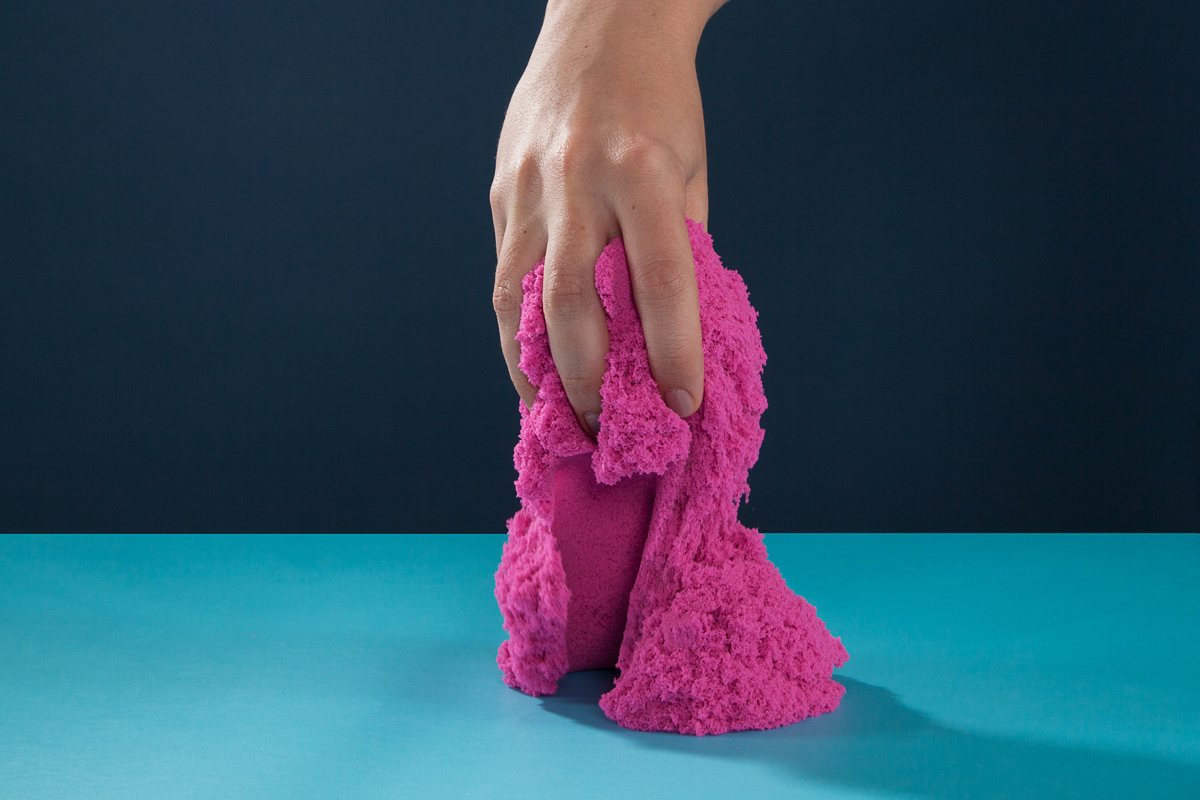
A mesmerizing material called "kinetic sand," which can be molded like clay but also somehow feels silky, is enjoyable for kids and adults alike.
A search on Instagram for #kineticsand, for example, turns up thousands of videos of people slicing, smashing and scooping the stuff, in what looks like a grand sensory experience.
But what gives kinetic sand its transfixing effects? [Science Experiments for Kids]
Kinetic sand is regular sand that's been coated with silicone oil, said Rick Sachleben, a member of the American Chemical Society.
"Silicone" doesn't refer to one specific material but rather a group of materials that contain the elements silicon and oxygen. Silicones are polymers, meaning they're molecules made up of long chains of repeated units.
The compounds are used in "all sorts of products, from cosmetics, lotions, shampoos and conditioners, to lubricants and sealants," Sachleben said.
"Silicone oils have unique properties in that they can be liquids that flow freely, or semisolids that flow slowly in the absence of pressure, but act like rubbery solids under stress," Sachleben told Live Science. This characteristic is called "viscoelasticity," he said.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
But a substance's degree of viscoelasticity depends on the length of the polymer chains in the silicone oil, Sachleben said.
For example, "Imagine long (very long!) strings of spaghetti," Sachleben wrote in an email. "They stick together, so [they] can hold a shape, but place a ball of them on the counter and, over time, they slowly sink down into a low pile. Longer strings [of spaghetti] hold their shape better than shorter ones."
Similarly, with kinetic sand, the polymer chains within the silicone oil make the sand particles stick together so you can form them into a ball. However, the ball will slowly flatten out over time.
But the silicone-oil-coated sand particles stick only to each other, not to other surfaces, Sachleben noted. This is why kinetic sand doesn't seem "sticky" and is easy to clean up, he said.
Originally published on Live Science.

 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus